What is the smallest unit of an element?
The Atom
What is an element?
Substance made of one type of atom
What are the three states of matter?
How are elements arranged on the periodic table?
Increasing Atomic Number, Groups/Families (columns) and Periods (rows), and Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids.
What element is in group 16 period 4?
Selenium
Name the three subatomic particles and their charges?
Proton (+), Neutrons (0), Electron (-)
What is a compound?
Describe particle motion in a solid
Vibrate in fixed positions - can not move past one another BUT still moving! Holds its shape because of this
What does the atomic number represent?
The Number of Protons the element has.
What causes an atom to have a neutral charge?
The number of electrons must equal the number of protons for the atom's overall net charge to be 0.
Where are protons and neutrons located in an atom?
How are compounds and molecules similar but different?
Both are made of more than one atom; compounds must have two or more different elements bonded togehter; molecules can be compounds and also be two of the same type of atoms bonded together (aka an element).
Move freely and spread apart moving fast and filling their container.
Why do elements in the same group have similar properties?
They have the same number of valence electrons (electrons in their outer ring).
What gives an atom its mass? Where in the atom is it located?
The protons and neutrons give the atom its mass and they are both located in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
What determines the identity of an element?
Number of Protons (Atomic Number)
Give an example of a compound and list its elements.
Water (H2O) - Hydrogen and Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) - Carbon and Oxygen
Methane (CH4) - Carbon and Hydrogen
What happens to particle motion when a solid melts?
When a solid melts, it is turning into a liquid and the particles will begin to move past each other. The particles gain energy (increase in temperature) and move faster, weakening the bonds of attraction between the particles.
Name one property that metals share. Name one property that nonmetals share. Name one property that metalloids share.
Metals: Shiny, Good Conductors, most are solid
Nonmetals: Dull, Poor Conductors, brittle
Metalloids: Share a little bit of both metals and nonmetals - Semiconductors
Draw and label an atom showing protons, neutrons, and electrons.
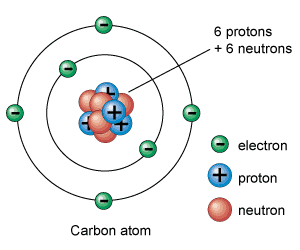
Explain why electrons, whose mass is significantly smaller than protons and neutrons, are not considered the smallest unit of an element.
Electrons are subatomic particles, not the whole element. It is the combination of protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up the atom, and atoms are the smallest unit that make up an element.
Why are there only a finite (limited) number of elements but an almost infinite number of compounds?
Limited elements combine in many ways to form compounds
What happens as a liquid freezes?
When a liquid freezes, it is turning into a solid and the particles will begin to lock into place. The particles lose energy (due to decrease in temperature) and move slower (BUT still moving - vibrating), strengthening the bonds of attraction between the particles.
Where are nonmetals located on the periodic table?
Where are metals located on the periodic table?
Where are metalloids located on the periodic table?
Nonmetals: On the right side
Metals: On the left side
Metalloids: Between metals and nonmetals
How many elements are in the compound H2SO4 and what are they?