This structure processes conditioned fear responses
Amygdala
The #1 excitatory NT in the brain
Glutamate
The only sensory modality that does not route through the thalamus before reaching the primary sensory cortex
Olfaction
The conduction of an action potential in a myelinated neuron ("jumping" AP)
Saltatory conduction
This drug is used to treat bipolar disorder and shares a name with a popular Nirvana song
Lithium
Name the structure your Jeopardy host is point to in the image: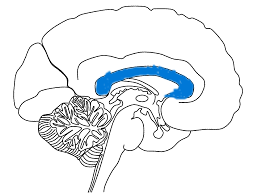
What is the corpus callosum?
This NT is present at the NMJ and is required to facilitate movement.
Acetylcholine
This mechanoreceptor is responsible for detecting deep pressure and vibration.
Pacinian corpuscle
The point at which the charge of a neuron is below resting potential (~-70)
hyperpolarization, hyperpolarized neuron
This type of amnesia is characterized by the inability to form new memories.
Anterograde amnesia
This structure on the neuron is where saltatory conduction occurs
Node of Ranvier
This enzyme breaks down dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
Monoamine oxidase
This photopigment is involved in signal transduction in visual processes (especially in the periphery of the visual field)
Rhodopsin
The type of potential that decreases the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential
IPSP or inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Schizophrenia
What structure is highlighted in this diagram? (more specific than occipital lobe)
Striate cortex or primary visual cortex
This drug increases the activity of monoamine NTs, prolonged & frequent use of this drug is likely to result in drug-induced psychosis and formication (skin-picking)
After optic nerve fibers cross the optic chiasm, they pass through this region within the thalamus.
Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
1. Electrostatic pressure
2. Diffusion
This condition is characterized by the inability to perceive moving objects
Akinetopsia
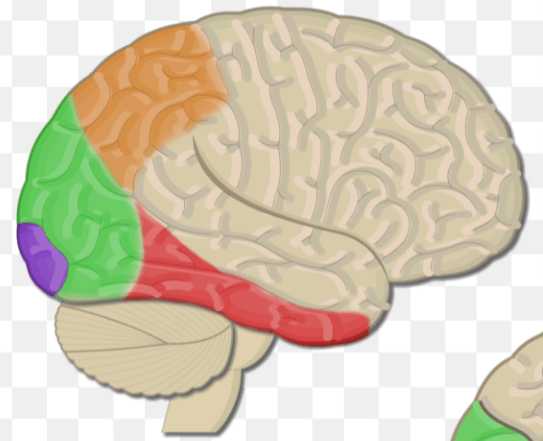 What structure is highlighted in red in this diagram?
What structure is highlighted in red in this diagram?
Inferotemporal cortex
These drugs can cause undesirable side effects such as Parkinsonian symptoms and tardive dyskinesia
First-generation antipsychotics
This condition is characterized by the lack of coordination between visual input and motor responses (a woman tries to grab a waterbottle but is unable to successfully grab it)
Optic ataxia
The 3 processes through which a neurotransmitter leaves the synapse
1. Reuptake
2. Enzymatic degradation
3. Diffusion
Taenia Solium (aka Tanya) is a pathogen involved in the development of which neurological condition (lays eggs in the brain)
Neurocysticercosis