What are the 4 Classifications according to the common patterns of symptom behavior?
Position Sensitivity, Weight Bearing Sensitivity, Constrained Posture Sensitivity, Pressure Sensitivity
What are the LBP classifications based on intervention strategies?
Manipulation, Stabilization, Specific Exercise, Traction
How many vertebrae are there in the entire vertebral column?
33 (7 C, 12 T, 5 L, 5 S, 4 Co)
What ligament in the vertebral column limits extension?
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)
Which area(s) of the spine has the greatest amount of mobility?
Cervical and Lumbar Spines
What is the name of the structure formed by the Internal Oblique, External Oblique, and Transversus Abdominis?
Rectus Sheath
Which areas do the lumbar spine refer symptoms to? (Name 2)
- Abdomen
- Lower T Spine
- SI Region
- Entire LE (hip/knee/ankle/foot)
What myotome corresponds to hip flexion?
L2
What innervates the muscles of the back?
Dorsal Rami
Name the condition that is consistently aggravated by specific postures/positions while also being relieved by other postures/positions?
Position Sensitivity
A patient presents with an "instability catch" or aberrant movement during lumbar ROM; which of the Fritz classifications would you be tempted to identify her as?
Stabilization
Name the primary curves of the vertebral column
Thoracic and Sacral
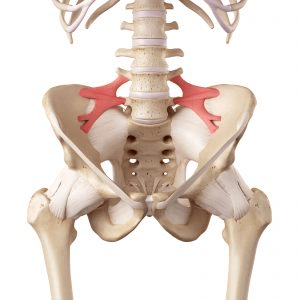
Identify This Structure
Iliolumbar Ligaments (resists flexion, extension, axial rotation, and lateral bending of L5 on S1)
Which part of the disc has the highest percentage of proteoglycans?
Nucleus Pulposus (due to necessity of resisting compressive loads)
Name the erector spinae muscles from most medial to most lateral
Spinalis, Longissimus, Iliocostalis
What DTR Grades can be considered normal?
In general, what dermatomes correspond to the anterior/ventral LE?
L1 - L5
What ligaments create the greater and lesser sciatic notches?
Sacrotuberous Ligament, Sacrospinous Liagment
A patient arrives in the clinic complaining of low back pain, as you examine the patient's bony alignments via palpation of the pelvic girdle landmarks you notice the patient cringing away from your touch; which Vollowitz 4 does this indicate?
Pressure Sensitivity
You suspect a nerve root compression based on signs and symptoms presented and discover that no movements centralize the symptoms; what classification is indicated?
Traction
What makes up the mobile segment (the smallest unit in the spine)
2 Adjacent Vertebrae, Intervening Intervertebral Disc, All Soft Tissue that Secure them Together
This ligament limits forward flexion and reinforces the posterior portion of the annulus fibrosus, it is narrow in the Lumbar Spine
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)
What are the 2 functions of the intervertebral discs?
1. Separate 2 Vertebral Bodies (also acceptable: increase available motion)
2. Transmit Loads (from 1 vertebral to the next)
What is the function of the multifidus?
Rotation (to opposite side)
What are the two most important nerves in the Lumbar Plexus?
Femoral Nerve (muscular innervation of anterior thigh)
Obturator Nerve (muscular innervation of medial thigh)
What dermatome corresponds with the heels and medial calf?
S1
What do the mesoderm, ectoderm, and endoderm give rise to? (partial credit available)
Mesoderm: MSK (+ Circulatory System + Dermis)
Ectoderm: NS (+ Epidermis)
Endoderm: GI (+ Lining of Organs)
These types of patients experiences an increase in symptoms at night, when waking up, during driving, and standing
Constrained Posture Sensitivity
Name 2 of the characteristics that fall in the Manipulation Criteria?
- No symptoms distal to the knee
- Recent onset of symptoms (< 16 days)- Low FABQ score (< 19)
- Hypomobility of the lumbar spine
- Hip IR ROM > 35 degrees for at least 1 hip
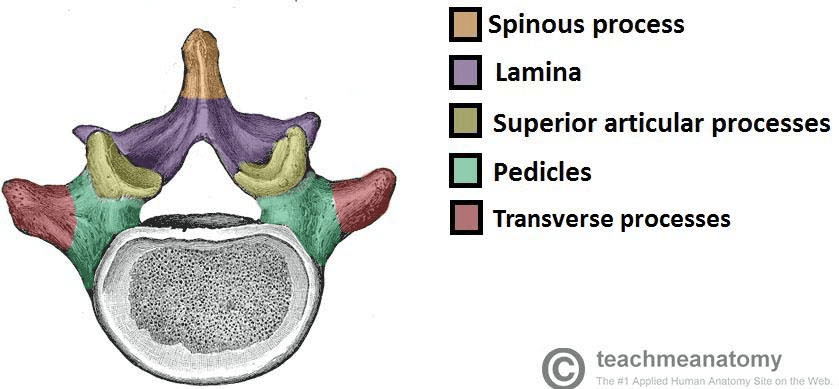
All of the highlighted structures can be identified as the...
