microbials
These are the disease manifestations in advanced HIV patients of a double stranded DNA virus that establishes latency in the myeloid cell lineage and is transmitted through body fluids
What is retinitis in advanced HIV disease?
Could also present with mono-like illness and possible pneumonia and GI disease in transplant patients. This is describing Cytomegalovirus.
Gram positive, coagulase positive cocci in clusters
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
This is a gram negative, glucose fermenting, oxidase negative, lactose negative, urease positive bacilli.
What is proteus?
If this was urease negative, further testing would be needed to identify if it were Salmonella or Shigella
Outer membrane pores are an example of this form of antibiotic resistance
What is intrinsic resistance?
Gram negative, facultatively anaerobic fermentative curved rods that are oxidase positive and have a polar flagella. Can cause "rice-water" stool.
What is Vibrio cholerae?
This is a virus, not found in the Herpes family, which has increased risk in the case of T-cell deficiency
What is JC/BK virus?
Rod-shaped bacteria that is able to prevent lysosome fusion with phagosome
What is M. tuberculosis?
These aspects of gram negative bacteria which results in toxic/septic shock or severe inflammatory response including fever, leukopenia, hypotension, acidosis, DIC, and even death. This part of gram negative bacteria includes an O-antigen.
What are lipopolysaccharides?
MRSA evades the activity of ceftriaxone due to its ability to produce the penicillin-binding protein PBP2a, which has reduced affinity for this cephalosporin
What is Ceftaroline?
Steps of gram staining
What is crystal violet staining then potassium iodide solution then decolorization which is the use of ethyl alcohol or acetone then safranin staining?
A mother and infant with this bacteria would present with meningitis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Transmission of the bacteria across the placenta can lead to fetal demise or preterm delivery. This bacteria is a gram positive, catalase positive, beta hemolytic rod with a positive CAMP test.
What is Listeria monocytogenes?
These aspects of gram positive bacteria are involved in ion binding, charge maintenance, membrane integrity, adherence, and anchor proteins.
What is lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acids?
Salmonella and shigella invade the cell using this system to inject virulence factors into host cells and effect actin filaments
What is type 3 secretion system?

This is the best parameter to predict efficacy for Vancomycin
What is AUC/MIC?
This molecule, only found in gram positive bacteria, non-specifically activate large numbers of CD4 T cells by promoting the binding of TCR to MHC class II molecules resulting in proinflammatory cytokine production
What is superantigens?
Three encapsulated bacteria with vaccines available (Name all three).
This is cause by exotoxin damage due to a gram positive, club-shaped, aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, catalase positive, non-motile bacteria. This toxin is made of two polypeptides and one of the polypeptides can cause the inactivation of the elongation factor (EF-2).
What is pseudomembrane formation or "the strangling angel"?
There are two proteins found in gram negative, lactose positive, indole positive bacillus. One strain of this bacteria is most common in developing countries and leads to diarrhea. This bacteria contains these two proteins lead to loss of electrolytes, water, and nutrients from intestinal cells.
What are heat labile and heat stable toxins?
This is caused by competition with pyridoxine by a tuberculosis drug that diffuses into all body fluids including the CSF
What is neuropathy?
The five bacterial toxins that are encoded on the lysogenic phage
What is Group A strep erythrogenic toxin, Botulinum toxin, Cholera toxin, Diptheria toxin, and Shiga toxin?
In severe cases, this bacteria can cause hydrops fetalis. All should be screened and treated for this bacteria during pregnancy.
What is Syphilis?
This is the smallest free-living organism which can be tested for using a test where IgM antibodies bind the antigen on human RBCs at 4oC.
What is Mycoplasma pneumo?
This is diagnostic test of choice for a gram negative, oxidase positive bacterial infection that occurs only in humans and is typically transmitted by sexual contact. Men present with symptoms of urethritis while women present with symptoms of cervicitis. Neonates can present with conjunctivitis.
What is NAAT (PCR)?
The infection described is N. gonorrhea
This condition causes tingling/pruritis and erythema of the face, neck, and skin. This condition is caused by a drug whose pharmokinetic profile is based on the area under the curve and above the minimum inhibitory concentration. This drug is used to treat certain gram positive cocci and is inactive against gram negative bacteria.
