Fill in the blank.
What makes gram-negative bacteria more resistant than gram-positive bacteria.
Gram negative bacteria have a thick layer of lipopolysacharride, its chemical composition makes the bacteria more resistant towards medications.
What is a protist? Why does it have it's own separate kingdom?
Describe Heterotrophic, Mixotrophic, and Autotrophic. What is the benefit of an organism being a mixotroph?
Heterotrophic: The ability to consume others for nutritional purposes.
Mixotrophic: The ability to harness qualities of both heterotrophs and autotrophs. Meaning that a mixotroph can use inorganic compounds to generate their nutrition and consume others to gain nutrition as well.
Autotrophic: Utilizing light from the sun to generate energy to create their own nutrition such as glucose.
Identify the Supergroup, Clade, and Species of this protist. Give 1 example of a characteristic unique to it.
SG: Excavata
Clade: Parabasala
Species: Trichonomas Vaginalis
A common sexually transmitted disease (STD) that moves by the way of flagella.
What is the shape, arrangement and gram stain of this bacteria?
Coccus, Staphylo-arrangment, gram positive
Do you think something can be both hydrophilic and hydrophobic? Give an example.
Yes, the permeable plasma membrane. The PM consists of a substance called phospholipids that is arranged in a bilayer structure (hence phospholipid bilayer). It has a hydrophobic exterior and hydrophilic exterior.
What are some common features/characteristics about protists?
Can be multicellular, unicellular, heterotrophic, autotrophic, mixotrophic. Variety of anatomical symmetry. Ability to form cysts.
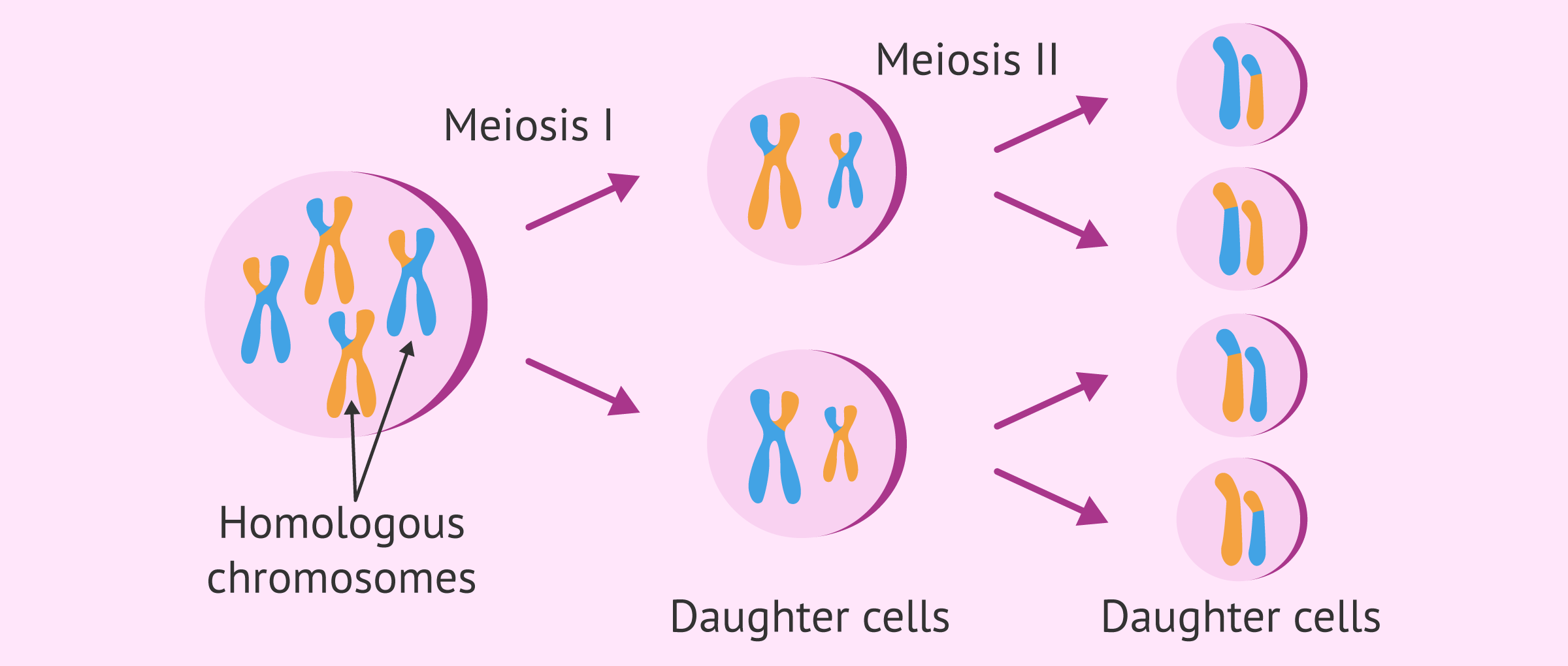
Describe Asexual Reproduction.
