One of the characteristics of life (there are multiple possible answers).
What is the ability to respond to a stimulus, growth, reproduction, etc?
This type of cell.
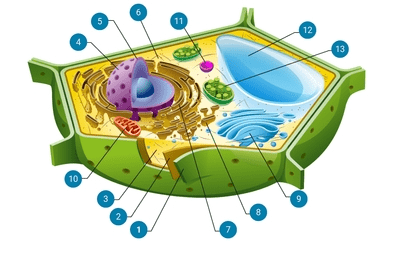
What is a plant cell (also acceptable eukaryotic cell)?
The energy source for photosynthesis.

What is a sunburn (okay not really just sunlight)?
Cell division that makes gametes.

What is meiosis?
True or false. Just because we have biotechnology to use, humans should use the biotechnology to the fullest extent.
What is false?
True or false. All mutations are bad.

What is false?
One thing that we used these tools for during class.

What is for fun? Also what is to build cells?
The four types of organic molecules, I know you can do it!
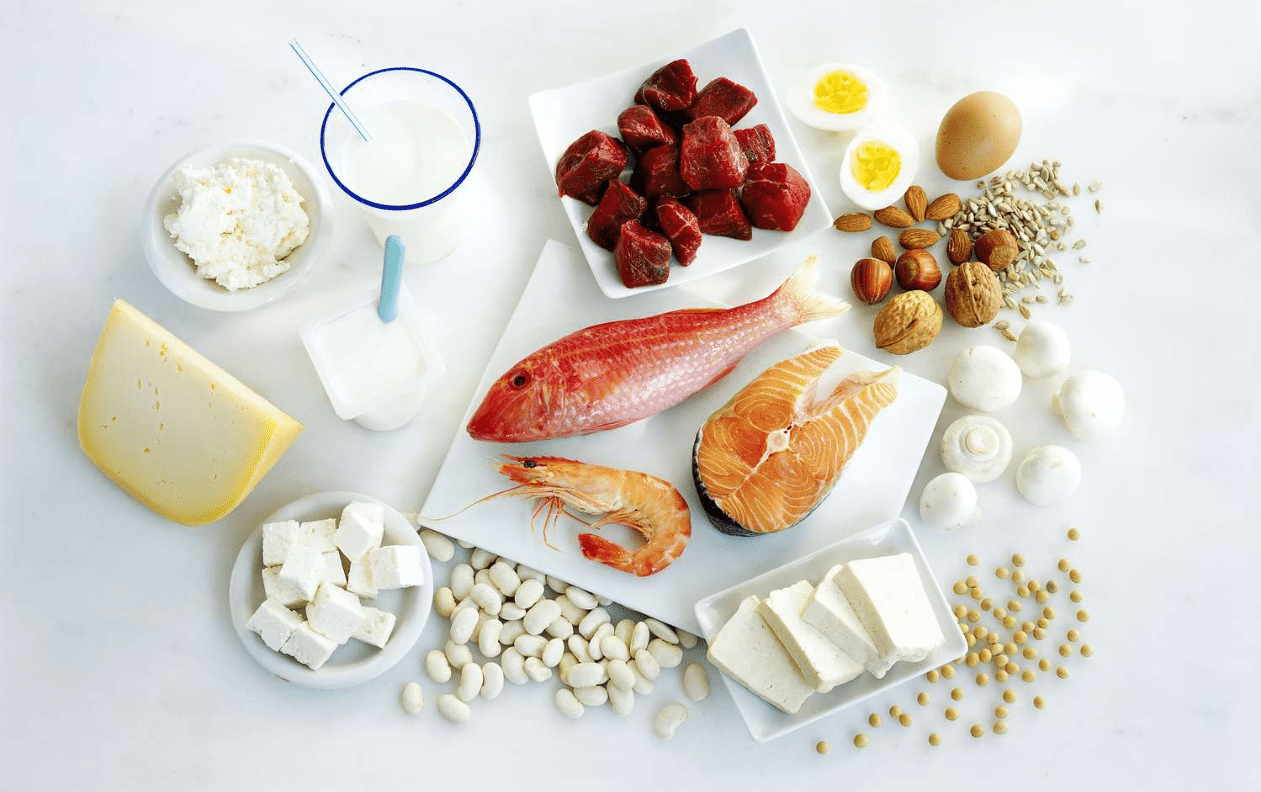

