The inferior wall of the heart can be viewed through which leads?
II, III, aVF

Seen on ECG when atrial depolarization occurs
P wave
is a result of atrial depolarization which occurs due to SA node activity spreading throughout the atria causing contraction
100 bpm
What leads are used to determine the mean electrical axis?
*Bonus point: Normal QRS axis is between which two degrees?
I, II, III, avL, aVR, aVF
* -30 and +90
The QRS complex represents what phase of the ventricular action potential?
*Bonus point: Which ion channel is open in this phase?
Phase 0
Which leads give a lateral view of the heart?
Leads I, aVL, V5, V6
Delay in AV node depolarization is seen as what segment on ECG?
PR segment
(Conduction through the AV node is normally slow to allow for ventricle filling before ventricular contraction occurs)

50 bpm
A right or left axis deviation indicates what cardiac pathologies?
Right/Left ventricular hypertrophy or right/left bundle branch block
What phase of the ventricular action potential does the T wave represent?
Phase 3 (repolarization)
Occlusion of the right coronary artery will appear as an ST elevation in which leads?
II, III and aVF
Seen on ECG when ventricular depolarization occurs
*Bonus point: Describe the sequence of ventricular depolarization
QRS complex

67 bpm
MEA = + 30 (normal axis deviation)
A 27-year-old man comes to the physician for a general check-up. Physical examination is normal. His ECG is also normal and lead II is shown below. Which of the following phases of the cardiac action potential is most likely related to the labeled segment on his ECG?
Phase 2 (ST segment)
A (-) electrode placed on the left arm (LA) and a (+) electrode placed on the left leg (LL) gives rise to what lead?
III

Seen on ECG when the ventricles are completely depolarized
*Bonus point: Elevation in this segment on ECG is used to diagnose which cardiac pathology?
ST segment
ST elevation myocardial infarctions (heart attacks)

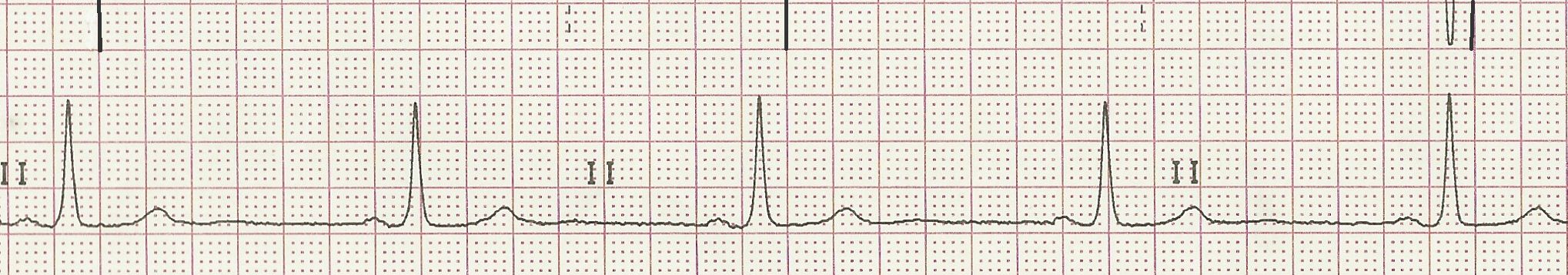
43 bpm

MEA = + 150
In what phase of the SA node action potential are funny channels opened?
Phase 4
A 61-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of chest discomfort. She has a 12-year history of migraines treated with a beta-blocker. Blood pressure is 138/82 mmHg, pulse is 82/min and respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is within normal limits. ECG findings in an augmented unipolar lead show pathology in the lateral wall of the heart. A (+) electrode placed on the left arm gives rise to this lead. Which lead is being described?
aVL
A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician for shortness of breath that began after a flight from London. She has a 5-year history of hypercholesterolemia. Her blood pressure is 128/84 mmHg, pulse is 112/min and respirations are 20/min. Lung auscultation reveals crackles. ECG findings show an abnormality in atrial contraction due to a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following labeled components of the normal ECG below is most likely abnormal in this patient?
E (P-wave)
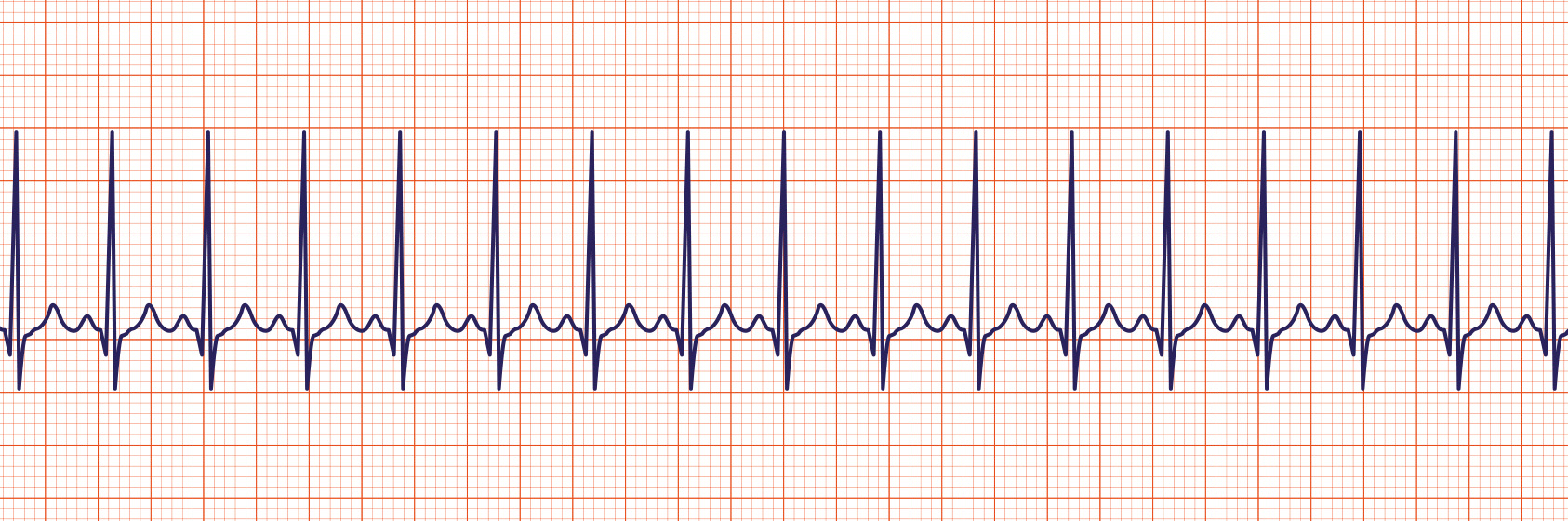
150 bpm
A 67-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of chest pain. He has a 15-year history of hypertension. His blood pressure is 188/92 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows mild swelling of his feet and ankles. ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most likely range of values for his mean electrical axis?
A. 0° to +90°
B. +90° to +/-180°
C. 0° to -90°
D. -90° to +/-180°
C. 0° to -90°
A 56-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of a 2-hour history of shortness of breath, nausea and palpitations. His pulse 132/min, respirations are 18/min, and his blood pressure is 162/96 mmHg. Cardiac auscultation shows an irregular heartbeat, varying from 120-140 bpm. ECG confirms atrial fibrillation. Administration of an experimental drug that inhibits the T-type calcium channels, lowers his heart rate to 92/min. There is no change in cardiac contractility or diastolic aortic pressure. This drug is most likely to cause which of the following effects on the cardiac action potentials?
A