What is the pacemaker of the heart?
What is SA Node
What is the HR for NSR?
60-100
What small sticky pads are used to detect the heart's electrical signal?
What are electrodes
Point to the P wave
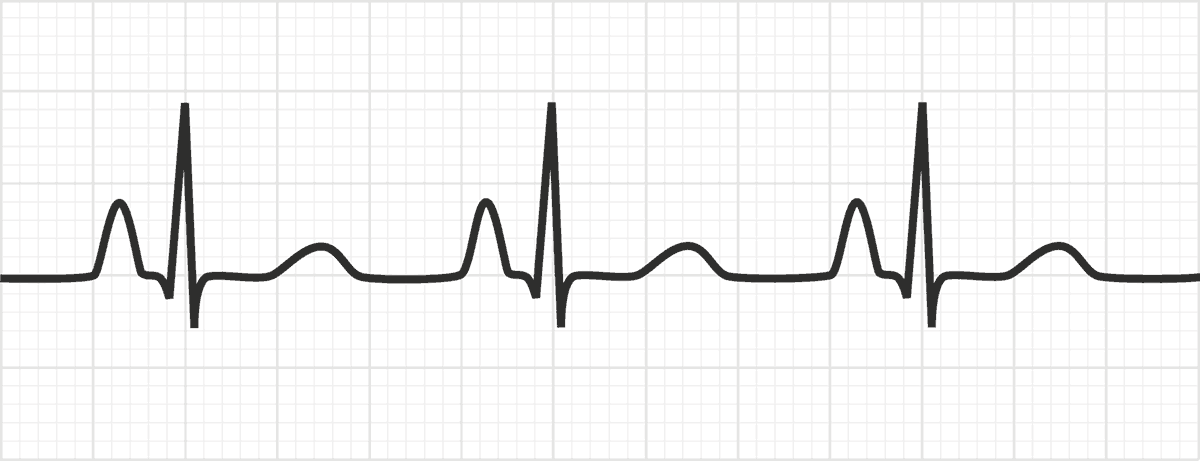
Correct
What is the backup pacemaker of the heart?
The Av node.
How many chambers of the heart are there?
Four
What is the HR for Sinus tachycardia?
greater than 100
What is the patient and the EKG device
What comes after the p wave but before the QRS?
PR interval
What is the intrinsic rate of the AV node?
40-60 BMP
What muscular wall of the heart called?
What is myocardium
Your r-r is irregular, and there are no defined P waves. What arrhythmia is it?
Afib
What is a cardiac cycle?
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occur during one complete heartbeat.
What is located after the AV node before the left and right bundle branches?
What is the Bundle of His.
What are the four valves of the heart?
Tricuspid Valve
Pulmonary Valve
Mitral Valve
Aortic Valve
What are the two arrhythmias not compatible with life?
Asytole and VFIB
The two measurements on a grid paper are _____ and _____. (fill in the blank)
what is voltage and time,
Represents the end of ventricular conduction and the beginning of recovery; a change may indicate MI
What is ST segment
Can you describe a normal heart conduction pathway?
SA node, nodal pathways, AV node, buddle of his, L/R buddle branches to the Purkinje fibers
Can you describe how blood flow through the heart?
Right atrium: Deoxygenated blood in.
Right ventricle: Pumps to lungs.
Lungs: Oxygen in, carbon dioxide out.
Left atrium: Oxygenated blood in.
Left ventricle: Pumps to body.
Body: Uses oxygen, returns deoxygenated blood to star
How does an EKG work?
The EKG machine amplifies the electrical signals to make them more visible on the EKG strip or monitor and records them in real-time.
What does the QRS wave represent
Ventricular depolarization