Big Infection
Murderers
These are the most common organisms leading to CAUTI (must name both)
GNR
Entereococcus
Definitive diagnosis of necrotizing soft tissue infection is made how?
Intra-operatively
- surgical debridement with murky/purulent fluid along fascial planes and necrotic tissue
A patient presenting with diffuse peritonitis and hypotension who was discharged several days after R hemicolectomy requires this as immediate treatment.
Abx and operative exploration
Contaminated
(open, fresh, accidental wounds, gross spillage from the GI tract)
Typically a bacteriocide, this infrequently used family of antibiotics exhibit concentration-dependent killing
Aminoglycosides (streptomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, neomycin)
This number of CFU/mL is support for diagnosis of a UTI
100 000CFU/mL
Name the THREE classifications of surgical wound infections
Superficial (skin and subcutaneous tissue)
Deep incisional (subfascial)
Organ space (deep intraperitoneal)
Name the three types of peritonitis and name a cause of each
primary - aka SBP (cirrhosis, ascites due to CHF, renal failure)**
secondary - due to intraabdominal pathology (perforation, inflammation)
tertiary - recurrent peritonitis after surgery (eg pancreatitis, bowel necrosis)
2-8% vs 6-15%
A superficial SSI occurs within 30 days of surgery and involves the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Name the other criteria (4) that can make the diagnosis.
Purulent drainage
Isolated organism from culture
S/S of infection (pain, erythema, etc)
Diagnosed as such by attending surgeon (?!)
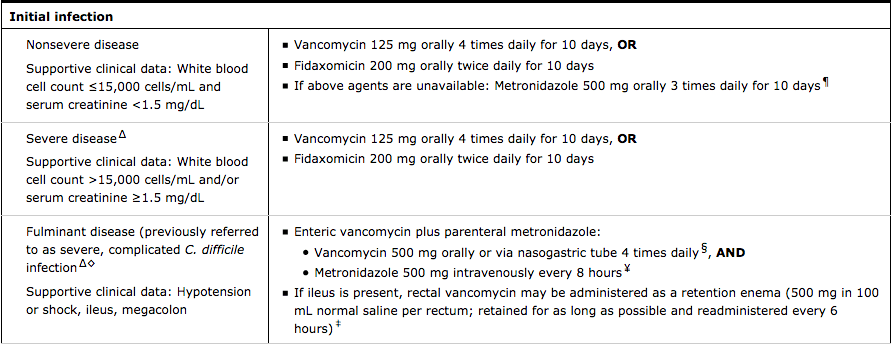
This is the initial drug of choice for treatment of initial episode of Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile colitis.
PO vancomycin
Name 3 characeristics of patients at increased risk of developing fungal infections
- poorly controlled diabetics
- chronic immunosuppression (transplant patients/IBD)
- HIV+ (AIDS)
acute appendicitis
diverticulitis
perforated duodenal ulcer
ectopic pregnancy
ovarian torsion
PID
Name 6 MODIFIABLE risk factors of surgical site infections
Obesity
Alcoholism
Pre-op albumin <3
Current Smoker
Aseptic/sterile technique
Procedure duration
Abx perioperatively
Room ventilation
Initial management of necrotizing skin infections should include coverage with Clindamycin for what purpose?
Ability to suppress group A Streptococcus toxin production
These are signs of pneumonia in intubated patients (name 5, additional 200 for sputum requirements)
increased O2 demand
increased PEEP requirements
Increased volume
Change in quality of sputum
Leukocytosis
Fever
Tachypnea
New or progressive infiltrate on CXR
Sputum specimen with 105 organisms/mL
Name the most common pathogens of the Upper GI tract (stomach+proximal small bowel) and lower GI tract (colon).
BILIARY BONUS
Which organisms infiltrate the biliary tree?
Upper - facultative aerobes (E. coli)
Lower - anaerobes (B Fragilis)
BILIARY-- sterile, but can be infected with E coli, Enterococcus and Klebsiella
This McGill University professor and surgeon made strides in the classification of a common cause of intra-abdominal infections.
John Hinchey

Appropriate pre-operative Abx for a patient undergoing elective colectomy with a life-threatening penicillin/cephalosporin allergy include which agents?
Clinda+aminoglycoside or
Clinda+fluoroquinolone or
Flagyl+aminoglycoside or
Flagyl+fluoroquinolone
Name 3 Abx regimens that can be given to a patient with acute appendicitis prior to transfer to a surgical center for appendectomy?
(PGY3-5 must name 5)
Pip-Tazo
Invanz
Ceftriaxone-flagyl
levo-flagyl
unasyn
gent+flagyl/clinda
This is type of HAI is noted to be the most financially costly per the CDC
SSIs
Name the 4 operative wound classifications and give an example of each
(I)Clean (skin/tissue excisions without inflammation)
(II)Clean-contaminated (GI/Resp/GU electively entered)
(III)Contaminated (GI/GU with unplanned spillage)
(IV)Dirty (chronic inflammation/old wound/pus)

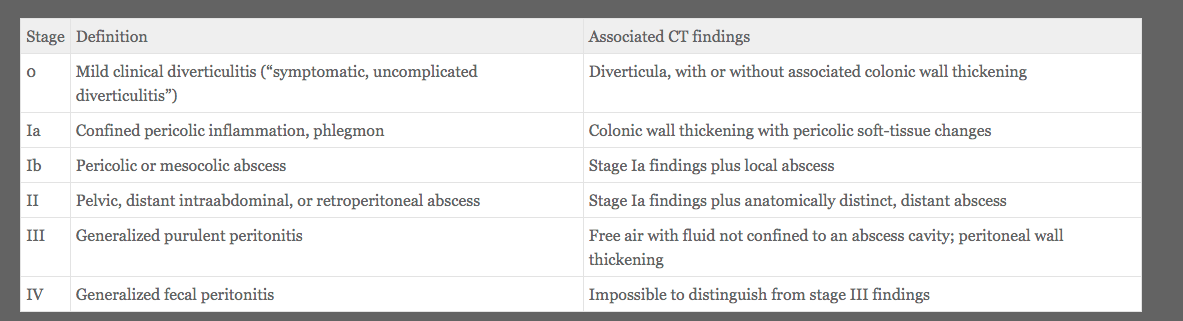
Describe the Hinchey classification of Acute Diverticulitis
(According to the Gospel of Cameron)
List 5 non-pharmacologic methods to prevent SSIs
Showering/Bathing prior to surgery
Decolonization with Mupirocin+/-chlorhexidine body wash
Alcohol-based prep
Handwashing with soap/water vs alcohol
FiO2 @80% intra-op and post-op
Use of wound protector
Smoking cessation 4-6w pre-op
Name 3 conditions which would require consideration for prophylaxis for antibiotics in a patient undergoing dental work.
prosthetic heart valves
prosthetic rings/chords
h/o infectious endocarditis
unrepaired cyanotic heart disease
repaired congenital heart disease with residual shunt
heart transplant with valvular regurg