Which of the following equations can be used to directly calculate an object’s momentum, p?
A. p = MV
B. p = FΔT
C. I = M ΔT
D. Δp = FΔT
A. p = MV
A billiard ball collides with a stationary identical billiard ball in an elastic collision and donates 100% of its momentum to the second ball. After the collision, which of the following is true of the first ball?
A. It maintains its initial velocity.
B. It comes to rest.
C. It has one-half its initial velocity.
D. It moves in the opposite direction
B. It comes to rest.
Which phrase best defines the term energy?
A. Energy is the ability to do work.
B. Energy is the force and object can exert.
C. Energy is the amount of matter present in an object.
D. Energy is the amount of heat an object can give off.
A. Energy is the ability to do work.
When the FORCE of a spring is plotted as a function of the distance it is stretched the graph will be _________
A. Curved
B. Linear
C. Unknown
D. Sin Wave
B. Linear
Which has a greater momentum—a truck with a mass of 2250 kg moving at a speed of 25 m/s or a car with a mass of 1210 kg moving at a speed of 51 m/s?
The CAR has greater Momentum
56250 Kg m/s Vs 61710 Kg m/s
If a force is exerted on an object's momentum, which statement is true?
A. A large force always produces a large change in the object’s momentum.
B. A large force produces a large change in the object’s momentum only if the force is applied over a very short time interval.
C. A small force applied over a long time interval can produce a large change in the object’s momentum.
D. A small force always produces a large change in the object’s momentum.
C. A small force applied over a long time interval can produce a large change in the object’s momentum.
Two objects with different masses collide and bounce back after an elastic collision. Before the collision, the two objects were moving at velocities equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. After the collision,
A. the less massive object had gained momentum.
B. the more massive object had gained momentum.
C. both objects had the same momentum.
D. .both objects lost momentum
A. the less massive object had gained momentum.
Two marbles, Marble "A" is twice the Mass of marble "B". They are dropped to the ground from the roof of a building. Just before hitting the ground, marble "A" has
A. as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
B. twice as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
C. half as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
D. four times as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
E. impossible to determine
B. twice as much kinetic energy as the lighter one.
When the ENERGY of a spring is plotted as a function of the distance it is stretched the graph will be
A. Curved
B. Linear
C. Unknown
D. Sin Wave
A. Curved
A 2 Kg model Airplane possesses 50 J of total KE. Wind does -25 J of work upon the object. What is it's velocity after the headwind?
5 m/s
A 75 kg person walking around a corner bumped into an 80 kg person who was running around the same corner. The momentum of the 80 kg person ______
A. increased.
B. remained the same.
C. decreased.
D. went to zero.
C. decreased.
Two objects stick together and move with a common velocity after colliding. Identify the type of collision.
A. elastic
B. inelastic
C. nearly elastic
D. Exact
B. inelastic
Wanda claims that she has invented a machine which continuously puts out 100 units of energy while consuming only 10 units of energy . This machine violates
A. Conservation of energy
B. Conservation of momentum
C. no physical law
A. Conservation of energy
Two identical springs that are attached to a box in two different ways. The box is then pulled to the right. Which box experiences the greater Net Force when pulled?
A, B, None, Same
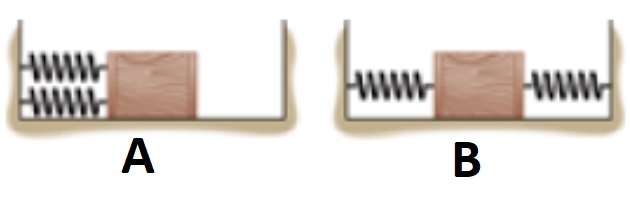
Same
A 2000 Kg truck is traveling 10 m/s when everything quits. ONLY friction is applying ANY work at this point. 100 m later the truck is traveling 5 m/s. How much work did friction do in this time?
75000 J
Two objects with different masses collide and bounce back after an elastic collision. Before the collision, the two objects were moving at velocities equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. After the collision _____
A. the less massive object had gained momentum.
B. the more massive object had gained momentum.
C. both objects had the same momentum.
D. both objects lost momentum.
A. the less massive object had gained momentum.
What is the effect of an impulse on an object at rest?
A) It remains at rest
B) It starts moving
C) It moves in the opposite direction
D) It changes its mass
B) It starts moving
Which is the best definition of the term Potential energy?
A. Potential energy is stored in an object
B. Potential energy is the work that an object does.
C. Potential energy is the energy due to temperature.
D. Potential energy is the energy due to motion.
A. Potential energy is stored in an object
If two different springs are stretched by the same force, but one spring stretches more than the other, what can be said about the spring constants of the two springs?
A) The spring that stretches more has a higher spring constant.
B) The spring that stretches less has a higher spring constant.
C) Both springs have the same spring constant.
D) The spring constants cannot be determined from this information.
B) The spring that stretches less has a higher spring constant.
A spring pitcher throws a 0.25 Kg softball at 10 m/s. If the spring were cocked back 0.5 m what would be the required spring constant (k)
100 N/m
Two swimmers relax close together on air mattresses in a pool. One swimmer’s mass is 48 kg, and the other’s mass is 55 kg. If the swimmers push away from each other ______
A. their total momentum triples.
B. their total momentum doubles.
C. their momenta are equal but opposite.
D. their total momentum decreases.
C. their momenta are equal but opposite.
Two objects move separately after colliding, and both the total momentum and total kinetic energy remain constant. Identify the type of collision.
A. elastic
B. inelastic
C. nearly elastic
D. perfectly inelastic
A. elastic
An object is moving uphill and slowing down. Which one of the following statements is true of the object?
A. Both its kinetic energy and its potential energy are constant.
B. Its kinetic energy is increasing and its potential energy is decreasing.
C. Its kinetic energy is decreasing and its potential energy is increasing.
D. Its kinetic energy is decreasing and its potential energy is constant.
E. Its kinetic energy is constant and its potential energy is increasing.
C. Its kinetic energy is decreasing and its potential energy is increasing.
When a spring is compressed, what happens to the potential energy stored in the spring?
A) The potential energy decreases.
B) The potential energy remains the same.
C) The potential energy increases.
D) The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
A) The potential energy decreases.
Two Springs are in SERIES. Spring 1 has a K = 150 N/m and Spring 2 has a K = 300 N/m. What is the combines Spring Constant?
100 N/m