Which part of the cell is small membrane-bound sac that is used to transport molecules such as proteins?
A. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
B. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
C. Vacuole
D. Cytoskeleton
E. Vesicle
E. Vesicle
Anaerobic respiration takes place when there is no
A. CO2
B. Glucose
C. O2
D. enzymes
C. O2
Which of the choices below gives the products of glycolysis?
A. 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate
B. 2 ATP, 2 CO2, 2 pyruvate
C. 8 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 pyruvate
D. 1 FADH2, 4 NADH, 2 pyruvate
E. 6 CO2, 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP
A. 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate
Which of these describe an instance when mitosis is the most likely process to occur?
A. A mouse produces sperm cells
B. A yeast cell dies after exposure to UV light
C. A bacteria grows into a colony
D. A chromosome is being copied
E. A puppy grows into a dog
E. A puppy grows into a dog
Glycine binds to the glycine receptor and causes changes in neurotransmission in the spinal cord and brain stem by allowing chloride ions across the membrane. Why can’t chloride ions cross the membrane?
A. They’re too large
B. They’re too polar (charged)
C. They’re too non-polar
D. They’re too small
B. They’re too polar (charged)
Which of these is NOT found in animal cells?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Cytoskeleton
C. Cell membrane
D. Cell wall
E. Mitochondria
D. Cell wall
The point of cellular respiration is to convert ___ into ___
A. CO2 … O2
B. O2 … CO2
C. glucose … O2
D. glucose … ATP
D. Glucose ... ATP
Which of the choices below gives the products of the citric acid cycle (including the oxidation of pyruvate) per molecule of pyruvate?
A. 3 ATP, 4 NADH, 2 FADH2, 3 CO2
B. 8 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2
C. 4 NADH, 1 ATP, 1 FADH2, 3 CO2
D. 1 CO2, lactic acid, 2 NADH
C. 4 NADH, 1 ATP, 1 FADH2, 3 CO2
What is the relationship of the sister chromatids to each other?
A. They are identical to each other
B. They are similar to each other, but not identical
C. They are completely different
A. They are identical to each other
The glycine receptor is a membrane protein. This means it would be made up of what subunits
A. Amino acids
B. Phospholipids
C. Monosaccharides
D. Acetyl CoAs
A. Amino acids
Which of these is found in prokaryotic cells?
A. Mitochondria
B. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C. Cell membrane
D. Vesicle
E. Peroxisome
C. cell membrane
How many molecules of ATP are produced per molecule of glucose during fermentation
A. 0
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
E. 36-ish
B. 2
What happens to the NADH and FADH2 generated during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle?
A. It powers cellular work
B. It is converted directly into ATP
C. They are converted into CO2
D. They are used to generate glucose
E. They power the electron transport chain
E. They power the electron transport chain
Cancer cells contain
A. More cyclins than normal cells.
B. More Rb than normal cells.
C. More genes than normal cells.
D. Fewer genes than normal cells.
E. More mutations than normal cells.
E. More mutations than normal cells.
When glycine binds to the glycine receptor, it opens a protein channel and allows chloride ions to diffuse into the cell. This means that the concentration of chloride ions must be higher
A. Inside the cell
B. Outside the cell
C. Equal on both sides
B. outside the cell
Muscle cells require a lot of energy in order to power muscle contractions. Which organelle are they likely to have a lot of?
A. Cell membrane
B. Peroxisome
C. Cytoplasm
D. Mitochondria
E. Chloroplast
D. Mitochondria
Which area(s) of the cell are utilized during aerobic respiration?
A. Cytoplasm
B. Mitochondria
C. Chloroplast
D. A and B
E. A, B, and C
D. Cytoplasm and Mitochondria
During which process(es) is oxygen actually required (as in, the process itself requires oxygen)?
A. Glycolysis
B. Citric acid cycle
C. Oxidative phosphorylation
D. Citric Acid Cycle and Oxydative Phosphorylation
E. All three
C. ONLY Oxidative phosphorylation
A somatic cell in a koala has 16 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be in a koala cell after mitosis? (type it in!)
16
If you were testing the effect of different light intensities on photosynthesis by monitoring bubbles produced by a plant in water, what would be the independent variable?