What are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids?
The cell part labeled 10.
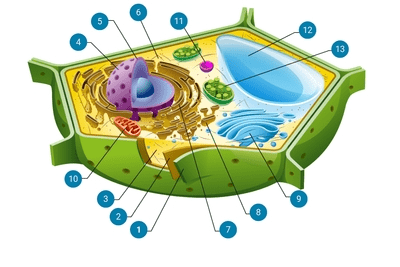
What is the mitochondria?
The preferred starting material for cellular respiration.
What is glucose (photosynthesis by itself as an answer NOT accepted)?
The number of cells made by mitosis and the term for the amount of DNA the newborn cells contain.
What is diploid cells with 2 cells made by mitosis?
This type of cross (NOT the name of the square) with two individuals heterozygous for 1 trait.
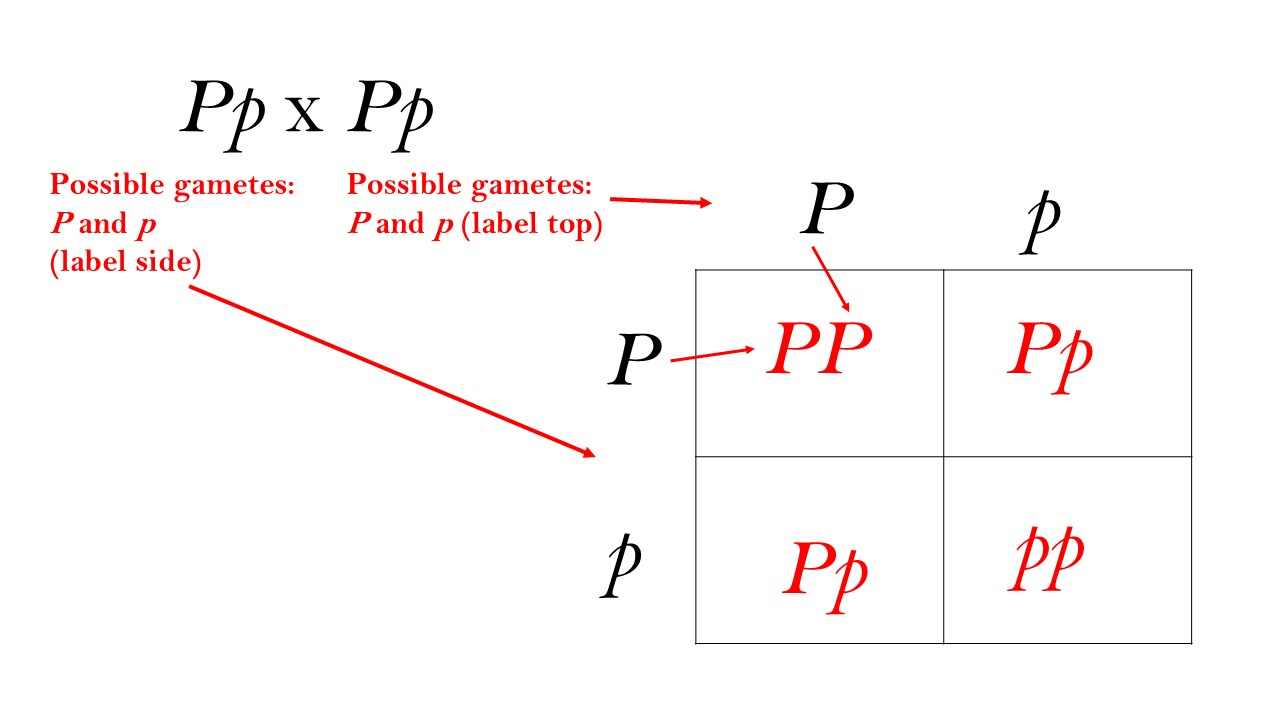
What is a monohybrid cross (NOT the punnett square)?
Two reasons that fossils are not found for all organisms. (Lots of possible answers)
What are that soft tissue is rarely preserved, some organisms are buried not to be found again, some fossils get destroyed by later activity, some organisms get eaten, etc?
ATP.
What is Adenine Triphosphate OR what is the energy source of the cell OR what is usable energy for the cell OR what is a nucleic acid (other answers possible)?
The three domains of life.
What are bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes?
The movement of water from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water.
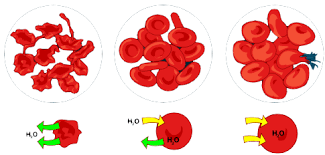
What is osmosis (diffusion not acceptable as osmosis is a specific type of diffusion)?
The part of cellular respiration that provides the most ATP.
What is the electron transport chain?
Complementary RNA sequence to the DNA template ATTCGGATA.
What is UAAGCCUAU?
The genetic code.
What is the code used to convert mRNA template to an amino acid sequence (also acceptable, DNA used to make RNA used to make protein although not quite correct)? (Other answers possible)
Natural selection and the raw material that natural selection needs to function.
What is survival of the fittest by using previously existing mutations for which organism is the fittest?
The expected reaction of a medium ground finch to a peacock feather display.

