Economics is the study of:
A: Changes in technology
B: The best way to run a society
C: How society decides what, for whom, and how much to produce
D: Household spending decisions
E: How people react to the world around them
C: How society decides what, for whom, and how much to produce
Knowing the amount of a good or service buyers would purchase at any given price tells you:
A: Supply
B: Demand
C: Excess supply
D: Excess demand
E: Equilibrium
B: Demand
The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising and, consequently, the purchasing power of currency is falling, is called:
A: Inflation
B: Deflation
C: Equilibrium
D: Symmetry
E: Disequilibrium
A: Inflation
The Latin phrase "ceteris paribus" is a common assumption in economic models, and roughly means:
A: "Holding all other things equal or constant"
B: "At a given time"
C: "Assuming normal conditions"
D: "In light of this change"
E: "Ignoring outside factors"
A: "Holding all other things equal or constant"
The basic economic problems are common to _____
(A) Mixed economy
(B) Socialism
(C) Capitalism
(D) All the above
(C) Capitalism
When demand and supply are equal, economists most commonly call this:
A: Inflation
B: Deflation
C: Equilibrium
D: Symmetry
E: Disequilibrium
C: Equilibrium
If a price increase in Product A increases the quantity demanded of Product B, then we know that Product B is a(n) ____ to Product A.
A: Complementary good
B: Substitute good
C: Normal good
D: Inferior good
E: Luxury good
B: Substitute good
The study of the economic behavior of individual units of an economy (such as a person, household, firm, or industry).
A: Economics
B: Macroeconomics
C: Microeconomics
D: Demography
E: Sociology
C: Microeconomics
If country A can produce more of good X than good Y in a day, even if they produce less of both goods than country B, then country A has a(n) ____ in good X.
A: Surplus
B: Shortage
C: Comparative advantage
D: Absolute advantage
E: Marginal advantage
C: Comparative advantage
The pricing of factors of production is called
(A) Distribution
(B) Exchange
(C) Production
(D) Consumption
(A) Distribution
The opportunity cost of a good is:
A: The time lost in finding it
B: The units of other goods given up in order to get another unit of that good
C: Money spent to buy a good
D: The effort it takes to access a good
E: The skill level needed to use a good
B: The units of other goods given up in order to get another unit of that good
When consumers' income increases, their spending on _____ will increase, while their spending on _____ will decrease.
A: Goods; services
B: Substitute goods; complementary goods
C: Inferior goods; normal goods
D: Normal goods; inferior goods
E: Luxury goods; services
D: Normal goods; inferior goods
In economics, "scarcity" occurs when:
A: There is too much competition in the market
B: The price of a good is so low that producers stop producing it
C: The price of a good is so high that consumers stop buying it
D: There is a shortage of resources to meet demand at price zero
E: Debt reaches an unsustainable level
D: There is a shortage of resources to meet demand at price zero
Please study this model carefully before answering the question. In the model above, to what does P1 refer?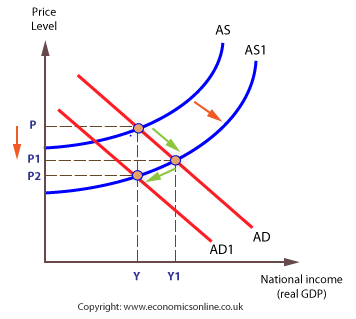 A: The price level at GDP level Y.
A: The price level at GDP level Y.
B: The price level at GDP level Y1.
C: The price of a good at supply Y1.
D: The quantity supplied of a good at price Y1.
E: The quantity demanded of good A at price Y1.
B: The price level at GDP level Y1.
The consumer will buy _____ at lower prices.
(A) Equal
(B) Less
(C) More
(D) Neither less or more
(C) More
In economics, a market is best described as:
A: A place to buy things
B: A place to sell things
C: The movement of prices in the absence of government intervention
D: A place, physical or virtual, where buyers and sellers interact
E: A local store
D: A place, physical or virtual, where buyers and sellers interact
What does the blue line labeled "S" represent in a basic economic model?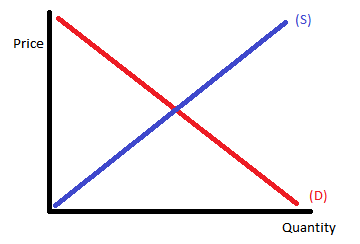 A: Demand
A: Demand
B: Scarcity
C: Supply
D: Services
E: Standard price
C: Supply
The most common way of measuring a national economy is GDP. This acronym stands for:
A: Growth in Domestic Productivity
B: Gross Domestic Product
C: Gain in Domestic Production
D: Greater Domestic Product
E: Gross Dollar Productivity
B: Gross Domestic Product
Please study this model carefully before answering the question. In the model above, to what does AD refer? A: Original demand.
A: Original demand.
B: Demand after a downward shift in prices.
C: Original supply.
D: Supply after a downward shift in prices.
E: The price level at GDP level Y1.
A: Original demand.
The demand for labour is _____
(A) Derived demand
(B) Direct demand
(C) Effective demand
(D) Elastic demand
(A) Derived demand
In a "free market" economy:
A: The government determines the price of goods and services
B: Private businesses work with the government to solve economic problems
C: Goods and services are provided for free
D: Private citizens are taxed, but corporations are not
E: Prices adjust naturally to reach equilibrium in the face of scarcity and demand
E: Prices adjust naturally to reach equilibrium in the face of scarcity and demand
What is the term for the situation in which a single supplier controls the market in a particular sector?
A: Monopoly
B: Oligopoly
C: Mixed economy
D: Planned economy
E: Competitiveness
A: Monopoly
An economic actor who is risk averse, when given a choice between two investments with similar predicted return, would be expected to choose:
A: Both investments
B: Neither investment
C: It is impossible to predict
D: The higher-risk investment
E: The lower-risk investment
E: The lower-risk investment
Please study this model carefully before answering the question. The movement in this model illustrates what phenomenon? A: Growth in production
A: Growth in production
B: Marginal productivity
C: Deadweight loss
D: Inflation
E: Deflation
E: Deflation
To explain rent, _____ economists make use of the term transfer earning.
(A) New Classical
(B) Today
(C) Classical
(D) Modern
(D) Modern