A. Wavelength of light
B. Light intensity
C. Bubbles produced
D. Type of plant
E. photosynthesis
B. Light intensity
What is the cell part circled in black? Type it in!
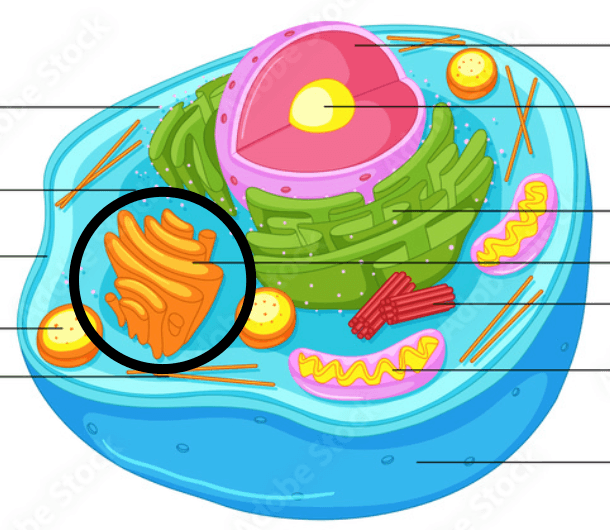
Golgi
Yeast is being kept in two test tubes: one under aerobic conditions and one under anaerobic conditions. Both are fed 2g of sugar. Which tube will have produced more CO2 after all the sugar is metabolized?
A. The aerobic tube
B. The anaerobic tube
C. Both the same
D. Can’t tell
A. The aerobic tube
During which process(es) is carbon dioxide produced?
A. Glycolysis
B. Citric acid cycle
C. Oxidative phosphorylation
D. Citric Acid Cycle and Oxydative Phosphorylation
E. All three
B. Citric acid cycle
Cells can commit programmed cell death by undergoing a process called apoptosis. Which of these would be the most likely to lead to apoptosis?
A. A mutation in p21 tumor suppressor gene.
B. A mutation in a proto-oncogene.
C. p53 tumor suppressor gene functioning correctly.
D. Phosphorylation by an active cyclin-CDK.
E. Mitosis occurring without cytokinesis.
C. p53 tumor suppressor gene functioning correctly.
The image below shows the process of (type it in!)
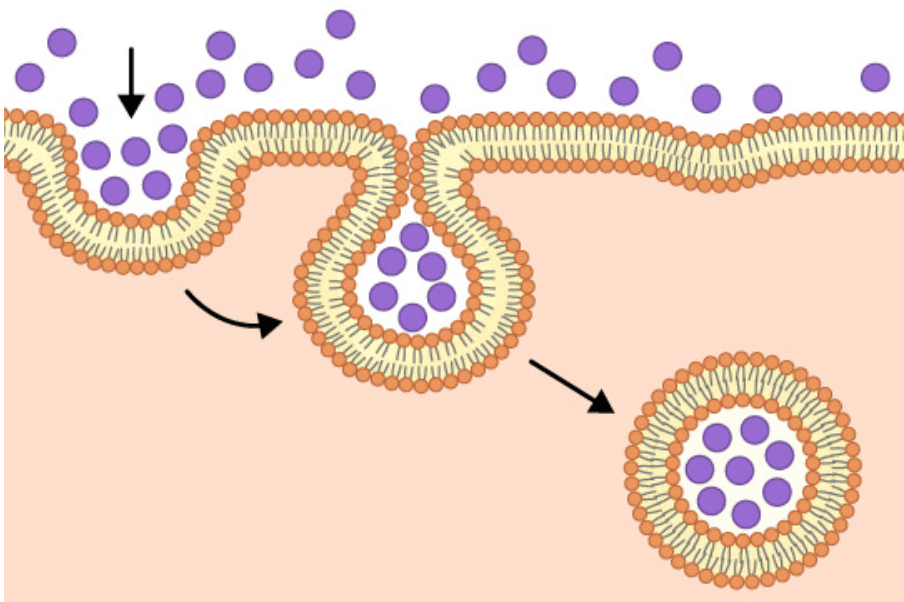
endocytosis