The process by which cells "Drink" fluids around them.
Pinocystosis
Active Transport requires energy to move resources in and out if its membrane, where Passive transport requires what to do the same?
Concentration Gradient
Define Reproduction, Irritability, and movement
Ability to produce more cells, to respond to stimuli, and to move
Plastids that contain yellow, orange, or red pigments used in photosynthesis are called what?
Chromoplasts
What is the bi-layer in the fluid mosiac model made of?
Phospholipids
The jellylike fluid inside the cell in which organelles are suspended.
Cytoplasms
Both of the membrane bound sacs found in cells:
Vesicles and Vacoules
What is this?
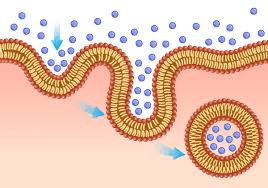
Endocytosis
False
Synthesis, Respiration
What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell?
Pro- No nucleus or membrane bound organelles
Eu - Nucleus and membrane bound organelles
What does the pre-fix glyco mean for the things in the bi-layer?
Glycogen
What do ribosomes do?
Protein synthesis
A vacoule found only in plant cells
What is this?

Exocytosis
There are three types of solutions, what are they called?
Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic
Ability to distribute molecules within the cell, and the ability to maintain internal stablity.
Cytoskeleton, what do?
Holds the cell together, helps the cell keep shape, aids in movement.
Which end of the phospholipid is Hydrophilic?
The Ball head
The holes in the cell wall that is modeled like swiss chess.
Plasmodesmata
What is a plastid and what are the three types?
Double-membrane bound organelles involved in the manufacturing or storage of food.
Chloroplasts, Chromoplasts, Leucoplasts
These two -sis words describe when a cell dies - either by internal rupturing or collapsing from lack of water.
Cytolysis and plasmolysis
The process of helping molecules pass through a membrane is what?
Facilitated Diffusion
What is secretion? Excretion?
Biosynthesized substances released, removing soluble metabolic waste.
Paired Organelles that organize fibers required for cell division. Found only in animal cells.
Centrioles
What is the main purpose of the fluid mosaic model.
a scientific model that describes the structure and function of cell membranes
The packaging plant of the cell responsible for storing proteins and lipids.
Golgi Apparatus
Threadlike proteins found in cell's cytoskeleton.
Microfilaments
The endocytic process by which a cell engulfs large, solid particles or cells
Phagocytosis
The amount of solute per unit volume
Concentration
Define Egestion, Digestion, and Ingestion
Digestion - Ability to break down molecules into nutrients.
Ingestion - The ability to take in nutrients that are dissolved.
Egestion - The ability to remove nonsoluable, undigested waste from the cell
the rapid movement of a cell's contents, including organelles and cytoplasm, that occurs within the cell
Cytoplasmic Streaming
The ability of cells to distinguish and communicate with other cells by binding to complementary molecules on their surfaces
Cell-To-Cell Recognition
What 4 things are found in this picture?
Nucleus, Rough ER, Smooth ER, Ribosomes
Where are these found?
Centrosome