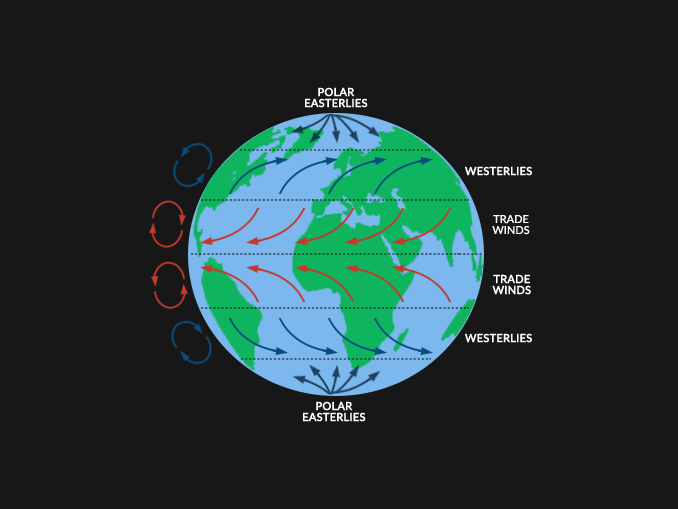
These winds blow steadily from East to West in the tropical region between the Equator and 30° latitude.
What are the Trade Winds?
In this color-coded weather symbol, you will see a large blue "H".

What is a High-Pressure System?
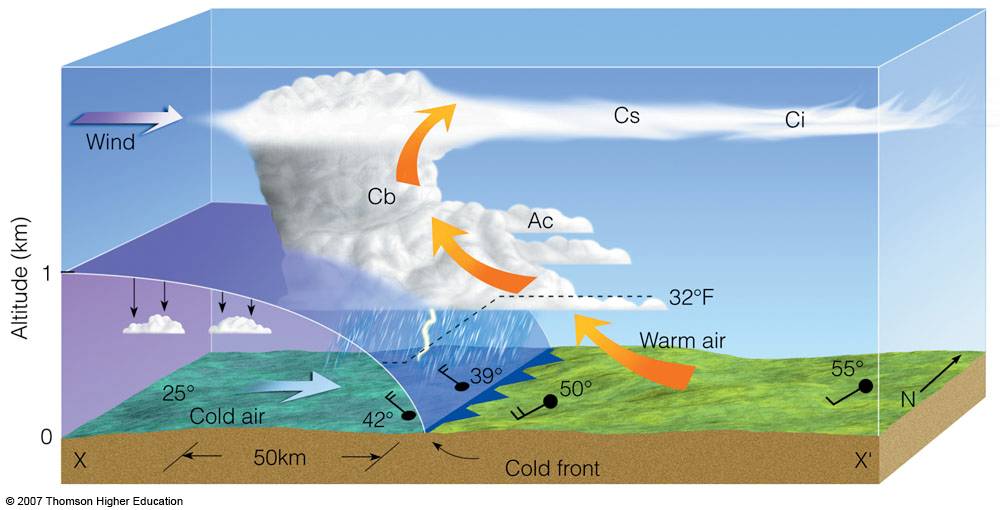
This weather front is represented by a blue line with triangles on it.

