The branch of science that studies language.
What is linguistics?
This is the model of language production that we learned.
What is the LRM (or, "Lemma") Model?
In bilinguals, languages are described as being this, thus control mechanisms are necessary to use them correctly.
What is 'competitive'?
This is what AoA stands for.
What is Age of Acquisition (or Appropriation)?
Involved in language control in bilinguals, the area of the brain highlighted (purple) below.
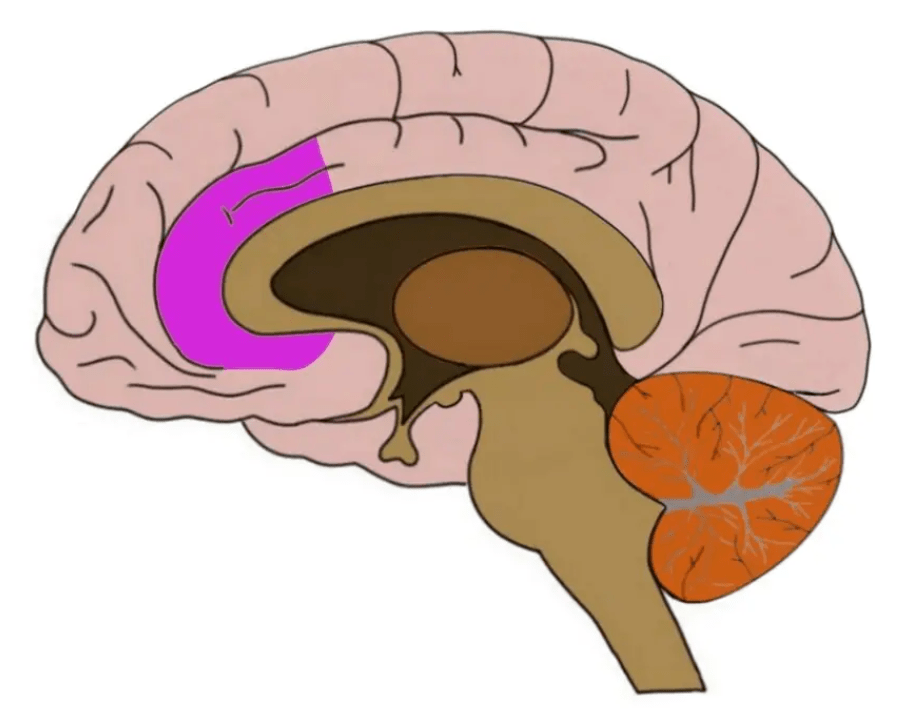
What is the ACC?
TOPIC:
Bilingual Language Control
In bilinguals, asymmetrical switch costs are the phenomenon wherein switching away from this language leads to a greater switch cost than switching away from the other one.
.
What is L2?
The process of auditory comprehension by which the brain calculates which frequencies are modulated over time.
What is spectrotemporal analysis?
Of the two parts of the model of language production that we learned, this is the name of the conceptual side.
What is Lexical Selection?
Bilinguals in a dense code-switching context would rely on this control mechanism, according to the ACH.
What is Opportunistic Planning?
The name of the model of neural adaptation to second language acquisition.
What is the Dynamic Restructuring Model?
This is the name of this specific region of the brain (in red) which performs the most fundamental aspect of language comprehension.
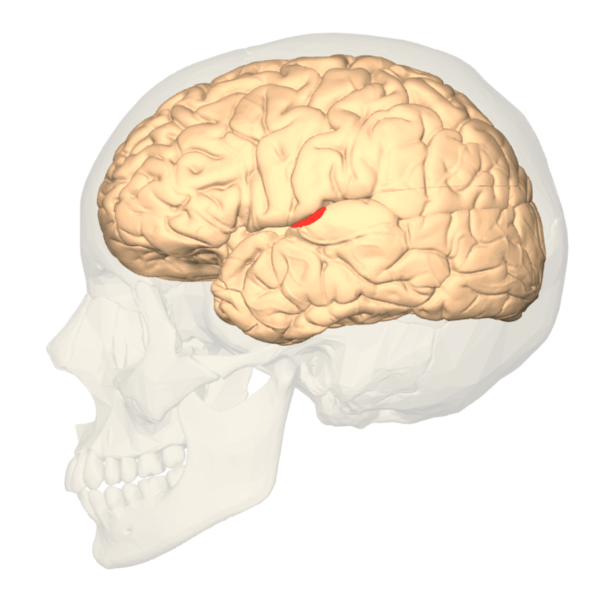
What is pdSTG?
