These are common causes of eosinophilia
What is CHINA
C: Collagen vascular disease (eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis)
H: Helminthic (parasitic worm) infection
I: Idiopathic
N: Neoplasia (most commonly lymphoma)
A: Allergy, atopy, asthma
Acute onset fever with allergic type symptoms (urticarial lesions, angioedema)
Recent H/o travel to Sub-Saharan Africa with exposure to freshwater lakes
Labs: high eosinophilia
Diagnosis
What is Katayama fever (will accept Acute Schistosomiasis): helminthic infection due to exposure to freshwater lakes
T/t: steroids initially followed by antihelminthic therapy (Praziquantel)

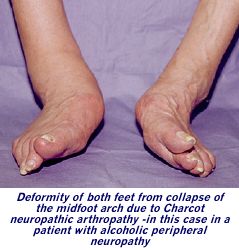
Diabetic neuropathic arthopathy presenting with foot/ankle erythema, warmth and swelling
Name the condition
What is Charcot joint?
Treatment: Casting and avoid weight bearing
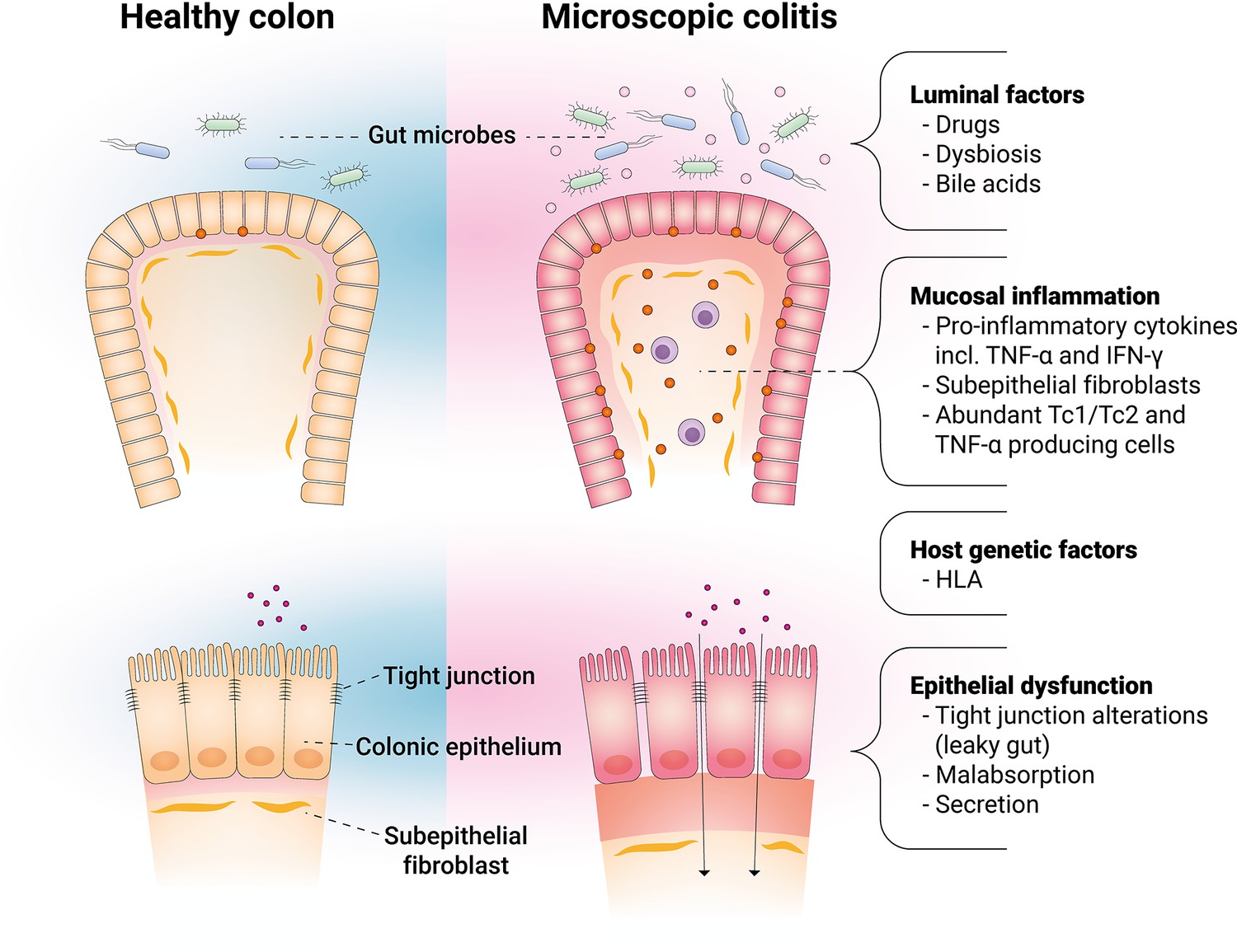
Chronic diarrhea without abdominal pain or weight loss commonly seen in women 45-60 years
Normal colonoscopy
Collagenous or lymphocytic on histology
Diagnosis?
BONUS (100): treatment
What is microscopic colitis
Treatment: antidiarrheal agents (loperamide or bismuth) for mild cases
Budesonide has the best documented efficaccy
Next test of choice in patients with normal or borderline resting ABI values
What is exercise treadmill ABI testing?