What is a Cold Front?
The curving of global winds caused by the Earth’s rotation is called this.
What is the Coriolis Effect?
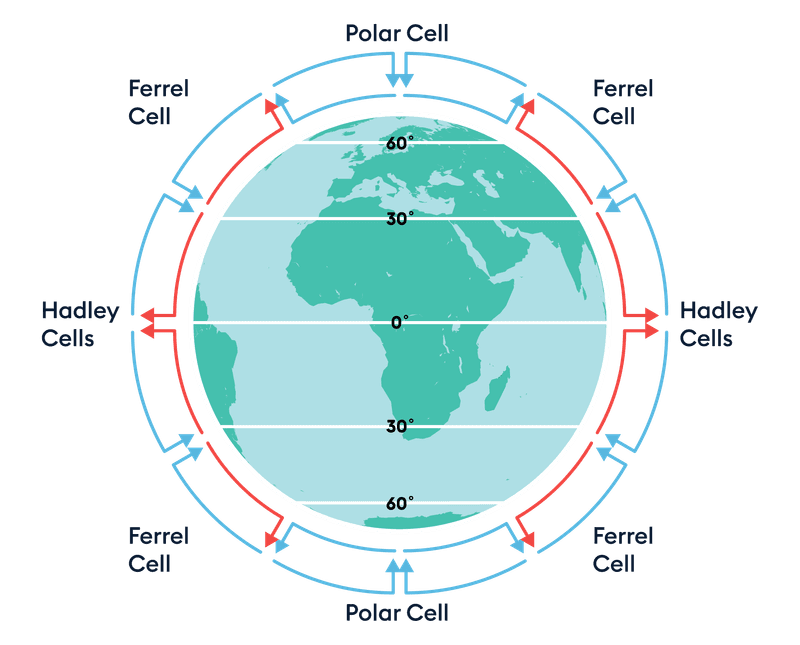
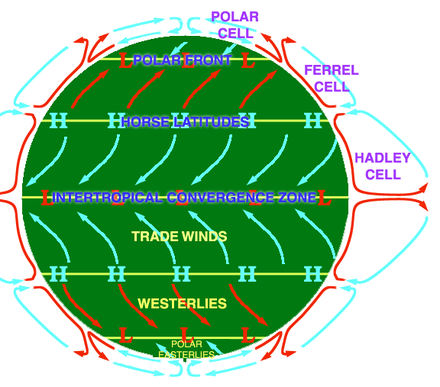
This circulation cell is located closest to the Equator (0' to 30')
What is the Hadley Cell?
These winds blow from West to East in the temperate region between 30° and 60° latitude.
What are the Westerlies?
In a Low-Pressure system, the air moves in this direction.
What is Rises (or Up)?
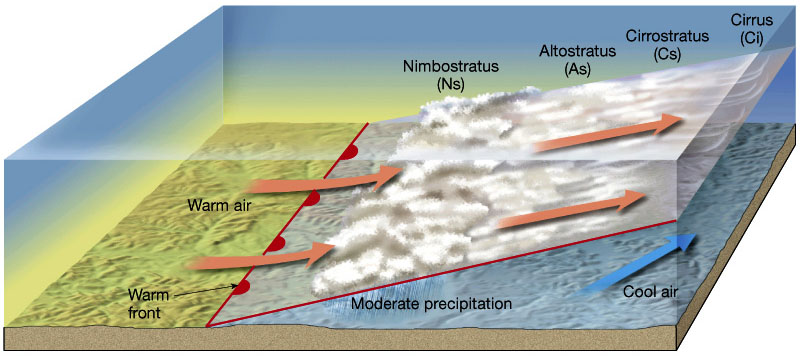
This weather front is represented by a red line with semi-circles on it.

What is a Warm Front?
Because of the Coriolis Effect, winds in the Northern Hemisphere curve to this side.
What is the Right? (East)

This circulation cell is located between 30' and 60' latitude.
What is the Ferrel Cell?
These fast-flowing, narrow air currents are found high in the atmosphere, not at the surface.
What are Jet Streams?
In a High-Pressure system, the surface winds flow in this direction relative to the center.
What is Outwards?
In science, if you add the Latin word "Nimbus" to a cloud's name, it tells you that the cloud is currently producing this.
What is Rain?
The Earth rotates in this direction when viewed from above the North Pole.
What is Counter-Clockwise?
This circulation cell is located at the very top and bottom of the Earth (60' to 90').
What is the Polar Cell?
These winds blow cold air from the poles toward the 60° latitude line.
What are the Polar Easterlies?
This type of pressure system is usually associated with "Dry and Stable" weather.
What is a High-Pressure System?
In a cold front, this type of air pushes under the warm air, forcing it up quickly.
What is Cold Air?
Someone standing here travels a longer distance in one day than someone standing at the North Pole.
What is the Equator?
At 30' North latitude, the air between the Hadley and Ferrel cells is doing this.
What is Sinking?
Long ago, sailors relied on these specific steady winds to help them travel across the seas to trade goods.
What are the Trade Winds?
Wind is created when air moves from an area of _____ pressure to an area of _____ pressure.
What is High to Low?
On the weather map, rain and storms are shown happening in what orientation/location to the cold front line.
What is Behind (or Along) the line?
Two things are responsible for creating global winds: The rotation of the Earth and this.
What is the Uneven Heating of the Earth (by the Sun)?
At the Equator (0'), the air is doing this, creating a Low-Pressure zone.
What is Rising?