Assessment
What is microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms
What is the nursing process ?
An organized sequence of problem-solving steps used to identify and to manage the health problems of clients
Identify the cell in the photo

Erythrocytes
What is carbohydrates
Many of this class of molecules have a common formula Cx (H2O)y which is carbon (carbo) and water (hydrate). Carbohydrate compounds are also known as sugars or saccharides. Carbohydrates are called polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones. This means that carbohydrates contain hydroxyl (OH) and carbonyl (C=O) functionalities,
what is community health
A group of people who share common interests, who interact with each other, and who function collectively within a defined social structure to address common concerns
A group of people living in the same place or having a characteristic in common
A social group of any size, whose members reside in a specific locality, share government, and often have a common cultural and historical heritage
what is psychology ?
Is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
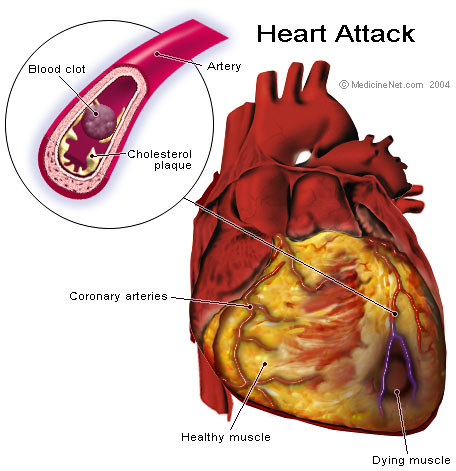
What is a heart attack?
a condition in which blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked, causing heart cells to die
Real father of Jesus
God
Microorganisms?
Microorganisms are a large & diverse group of microorganisms that exist in single cells or clusters
What is communication?
Communication can be defined as the process by which people share ideas, experience, knowledge and feelings through the transmission of symbolic messages
What is hematocrit
The percentage of whole blood volume contributed by formed elements
Dietary carbohydrates
Sugars
Starch
Fibre
define health according to WHO
A state of physical, mental and social wellbeing, and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity
William Wundt founded whichpsychological school of thought?
Structuralism
Ascorbic acid common name
vit c
What are the atria?
the two upper chambers of the heart. There is a right atrium (which receives unoxygenated blood returning from the body) and a left atrium (which receives oxygenated blood returning from the lungs).
Which microorganism is acellular
virus
Two forms of communications and what is their definitions
•Verbal-refers to our use of words
• nonverbal- refers to communication that occurs through means other than words, such as body language, gestures, and silence
erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets
Formed elements
Give an example of an monosaccaride, disaccharide and polysaccharide
Sugars
◦Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose and galactose)
◦Disaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose)
Starch and fibre
◦Polysaccharides
WHAT IS COMMUNITY HEALTH
A field of public health
A discipline which concerns itself with the study and improvement of the health characteristics of biological communities
which approach is focused on COMPONENTS of the MIND, it probes the functions and purposes of the mind and behavior in the individual’s adaptation to the environment
functionalism
I am an enriched media.
What is chocolate media?
The method that is designed to achieve lawn growth. What plate am I?
What is Muehler Hinton plate?
This person in 1847-1850 introduce antibotics and German-Hungarian physician also known as the father of infection control
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis or Semmelweis
Active listening?
the process of fully attending to what the patient is communicating being aware of the client’s emotional state and using verbal and non-verbal skills to encourage the client to continue speaking
Give two functions of the blood
transportation of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones, and metabolic wastes.
Regulation of the pH and ion composition of interstitial fluids
The restriction of fluid losses at injury sites. Defense against toxins and pathogens. The stabilization of body temperature
Human needs how much percentage of calories from carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
◦Total carbohydrates 45%-65% of total calories
Levels of Prevention are describe them
•Primary –prevention of the occurrence of a condition or problem, health promotion, illness and injury prevention
•Secondary – screening, diagnosis, treatment
•Tertiary – prevention of consequences, treatment of consequences, prevention of recurrence
is a concept whose value change from case to case
Variable
Created the first laboratory of expiremental psychology in 1879
William Wundt
Father of modern psychology
Sigmund Freud
Give the 5 major kingdoms of microbes and state what can be found under two major ones
Eukaryotes
- Algae, Protozoa, Fungi, Slime molds
2.Prokaryotes
◦ Bacteria, Archaebacteria
3.Viruses
4. Prions
Give 5 verbal communication skills? and explain two
- Pace (speed) & intonation (rise and fall of the voice in speaking) – will modify the feelings and impact of the message. Intonation can express enthusiasm, sadness, anger, or amusement. Pace may indicate interest, boredom or fear.
- Simplicity - using commonly understood words, being brief and complete. Avoid the use of medical jargons. Using appropriate terms for age of client.
- Clarity (saying exactly what is meant) & brevity (using the fewest words necessary) – clear direct messages are more effective. To ensure clarity the nurse must speak slowly and enunciate carefully.
- Timing & relevance – regardless of how clearly one speaks the timing must be correct and the message must be relevant-be of interest or concern.
- Adaptability – spoken messages must be altered in accordance to clients behavioral cues (if client is upset - find out why) what is said must relate to the individual.
- Credibility – worthiness of belief/trust. To foster communication be consistent, dependable, and honest.
- Humor – can be positive, can be used to help client adjust to difficult and painful situations. Laughing can reduce tension, release physical stress as well as emotional stress.
What is the brachiocephalic artery?
The first major branch off of the aorta and the major artery to the forelimbs and head.

differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids
◦Every carbon is filled or “saturated” with hydrogen
Unsaturated fatty acids
◦Not filled with hydrogen
◦Less heavy, less dense
◦Monounsaturated: one unfilled spot
◦Polyunsaturated: two or more unfilled spots
State two physical environment that affects health
◦Geography
◦Climate
◦Terrain
◦Natural resources
◦Structural entities( buildings such as schools, workplaces and homes)
which research method is
is primarily exploratory It is used to gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations.
Some examples include;
Ethnography,Narrative, Case Study
Qualitative
What are the subclavian arteries?
Both a left and right, blood vessels that supply blood to the shoulders and upper limbs.

What are the carotid arteries?
The major arteries that supplies blood to the head and brain.

Give two major shape categories of bacteria and describe their shape
Bacilli (rod) Cocci (circular)
List 7 non verbal communication skiled
- Pace (speed) & intonation (rise and fall of the voice in speaking) – will modify the feelings and impact of the message. Intonation can express enthusiasm, sadness, anger, or amusement. Pace may indicate interest, boredom or fear.
- Simplicity - using commonly understood words, being brief and complete. Avoid the use of medical jargons. Using appropriate terms for age of client.
- Clarity (saying exactly what is meant) & brevity (using the fewest words necessary) – clear direct messages are more effective. To ensure clarity the nurse must speak slowly and enunciate carefully.
- Timing & relevance – regardless of how clearly one speaks the timing must be correct and the message must be relevant-be of interest or concern.
- Adaptability – spoken messages must be altered in accordance to clients behavioral cues (if client is upset - find out why) what is said must relate to the individual.
- Credibility – worthiness of belief/trust. To foster communication be consistent, dependable, and honest.
- Humor – can be positive, can be used to help client adjust to difficult and painful situations. Laughing can reduce tension, release physical stress as well as emotional stress.
Carried deoxygenated blood to the heart from the lungs
Incorrect deoxygenated blood leaves the heart through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
Give 2 essencial fatty acid state the number of carbons, their number and one source
Linoleic Acid (polyunsaturated fatty acid) Omega 6
◦18 carbons
◦2 double bonds
◦Polyunsaturated
◦Found in corn and soybean oils
◦
Linolenic Acid* (polyunsaturated fatty acid) Omega 3
◦18 carbons
◦3 double bonds
◦Polyunsaturated
◦Found in soybean and canola oils
State 4 Biological environment factors that affects health
◦Flora
◦Fauna
◦Bacteria
◦Viruses
◦Moles
◦Fungi
◦Toxic substance
◦Food water supplies
This is the body’s electrochemical communication circuitry sytem that is made up of nerves
Nervous system
The walls of the lymphatic vessels are similar to those of cardiovascular
Veins
The lymphatic trunk that drains the upper limb is the
Subclavian trunk
What are the steps in gram reaction and what reagent Is used at each ?
1.Primary stain- crystal violet is added to fixed specimen of bacteria. Both Gram negative bacteria and Gram positive bacteria become purple.
2.Mordant- Iodine is added to set the stain
3.Decolourization- Ethanol is added. Gram negative bacteria lose their colour because there is relatively little peptidoglycan to hold the stain. Gram positive bacteria retain the stain because of the thick layer of peptidoglycan.
4.Counterstain- safranin is added. This turns decolourized Gram negative bacteria pink and Gram positive bacteria deeper purple.
6 barriers to communication
•Stereotyping
•Agreeing and disagreeing
•Being defensive
•Challenging
•Probing
Testing
•Rejecting
•Changing topics
•Unwarranted reassurance
•Passing judgment
•Giving common advice
How does oxygenated blood flow through the heart?
Oxygenated blood enters the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Then the mitral valve opens and the blood exits into the left ventricle. The mitral valve closes, and the blood is pushed into the aorta, where it travels to the rest of the body.