What is to ignore the display?
Description of an ionic bond.
What is the formal transfer of at least one electron from one element to a separate element (Sodium transferring an electron to chlorine is an example)?
One example of when a cell needs to use energy.
What is (lots of possible answers) to generate a concentration gradient or to duplicate DNA? (Okay this one REALLY is not worth 400 points but that is fine)?
A cell does this when oxygen is in low supply and WHY the cell prefers there to be oxygen present.
What is fermentation occuring with low oxygen present even though fermentation is much less effective at making ATP as usable energy than aerobic respiration using that uses oxygen?
Phases of meiosis in order.
What is Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, (cytokinesis acceptable if added but not needed), Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, (cytokinesis acceptable if added but not needed).
A description of the codominance for human blood types.
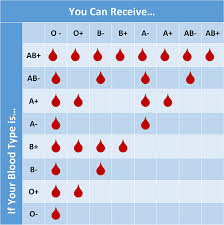
What is A, B and D/ Rh factor are all dominant alleles that can be expressed on the same red blood cell with O being a recessive allele that does not code for a protein.
1 example of homologous structures and 1 example of vestigial structures.

What are leg bones of humans and leg bones of monkeys compared to hind limbs in whales? Other answers are possible.
Note: Arm bones of humans, arm bones of monkeys and arm bones for front flippers in whales would all be homologous structures.
The central dogma of Biology.
Hint, it is not limited to dogs or to mothers.
Two characteristics of water that impact life.