This term describes the frequency-based layout of the gradients in the primary auditory processing area of the brain.
What is tonotopy?
An "abstract word node" that serves as a 'pointer.'
What is a lemma?
The temporal cost of changing from one language to another, due to the necessity of control mechanisms in language control.
What is a switch cost?
One might use this image-based task to test a bilingual's L1 or L2 proficiency.
What is the MINT-Sprint?
The name of this area of the brain (red), which teams up with a neighboring region to accomplish the control mechanism of conflict monitoring in bilinguals during language processing.
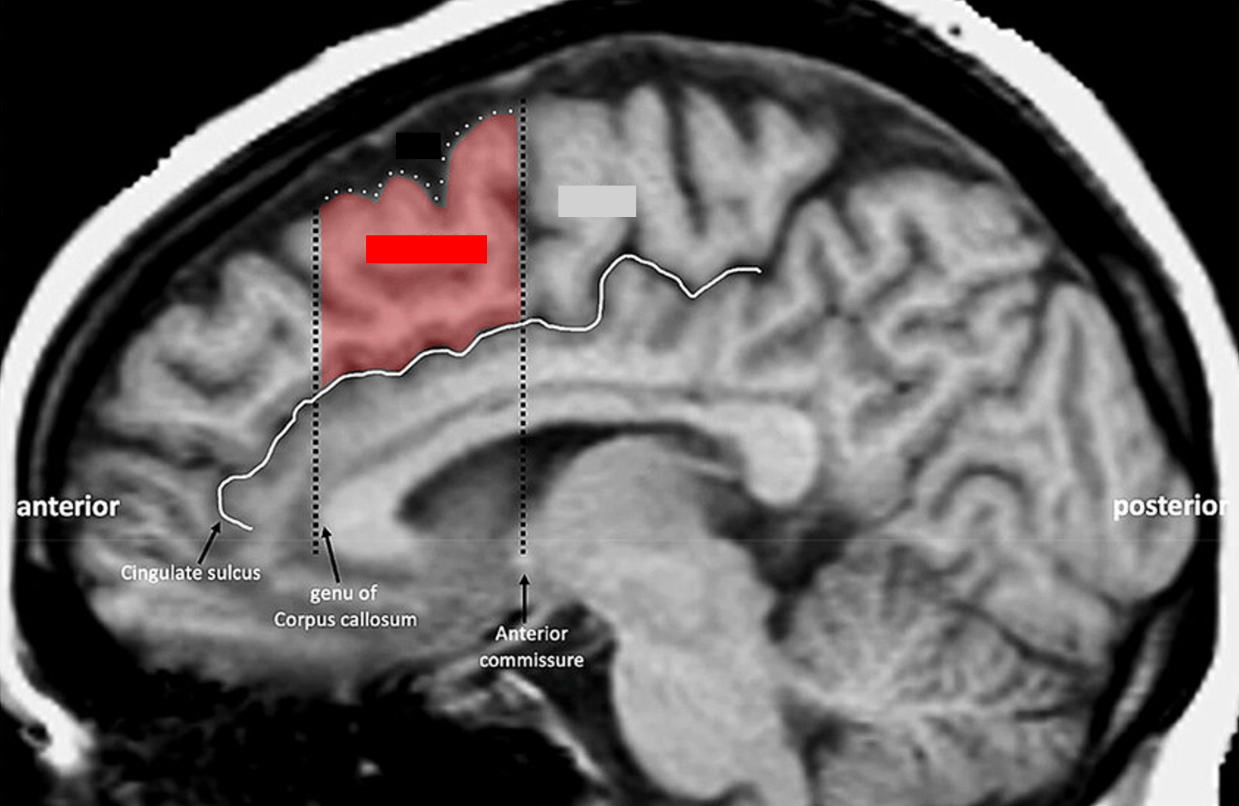
What is the Pre-SMA?
A term representing the idea that the brain's ability to process language is a composite of many different biologies that are not necessarily language-related.
.
What is 'emergent'?
Of the two parts of the the model of language production, this is the part that features competition.
What is Lexical Selection?
A bilingual in a dual-language context would engage this control mechanism, which would (when necessary) subsequently initiate control mechanisms like selective response inhibition and task engagement/disengagement.
What is Salient Cue Detection?
For instance, when discussing this aspect/factor of a bilingual's language experience, one might call them 'compartmentalized.'
What is entropy?
The area of the brain seen below is associated with which of the five steps of the model of language production that we learned?
