As you rise upward in the atmosphere air pressure ____________
decreases
In which layer of the atmosphere does most weather occur?
Troposphere
Using the chart, which month shows the highest precipitation?
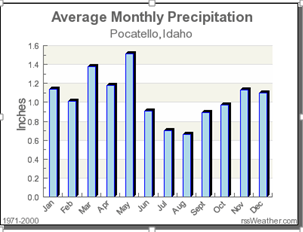
May
Name 3 types of Severe weather can we experience in Idaho?
Thunderstorms, Lightning, occasional tornado, high winds, snow storms, below freezing temperatures resulting in high wind chill, flash floods.
What are the three ways Earth is heated by the sun?
radiation, convection, conduction
Air has pressure because air has _____________
Mass
The Earth is tilted at 23.5 degrees. This causes Earth to be heated ________________.
unequally
Using the chart, during which season do we receive the most precipitation?
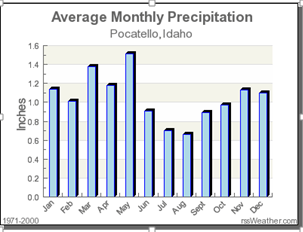
Spring
Weather forecasting has improved recently because of
Improved data gathering and better computer technology. Satellites looking at weather from space.
Our earth is primarily heated through the process of ________________. (wind)
Convection
Why is Earth's atmosphere important to all living things?
Provides all the gases that living things need to survive.
What type of front is most likely to create severe weather?
Cold Front
Describe the process by which clouds form
Warm air rises, cools until condensation occurs on small particles. Condensation forms clouds that can be in the form of water droplets, or ice crystals
Climate is classified by two major weather factors.
precipitation and temperature
What is the greenhouse effect?
The process by which gasses hold or trap air in the atmosphere.
Why does convection on earth take place?
Cold air or water is more dense than warm air or water and causing cold air or water to sink and warm air or water to rise.
Which phenomenon is NOT a result of Severe Weather?
Rexburg Flood 2014 Andover Tornado
Galveston Hurricane Japanese Tsunami
The Dust Bowl
Japanese Tsunami, caused by Earthquake.
Name four parts of the water cycle and describe each.
Evaporation: when water evaporates from lakes, puddles, streams, ocean
Condensation: forming of clouds
Precipitation: rain, snow, sleet or hail
Transpiration: Plants sweating
Run off: when surface water runs off land because it is too saturated.
Ground water: water that percolates through the Earth and stores in aquifers.
What should you do if caught in these types of storms:
Lightning
Hurricane
Tornado
Lightning: go inside or in a car, if in the open lay flat away from taller objects.
Hurricane: go in a room with no windows or evacuate as instructed.
Tornado: go into a basement or are of the house with no windows and close to the ground floor.
Increased greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, may cause increased warming of earth. why?
Trapping more heat in the atmosphere.
In class you learned that Earth's rotation causes the Coriolis Effect. Explain how this effect causes wind movement in the Northern Hemisphere.
Winds veer right and turn counter clockwise. Winds do not cross the equator.
Explain what takes place during a Severe Weather event like a Tornado.
Warm air rises and condenses resulting in an unstable environment. This can form a large cumulonimbus cloud that produces a mesocyclone. It is a low pressure system that causes high pressure air to rush towards it as it is rotating. This causes a vortex to appear and touch the ground. Tornadoes reach winds speeds up to 300 miles.
Using vocabulary from the water cycle describe what happens to a puddle on a sunny day.
The sun beats down on the puddle causing the water to evaporate into water vapor. As the water vapor rises it cools and condenses forming a cloud. If the cloud is large enough precipitation like rain can take place and the puddle then forms all over again on the ground.
What is the number one cause of death in severe weather events?
drowning:
Flash floods, Hurricane,
Storm Surge
Explain Albedo and its effect on global climate.
Albedo is the reflective property of a surface. Surfaces that are white, like clouds, ice, snow, have a higher albedo. When glacier ice melts and sea ice melts more heat is trapped on land and in the ocean causing temperatures to rise.