The cranial nerves in the supraorbital fissure
What are CN III, CN IV, V1, Vi
The orientation of white and grey matter in the spine and brain
Brain: outside grey/inside white
Spine: white outside/grey inside
The process in which the CNS form during pregnancy
What is neuralation
The three main sensory system pathways
What are the dorsal column/medial lemiscus, anterolateral/spinothalamic, spinocerebellar
The pathway from retina to the brain
what is the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, LGN, optic radiations (superior and inferior), primary visual cortex/striate cortex
The name for the topographic orientation of the motor and somatosensory cortex
what is the little homunculus
What happens to neuroplasticity as we age (two things mentioned in lecture)
What are the corticospinal (anterior/lateral) and corticobulbar pathways
The membrane in the ampulla where sterocillia project
What is the capula
The two key language areas of the brains and the lobe of the cerebral cortex they are in
What are broca's (frontal) and wernicke's (temporal) areas
The type of hypersensitivity that Myasthenia Gravis is and why
Type IIB/V hypersensitivity (antibody producing)
The pathway of motor neurons from the brain to the target tissue
Motor cortex, corona radiata, internal capsule, pyramids (decussate), go to grey matter in spine, LMN go to target tissue
The two structures that the conjunctiva fold into in the medial aspect of the eye
What are the plica semilunaris and caruncle
The part of the brain responsable for recognizing faces
The fusiform Gyrus
The two types of cranial edema and their mechanisms
Vasogenic = damage to blood brain barrier leading to increased fluid, increased pressure/damage, increased necrosis due to compressed vessels, increased inflammation, can then evolve to cytotoxic
Cyototoxic: Decreased ATP production due to some sort of ischemia, leads to inability to remove Na in neurons, leads to fluid following salt, leads to swelling and necrosis of cells, leads to disruption of BBB, leads to vasogenic edema, leads to more cytogenic edma
The three paths of the anterolateral tract in the brainstem and what each does
The cranial nerve that crosses in front of the pons
what is the trochlear nerve
The 3 classes of focal seizures and generalized seizures mentioned in the seizure lecture
Focal: Focal impaired, focal unimpaired, focal evolving into bilateral (secondary generalized)
Generalized: tonic clonic, myoclonic, absent
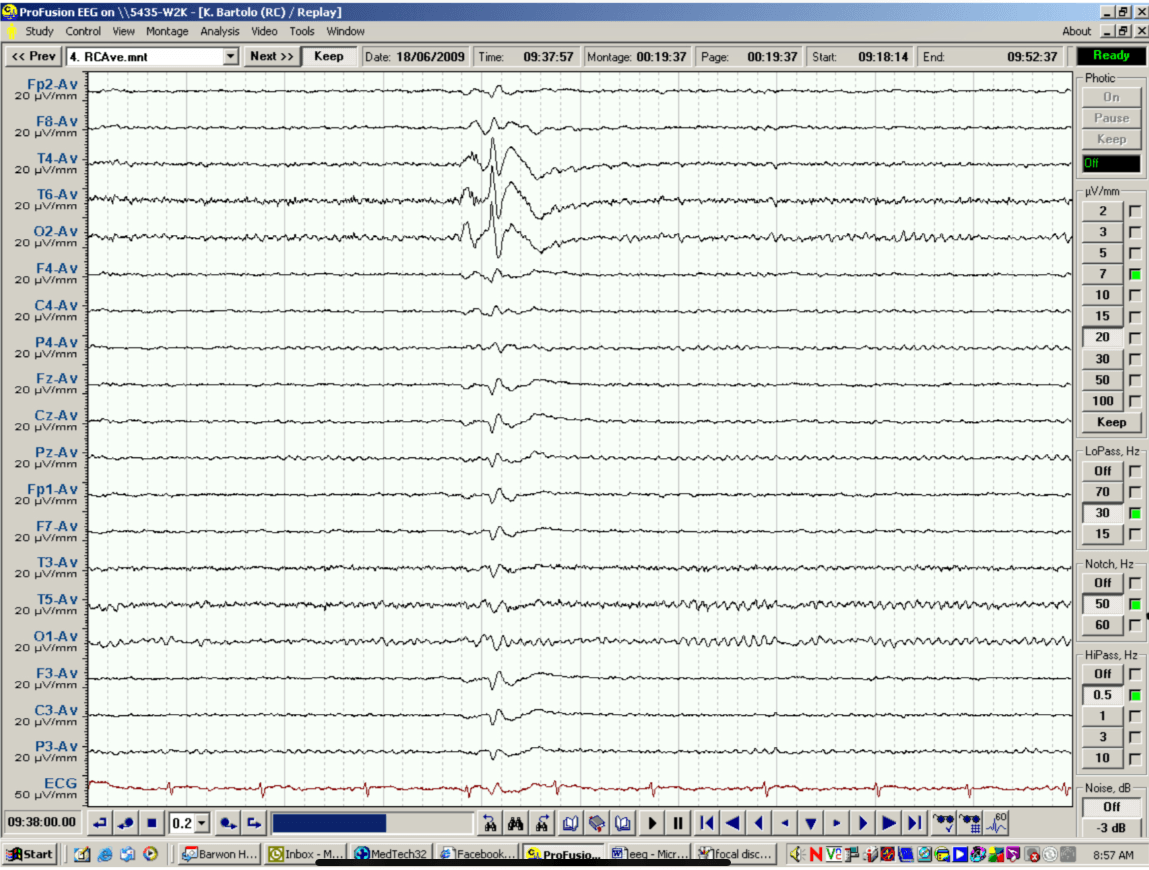
Interpret this EEG correctly
The difference between substantia nigra effects on the direct and indirect pathway and the pathway
Direct: Substantia nigra releases dopamine onto D1 receptors in caudate & putaman, which increases the release of gaba onto the globulus interna inhibiting it, which decreases gaba release onto the thalamus, which increases glutamate
Indirect: the substantia nigra releases dopamine onto d2 neurons, which decreases gaba release onto globulus externa, which increases gaba release onto subthalmic nucleus, which decreases glutamate release from the STN, which decreases gaba release from globulus interna, which increases movement