Typically involves mitosis, the spliting of a cell for the creation of daughter cells. Usually 2 diploid daughter cells.
Identify the Supergroup, Clade, and Genus of this protist. Give 1 example of a characteristic unique to it.

SG: Excavata
Clade: Diplomonadida
Genus: Giardia
Has 2 nuclei, moves with flagella, and is unicellular.
How does this structure affect the bacteria's survival?
Endospores provides a way for bacteria to protect their genetic information in times of adversity such as when resources are limited. They are incredibly resilient to heat, desiccation and chemicals. They have the ability to reactivate when conditions are right centuries later.
Two types of toxins present in gram negative bacteria
One is released as bacteria grow. The other is released as bacteria die (cell lysis).
Endotoxin and Exotoxin
What are the 3 main ways that protists move around in their eviornment?
Flagella: A long tail like structure, protists can have 2 or more (ex: Giardia)
Pseudopodia: "false-feet" involves movement of cytoplasm. (ex: Amoebas)
Cilia: Small hair-like structure that are reminiscent of Flagella. (ex: Paramecium)
Describe Sexual Reproduction.
Typically involves meiosis. Diploid cell splits into 4 haploid cells that become the gametes. They can be unified with another haploid eventually creating a unique diploid cell.
True or False: These protists are not in the same Supergroup. Explain why it is true or not.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/euglena-57ee66383df78c690faf9a1b.jpg)
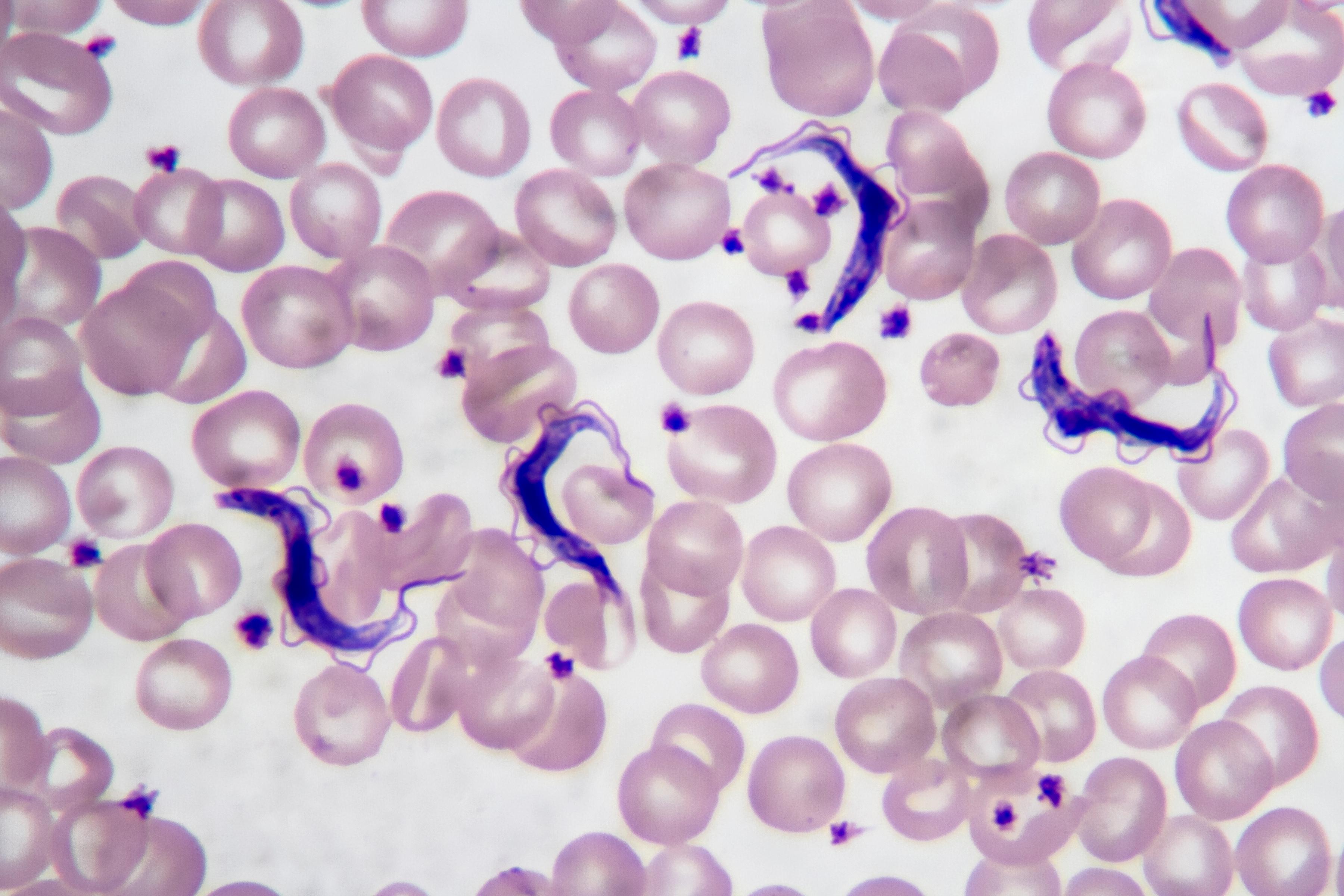
False. These 2 protist belong to the same SG Excavata. Because, they do belong to the same clade Euglenozoa. The top protist is Euglena and the bottom protist is Trypanosoma.