What is high heat capacity to transfer heat into foods, adhesion so water sticks to other stuff, cohesion so that water sticks together to let humans go surfing, solubility so that stuff can travel within water, etc?
Two examples of enzymes in cells and the functions of the enzymes you named.
What is DNA polymerase to make DNA, RNA polymerase to make RNA, Rubisco to add CO2 molecule to make glucose, lactase to break down lactose, amylase to break down starch, etc.
At least 2 of the reactants for the light independent reactions (Carbon cycle) of photosynthesis. (Our list has 3)
What are CO2, ATP and high energy electron carriers/ NADH?
The parts of the cell cycle and the function of at least 2 checkpoints within the cell cycle.
What is the G1 phase, S phase (checkpoint that DNA has duplicated), G2 phase (checkpoint that DNA is duplicated DNA is attached to the centromere) and mitosis with a metaphase checkpoint that DNA is properly aligned along the middle of the cell.
Incomplete dominance with 1 example.
What is a gene where the dominant allele only partially masks another allele such as some roses that can be red, pink (incomplete dominance) or white.
The mechanism(s) where a meteor impact caused the mass extinction of the dinosaurs. (relates to material throughout the semester)
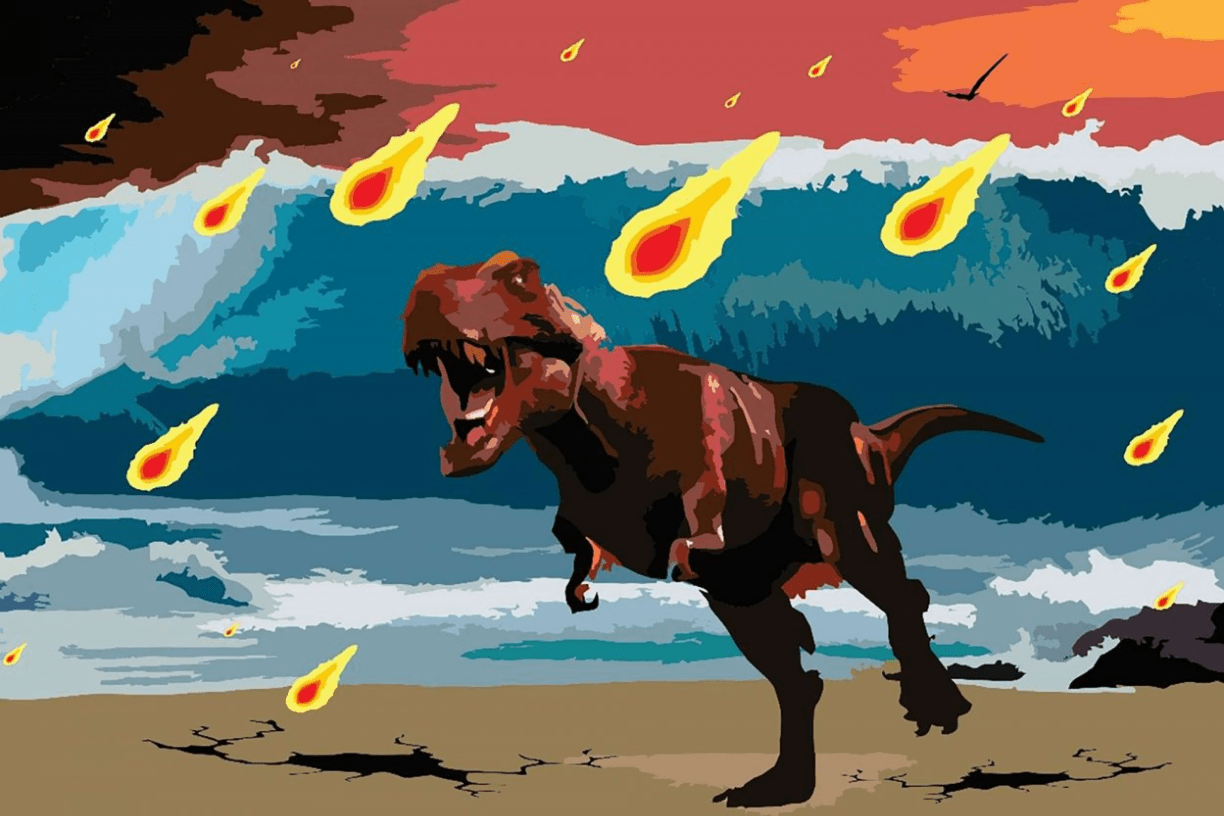

What is the impact causing large amounts of dust to rise up into the atmosphere, blocking out lots of sunlight so that plants had a hard time to survive and so the food source for the dinosaurs was depleted?
Make a hypothesis and briefly design one experiment for exercise for that hypothesis. You do not have to perform the experiment in class though!
What is lots of possible answers?