how is carbohydrates digest?
mouth -Salivary glands secrete saliva into the mouth to moisten the food. The salivary enzyme amylase begins digestion
stomach-Stomach acids inactivate salivary enzymes, halting starch digestion
small intestine and pancreas- Starch (pancreatic amylase) →small polysaccharide maltose
lactase-lactose
maltase-maltose
sucrase-sucrose
Factors affecting health policy Implementation
}Community planning
}Community resources
}Community commitment
}Leadership
}Degree of change necessary
List 7 main neurotransmitters
•GABA
•Acetylcholine
•Glutamate
•Norepinephrine
•Oxytocin
•Dopamine
•Serotonin
Similar to bacteria. (shapes, binary fission, prokaryotic cell)
Do not contain peptidoglycan.
Ribosomal RNA sequence is different.
Can grow in extreme environments, (salt con centration 10X seawater, very high temperatures).
Archaea
Prokaryotes
Has no membrane bound nucleus or organelles.
Genetic material in region of cell called nucleoid.
Can be round, cylindrical, or spiral.
Rigid cell wall with peptidoglycan.
Multiply by binary fission.
Bacteria
How does substrances and fluid transport acrosss cell membrane?
state 3 and define 2 :( hush
1.Simple diffusion
2.Osmosis
3.Active transport
4.Facilitated diffusion
5.Group translocation
6.Engulfment
Give 3 characteristics of the Nursing Process
Within the legal scope of nursing
Based on knowledge-requiring critical thinking
Planned-organized and systematic
Client-centred
Goal-directed
Prioritized
Dynamic
How is the cardiovascular system different than the circulatory system?
The cardiovascular system only deals with the structures that circulate blood. The circulatory system deals with the structures that circulate blood and/or lymph.
Give the 9 essential amino acids
histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine
. Following is not a risk factor for development of diabetes mellitus?
a)Sedentary life style
b)Protein energy malnutrition in infancy
c)High intake of vitamin – A
which neurotransmitter is is found throughout the Central Nervous System. It plays a key function in the brain in inhibiting many neurons from firing (BRAKE). It’s the brain’s brake pedal. Low levels of it is linked with anxiety
GABA
Helps organisms demonstrate hemolysis.
Blood agar
Media that inhibits gram positive organisms from growing and is selective for lactose fermenters.
What is MacConkey?
Binary Fission: Results in the separation of a single cell into two identical daughter cells each containing at least one copy of the parental DNA
Elongation
Replication of chromosomal DNA
Invagination of cell envelope, formation of two new cells.
Health history ?
•Is a current collection of organized information unique to an individual.
•Collected using the clinical interview
Proteins produce by the immune system that destroy foreign substances are called
Antibodies
Functions of Proteins
Building materials for growth and maintenance
As enzymes
As hormones
As regulators of fluid and electrolyte balance
Transporters
Antibodies
As an energy source
The three core functions of public health are
•Assessment
•Policy Development
•Assurance
Frontal lobe functions
In charge of emotions, reasoning, planning, movement and parts of speech
Useful in purposeful acts, creativity, judgment, problem solving- CEO
Damage to this area results in less control over fine movements, esp. in the fingers
What is the endocardium?
inner lining of the heart