What antibiotic is the most effective this case and why? What is the name of this phenomenon? Which bacteria is the most resistant to which medication?

Antibiotic D is the most effective because it displays the a Zone of Inhibition. The clearing within this zone signifies that bacteria are sensitive to the medication. Antibiotic A seems to be the least effective medication due to the lack of Zone of Inhabitation which signifies the active resistance that this bacteria has to the Antibiotic A.
Composition of bacterial cell wall. Present in both types. Thicker layer of it in Gram +, thinner layer in Gram -
Peptidoglycan
What is the difference between endospores and cysts?
Endospores is a structure produced by bacteria for the purpose of self-preservation in the midst of harsh conditions that are present. Cysts are produced by most often times parasitic protists as a means to protect itself from unfavorable conditions.
What features define the eukaryotic kingdoms of Animalia, Fungi, and Plantae?
Plantae: Multicellular, autotrophic, cell wall made out of cellulose, photosynthesis, multicellular dependent embryos (MDE)
Animalia: Multicellular, heterotrophic, no cell wall, MDE.
Fungi: Decomposers, Heterotrophic, Cell wall made of Chitin.
Identify the Supergroup, Clade, and Genus of this protist. Give 1 example of a characteristic unique to it.

SG: Archaeplastida
Clade: Rhydophyta
Genus: Not specified (Just Red Algae)
Red algae typically live in more profound waters in the ocean.
What is the difference between obligate aerobes, anaerobes, and facultative anaerobes? Identify which one is which on the picture.
Obligate aerobes: Has to use oxygen in order to conduct cellular respiration.
Obligate anaerobes: Unable to use oxygen to conduct cellular respiration, uses fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
Facultative anaerobes: Preferable uses oxygen if available, but has the ability of using fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
What is the shape, arrangement and gram stain of this bacteria?

Bacillus, Strepto-arrangment, Gram +
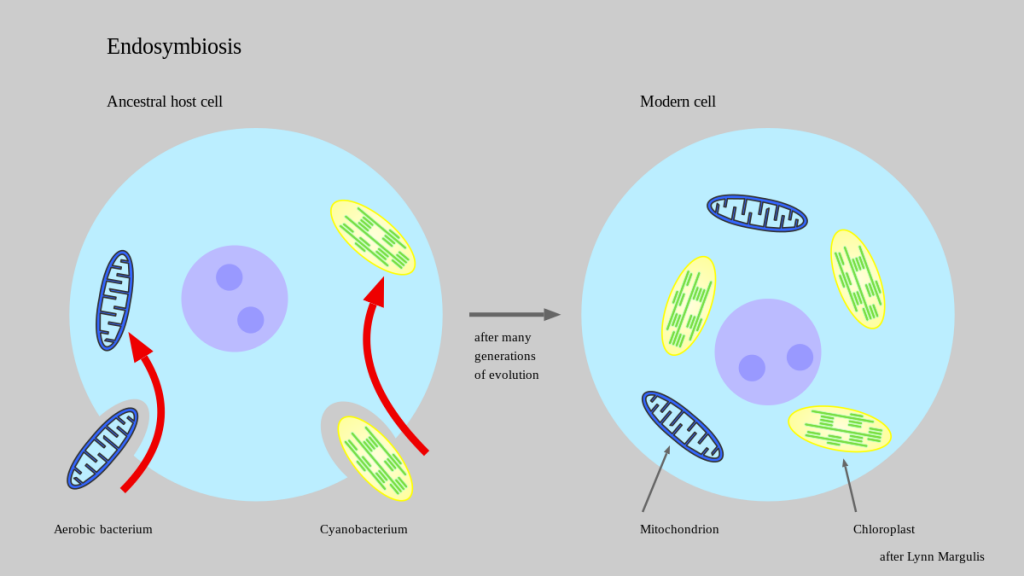
Describe Endosymbiotic Theory.
A theory that states that Chloroplast and Mitochondria once derived from a free-living single-celled organism that ended up inside another cells. Both chloroplast and mitochondria have their own separate DNA from the rest of the cell.
What is the reason why red algae tend to live in deeper waters?
Red algae are able to absorb wave lengths such as blue and green light that are able to reach into the depths of the ocean that brown and green algaes are unable to absorb at such depths. Phycocyanin & Phycoerythrin is are pigments that help red algae absorb those green & blue wavelengths.