Normal ABI >0.9 to <1.4
ABI <0.9: PAD
ABI <0.4: compatible with ischemic rest pain
ABI >1.4: calcified, non-compressible arteries. see if you can do a toe-brachial index
20% of patients with essential thrombocythemia develop this condition making treatment with aspirin difficult.
What is Acquired Von Willebrand disease
(Von Willebrand disease occurs due to qualitative or quantitative defects in Von Willebrand factor.)
Acquired occurs due to consumption of large vWF multimers secondary to platelet activation.
It is associated with increased risk of skin and mucosal bleeding with PC >1000000
First line empiric treatment for animal bites
What is amoxicillin-clavulanate?
Alternate regimens: Doxycycline
-moxiflocain
-TMP-SMX PLUS: Flagyl or clindamycin
Indications to treat subclinical hypothyroidism (3-4)
BONUS: 200 points if you get all the indications
What is pregnancy?
-TSH>10
-TSH 7-9.9: age >70: treat if symptomatic
age<70: treat
-TSH 6-9: age <70: treat is symptoms are convincing
-age >70: don't treat
B/L salivary and lacrimal gland enlargement
+/-: sclerosing cholangitis, idiopathic pancreatitis
Labs: increased eosinophils
-tissue biopsy shows IgG4 plasma cells
Diagnosis
What is IgG4 related disease
A fibro-inflammatory disease causing fibrosis and tumor like swelling of affected areas.
Typically seen in middle aged men
LOOK FOR: increased peripheral eosinophilia
T/t: steroids
Pulmonary mid-systolic murmur, tricuspid diastolic flow murmur and fixed split S2
What is ASD?
Hypocellular bone marrow with increased fat content and pancytopenia
Name the condition
BONUS question (100): what is an associated epithelial cell growth you should look for with this condition
What is aplastic anemia
BONUS: Aplastic anemia is often associated with thymoma
Fever
Relative bradycardia
GI/neuro signs and symptoms
CXR: possible unilobar infiltrate
Treatment:
What is levoquin (will accept newer macrolides-azithromycin)
Treatment for legionella pneumonia
Name the treatment avoided in Graves opthalmopathy which is known to worsen opthalmopathy
What is Radioactive iodine?
Avoid in Graves as it can worsen opthalmopathy unless patient has been pre-treated with steroids
REMEMBER: RA Iodine can trigger thyroid storm so pre-treating patients with PTU or a BB before RA iodine should be considered in elderly patients and those with severe pre--t/t thyrotoxicosis
Components of post-exposure prophylaxis of Hepatitis A.
What is Hep A vaccine and Immunoglobulin
HA Vaccine preferred from 12months-40 years of age as it provides a longer duration of protection
Ig alone is preferred in immunocompromised people and <12 months: mostly passive immunity
R atrial collapse during end-diastole is the earliest and most sensitive echocardiographic sign of this condition
What is cardiac tamponade
What is plasma exchange?
(Remember TTP has: Anemia, Thrombocytopenia, Renal failure +/- fever, confusion)
Coagulation studies will be normal
Fever, myalgia, purpura fulminans, headache
H/o splenectomy
Name the disease and causative organism
What is bacterial meningitis secondary to Neisseria
Treatment: Rocephin and Vancomycin
Capital of Ukraine
What is Kiev?
Middle aged woman
Fatigue, Pruritus
Hyperpigmentation
RUQ discomfort
Diagnosis:
What is PBC?
Diagnosis: increased alk phos, positive AMA
Sniff test showing restrictive defect, supine hypoxemia, reduced FVC in supine position and recent cardiac surgery
Diagnosis
What is unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis?
Rarely occurs due to phrenic nerve injury after cardiac surgery
O/E: Dyspnea at rest or exertion, supine hypoxemia
CXR: elevated hemidiaphragm

Sniff test: N diaphragm moved downward during inspiration. Here the paralysed side moves paradoxically upward
Generalized LAD is NOT seen in this condition characterized by massive splenomegaly, normocytic anemia, hepatomegaly
Peripheral smear: giant platelets and teardrop erythrocytes
What is primary myelofibrosis
Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly occur from extramedullary hematopoeisis
Death is usually from bone marrow failure +/or transformation to acute leukemia
Elderly patients presenting with AMS, focal seizures and fever should be treated with this medication empirically to avoid treatment delays
What is iv acyclovir?
HSV encephalitis presents with these symptoms
CSF testing: lymphocytic pleocytosis
Order HSV PCR NOT CSF culture or serologic testing for HSV
Iv acyclovir should be started within 24 hrs of symptom onset
Commonest genetic cause of primary hypogonadism
What is Kleinfelter's syndrome
Patients will present with gynecomastia and hypogonadism
KEEP IN MIND: Patients with Kleinfelters are at an increased risk of breast cancer
Treatment of post-prandial hypotension
Non-pharmacological:
-smaller or more frequent meals, increased salt and water intake, avoid alcohol, custom-fit compression stockings
-Severe: can try octreotide to reduce splanchnic vasodilation
Sudden cardiogenic shock
Pulmonary edema
Hyperdynamic precordium
A new systolic murmur
2-7 days following MI
Diagnosis
What is Papillary muscle rupture?