What Vancomycin Flushing Syndrome?
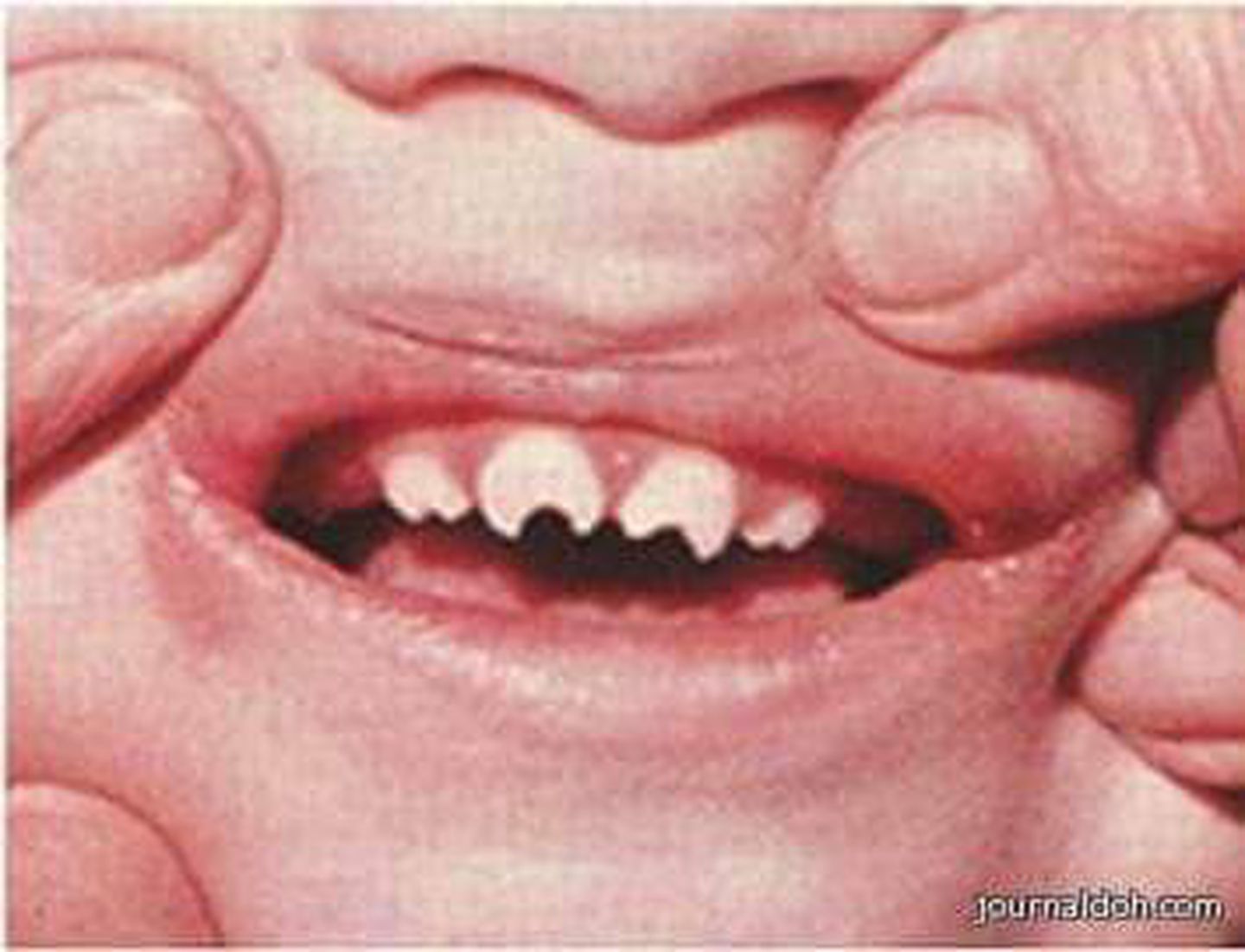
The teeth deformities that can be present in patients with late congenital syphilis
What is Hutchinson's teeth?
Can also have Saber's shins