Neural Arch
Identify the ligament(s) that limit lateral flexion
Intertransverse Ligaments (also acceptable: Alar Ligaments)
What determines the amount of motion at the intervertebral disc?
Ratio between Disc Thickness and Vertebral Body Height
What muscle creates lateral trunk flexion or "hip-hiking" when contracted unilaterally and lumbar extension when contracted bilaterally?
Quadratus Lumborum
What levels of the vertebral column do the Lumbar Plexus and Sacral Plexus nerves emerge from? (Partial credit available
Lumbar: L2 - L4
Sacral: L4 - S4
What myotome corresponds with plantar flexion/eversion?
S1
This term refers to a sensation that feels like a narrow band of sharp pain following a nerve path that can be accompanied by sensory or motor symptoms
Radicular
These types of patients change position very often during load bearing activities and will frequently shift from one end range lumbar position to another (with very little relief)
Weight Bearing Sensitivity
Patients with an Extension Specific Exercise Classification have what criteria? (Name at least 1)
- Directional preference for extension
- Symptoms centralize w extension
- Symptoms peripheralize w flexion- Symptoms distal to buttock
Vertebrae in the lumbar spine are most restricted in what motions?
Rotation
What are the first 2 ligaments to be damaged by excessive flexion?
Interspinous Ligament, Supraspinous Ligament
Name the 4 levels of herniations (bonus points for descriptions!)
Protrusion
Prolapse
Extrusion (where annular fibers are disrupted)
Sequestration
The pelvic diaphragm muscles are innervated by...
Branches of Sacral Plexus
Describe the following terms with one word:
- Neurapraxia
- Axonotmesis
- Neurotmesis
Neurapraxia: compression
Axonotmesis: stretch
Neurotmesis: severance
What myotome corresponds with dorsiflexion/inversion?
L4
When a patient forward bends, what combination of side bending and rotation will result in the greatest amount of movement
Side bending and Rotation in same direction
In a patient with Position Sensitivity, you notice that they tend to display passive positioning behaviors with less acute thigh - torso angles (i.e. standing is preferable to seating, sleeping supine is preferred to prone). What type of position bias might this patient have?
Extension Bias
Postpartum patients tend to fall under what classification?
Stabilization
What specializes the Lumbar vertebrae? (Name at least 1 characteristic)
- Large vertebral body
- Short and thick pedicles- Short and broad laminae
- Long slender TP
- Thick broad SP- Triangular shaped vertebral forament
This ligament resists forward flexion by resisting the separation of the laminae, it is strongest/thickest in the L Spine; its name comes from the slight yellow color this ligament usually has.
Ligamentum Flavum
In the IV discs, the collagen fibers of the annulus fibrosus are arranged in sheets/lamellae, these are arranged in concentric rings that surround the nucleus and are oriented in opposite directons by about 120 degrees to each other. What is the advantage from this?
Allows tensile force resistance in nearly all directions
Name the all muscles that contribute to increasing intra-abdominal pressure and forced expiration?
External Oblique, Internal Oblique, Transversus Abdominus, Rectus Abdominus
This refers to degeneration of an axon that occurs distal to the site of damage, wherein the myelin and distal axon are phagocytized
Wallerian Degeneration
What myotome corresponds with great toe extension?
L5
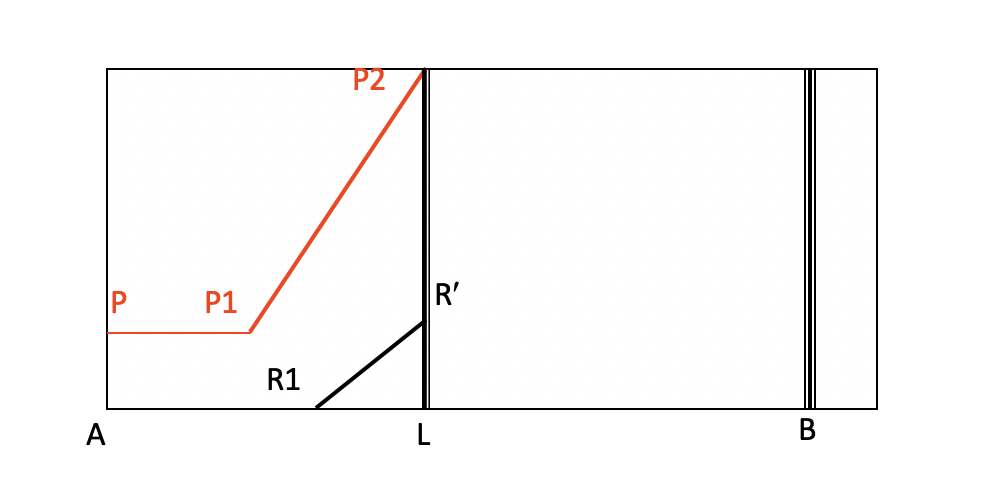
What 2 major conclusions can be drawn about the patient's pain from the Movement Diagram above?
Patient is in Constant Pain at rest
Pain in the Limiting factor (Pain Dominant)