What is the source of energy that controls the weather, atmosphere, and water cycle?
the sun
In which layer of the atmosphere does weather occur?
troposphere
In which layer of the atmosphere do we live?
troposphere
Draw the rain-shadow effect.
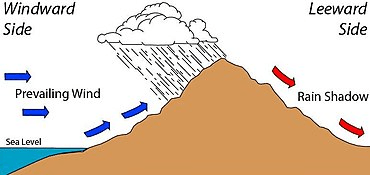
True or false: Land heats up and cools faster than water.
True
What gas makes up most of Earth's atmosphere?
nitrogen
Where should the ozone layer be found?
stratosphere
Why is the equator warmer than the poles?
It receives more vertical rays from the sun.
Gulf Stream
True or False: heated air is more dense than cooler air.
False
What happens to the sunlight that does not reach Earth's surface?
It is reflected or absorbed.
What is one advantage and one disadvantage of the greenhouse effect?
Advantage: It keeps Earth warm.
Disadvantage: It can trap too much heat.
Why do areas near the ocean have more moderate temperatures than areas further inland?
The ocean holds heat better than land, so it keeps the area warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer.
What causes wind to move faster?
large difference between air pressure
Why do winds on Earth appear to curve?
Earth rotates (Coriolis Effect)
Why is too much CO2 in Earth's atmosphere a problem?
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps the heat that would have been radiated back to space.
What happens to air close to Earth's surface after it is warmed by the sun?
It rises, forming a convection current.
In terms of pressure, how does a sea breeze form?
Land heats more than water during the day. There is high pressure over the ocean, and the air moves from high pressure to low pressure.
In terms of pressure, how does a land breeze form?
Land cools down faster than water in the evening. There is high pressure over the land, and the air moves from high pressure to low pressure.
What are two effects that cities have on climate?
The concrete in cities heats the air.
Pollution traps heated air.
Draw and label the graph of the temperature changes in the atmosphere. Label each layer and the axes.
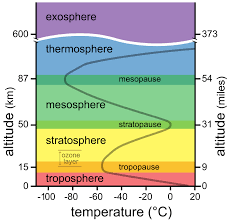
How does air pressure change as you go up in the atmosphere? Why does it change this way?
It decreases because there are less molecules above. Also, the ones above push down on the ones below.
What weather phenomenon causes the position of the jet stream to change and the eastern Pacific Ocean to be warmer than normal?
El Niño
How do ocean currents affect the land they touch?
Warm currents warm the land and cold currents cool the land. They make the land moister than areas further inland.
What process moves heat through the atmosphere?
convection currents