What is the pericardium?
membranous, fluid-filled sac enclosing the heart, which anchors it in place and protects it from being jostled about

List the four growth stages of bacteria
Lag,Exponential growth phase ,stationary and death
what is purpose of health history?
1.Provide the subjective database
2.Provides focus for the physical assessment
3.Identifying areas of strength and weaknesses
4.Identify patient health problems, both actual and potential
5.Identify supports
6.Identify teaching needs
7.Identify discharge needs
8.Identify referral needs
A paitient need 2 liters of packed red blood cells, The paitient is typed and cross-matched. The patient is typed and cross-matched. The patient has B+ blood. As a nurse you know the patient can receive what type of blood?
B+,O+,B-,O-
1 gram protein provides?
4 kilocalories (energy)
10-35% of total Calories
0.8g/kg body weight
are sub-populations within the larger population who possess some common characteristics often related to high risk for specific health problems
Aggregates
What is Broca’s aphasia and Wernicke’s aphasia
inability to produce language and inability to understanding language.
____________________ stain is done to tell whether a bacterial cell has a positive and negatively charged cell wall.
_______________ stain is done to be able to see microorganisms better using methylene blue.
Gram, simple
________________ media contains one or more agents that inhibit the growth of certain microbes
_________________ media allows multiple types of microorganisms to grow, but display visible differences between colonies.
selective, differential
Give 2 elements requirements, 2 environmental requirements and 1 growth factor required for bacteria growth
elements -Carbon,Oxygen, Nitrogen, phosphate,(K, Fe, Mn, Mg, Ca (trace elements))
environmental - temperature, hydrostatic pressure, pH, osmotic pressure
Growth factors -Amino acids and vitamins
Components of Health Process and explain all
§Assessment
•Data collection
•
Diagnosis
Analysis of data
Planning
Goals prioritized
Assessment
Data collection
Diagnosis
Analysis of data
§Planning
Goals prioritized
Which lymphatic area is larger in a child than and adult and what is the largest lymphatic system ?
Thymus,spleen
how many k/cals do carbs,protiens and fats yeild?
carbs 4kcal/g
fats 9kcal/g
proteins 4kcal/g
•The process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve their health
Health promotion
The body system consisting of a set of glands that regulate the activities of certain organs by releasing their chemical products into the bloodstream
Endocrine system
Which therapeutic communication technique is being used in this nurse-client interaction?
Client: "When I get angry, I get into a fistfight with my wife or I take it out on the kids."
Nurse: "I notice that you are smiling as you talk about this physical violence."
Making observations
A nurse states to a client, "Things will look better tomorrow after a good night's sleep." This is an example of which communication technique?
The nontherapeutic technique of "giving false reassurance"
what is a Thermophiles, Barophiles and Halophiles ?
Barophiles- thrive at high pressure
Thermophiles- thrive in high temperature
Halophiles- loves high salt concentrations by maintaining a high intracellular concentration of salt
Components of Health history give 4
•Biographic data
•Reason for seeking health care
•Present health or history of present health concern
•Past health history
•Family history
What are the lymphatic trunks and collecting ducts and functions
thoracic duct- recieves lymph from lower limbs
right lymphatic duct- recieves lymph from right side of head and neck, right upper limb
what is digestion? and give 5 organs within the digetsive system
the process by which thebody breaks down food into smaller pieces that can be absorbed by the blood and sent to each cell in your body
mouth,salivary glands oesophogus, liver, stomach, small and large intestine, gall bladder, duodeum and pancreas
Refers to all organized measures(public/private) to prevent diseases, promote health and promote life among the population as a whole
Public Health
what is the study of the degree and nature of heredity’s influence on behavior e.g.., twin studies, identical twins vs fraternal twins
Behavior genetics
A nurse is caring for a young mother who states that she is unhappy with her husband because he spends too much time with his friends during football season. The nurse agrees with the client that she is "right" and her assumption about her husband is inappropriately inattentive, which non-therapeutic communication technique is this an example of?
. Giving approval
The nurses standing 4 feet away from the client with her arms crossed. At what space is the therapeutic communication interaction most comfortable within most cultural situations?
3 to 6 feet