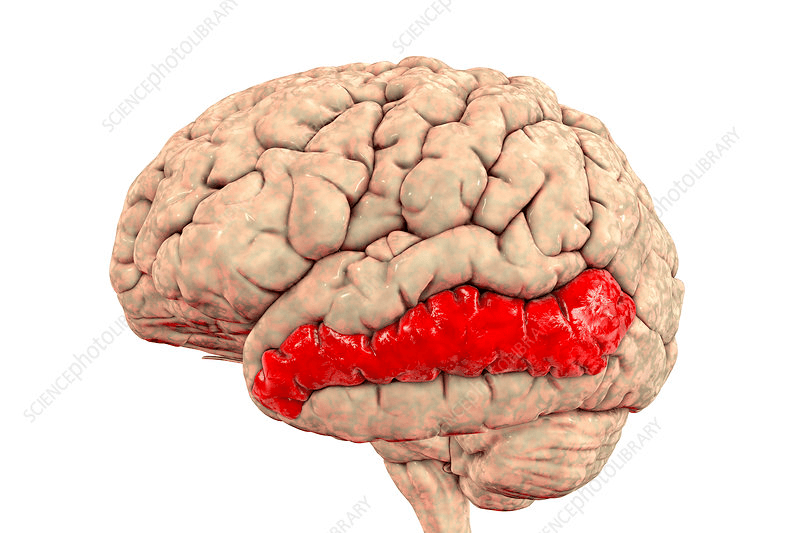
What is the Lemma Node?
In the language comprehension model we learned, the pMTG and pITS are the location of this part, which serves as a 'pointer' to word meanings.
What is the Lexical Interface?
In the model of language production that we learned, the grey matter most associated with the Syllable Node.
.
What is the Left pIFG?
Bilinguals put this type/category of control mechanisms into use before conflict arises.
What is a Proactive Control mechanism?
Aside from AoA, research suggests this factor of the bilingual experience directly influences the amount of overlap between L1 and L2 neural representation.
What is Linguistic Distance?
In bilinguals, the control mechanism associated with activation in the region of the brain seen below (yellow).
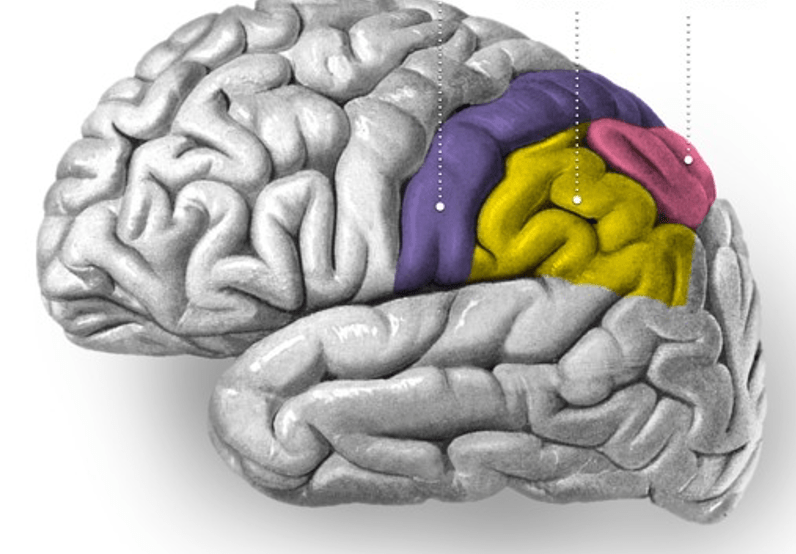
What is goal maintenance?
This skill is directly related to the cortico-basal gangliar-thalamic loop, a white matter tract and neurobiological prerequisite of language.
What is vocal learning?
The name of the break between the two parts of the model of language production, crossing which is "not entirely a trivial matter."
What is the Major Rift?
The grey matter area of a bilingual's brain most implicated, uniquely, in language-switching.
What is the Caudate?
This processing occurs in cortical regions during Stage 2 of the model of bilinguals' neural adaptation to language acquisition, while subcortical regions undergo the opposite process.
What is renormalization?
Of the five steps in the model of language production that we learned, this is the name of the step most associated with the area of grey matter circled below in black.
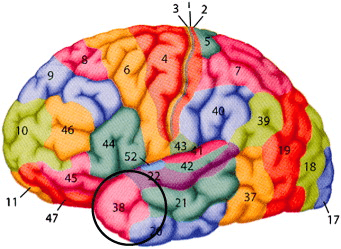
What is the Conceptual Node?