Station
Protein catalysts that decrease the activation energy needed to begin a reaction are called?
Extra credit:
By what mechanisms can these protein catalysts lower the activation energy EA?
Enzymes!
Enzymes can exert torsional stress on a particular bond, provide a microenvironment that is favorable for a reaction, transiently bind to a substrate, or hold reactants in an orientation that is favorable for the
reaction.
My DNA is unbound, I have no membrane bound organelles, and I lack a nucleus. What kind of cell am I?
Prokaryotic
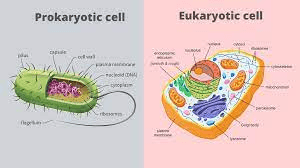
A selective barrier that allows sufficient passage
of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the
volume of every cell.
Plasma membrane / Phospholipid bilayer!
A theory stating that genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA, to RNA, to protein, or RNA directly to protein
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology.
Metabolism = _________ +_____________
Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
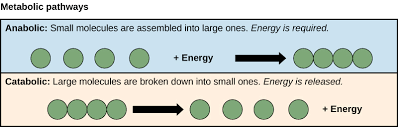
_____________ reactions: Require energy and yields products rich in potential energy.
Endergonic reactions!
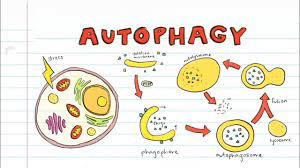
Lysosomes use enzymes to recycle the cell’s own organelles and macromolecules in a process called_________________________.
Autophagy
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily? Two components to this answer.
Small and Hydrophobic (non-polar).
A dihybrid cross, involving two traits, often results in a ______ phenotypic ratio.
A dihybrid cross, involving two traits, often results in a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio
What are the components of Cellular Respiration
1. Glycolysis (breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate)
2. The oxidation of pyruvate and citric acid cycle (completes the breakdown of glucose)
3. Oxidative phosphorylation which is both the electron transport chain and the process of chemiosmosis (accounts for most of the ATP synthesis)
Amino acids contain two key biological functional groups: an _____ group and a ______ group.
Amino acids contain two key biological functional groups: an amino group (–NH₂) and a carboxyl group (–COOH).
These line up at the metaphse plate in meiosis I during metaphase.
What are tetrads?
In meiosis, a tetrad is a structure formed during prophase I that consists of four chromatids, representing a pair of homologous chromosomes that have paired up
The membranes of winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold by ____________ the proportion of ________ phospholipids in the membrane.
Increasing the proportion of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane!
A short sequence of DNA nucleotides (around 150-200 base pairs) that is synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
Okazaki fragment!
How many molecules of ATP are formed in glycolysis when each molecule of glucose is oxidized to pyruvate. Please state both net production and total production.
Total = 4 ATP
Net = 2 ATP
In glycolysis, 2 ATP molecules are consumed, producing 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvates per glucose molecule.
The reaction Glutamyl Semialdehyde > Proline is spontaneous. Thus it is an _______ reaction with a ______ ∆G.
The reaction Glutamyl Semialdehyde > Proline is spontaneous. Thus it is an exergonic reaction with a negative ∆G.
The brief stage at which chromosomes migrate to the mid plate.
What is prometaphase?
Sodium Potassium Pump: How many sodium ions are moved out of the cell, how many potassium ions are moved into the cell, for each ATP consumed?
The Na+ K+ ATPase pumps 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2K+ into the cell for every single ATP consumed.
(321 Nokia)
The study of how cells regulate gene activity without altering the underlying DNA sequence
Epigenetics!
The main products of the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle) are?
The main products of the Krebs cycle are carbon dioxide, NADH, FADH2, and GTP (which is quickly converted to ATP).
Proline binds to enzyme 1 at a position remote from enzyme 1's active site, and this binding changes
the activity of the enzyme. Therefore, proline functions as a(n) ______ inhibitor.
Proline binds to enzyme 1 at a position remote from enzyme 1's active site, and this binding changes
the activity of the enzyme. Therefore, proline functions as an allosteric inhibitor.
The endomembrane system regulates protein
traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell.
• The endomembrane system consists of 6 components, what are they?
The endomembrane system consists of
• Nuclear envelope
• Endoplasmic reticulum
• Golgi apparatus
• Lysosomes
• Vacuoles
• Plasma membrane
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are also known as ___________. They are named this way because their structure involves a protein that spans the cell membrane __________ times.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, serpentine receptors, or heptahelical receptors. They are named this way because their structure involves a protein that spans the cell membrane seven times
The enzyme responsible for preventing DNA from getting tangled, as well as relieving pressure in supercoiled DNA during DNA replication.
DNA topoisomerase!
In the electron transport chain (ETC), protons are pumped from the _____)___ to the __________ to create a proton gradient for ATP production.
In the electron transport chain (ETC), protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix (inside the mitochondrion) to the intermembrane space (between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondrion).