Phylogenetics
Phylogenetics
Prokaryotes
Protists
Plants 1
Plants 2
What organelles arose because of the endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria and chlorophyll
What are endospores? What types of environmental conditions are they resistant from?
Dormant bodies
Can remain viable for centuries!
Resist heat, drying, freezing, radiation, and chemicals
What does it mean to be an obligate aerobe? How about an obligate anaerobe? Facultative anaerobe?
obligate aerobe: metabolism requires oxygen
facultative anaerobe: can metabolize with or without oxygen
obligate anaerobe: metabolism cannot occur with oxygen present
Our best hypotheses think that plants originated from…
Green algae, specifically charophytes
What is an angiosperm?
A flowering plant, which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.
What are the 3 domains and the 6 kingdoms?
Domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
Kingdoms: Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, and Protista
Describe what taxis is, including the two subtypes
•Move toward an attractant or away from a repellant
oChemotaxis
oPhototaxis
What does it mean to be symbiotic? Name two symbiotic relationships.
involving interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association.
Zooxanthellae have a symbiotic relationship with coral reefs; the protists act as a food source for coral and the coral provides shelter and compounds for photosynthesis for the protists.
Termites have a mutualistic relationship with protozoa that live in the insect's gut. The termite benefits from the ability of bacterial symbionts within the protozoa to digest cellulose
What is sporopollenin, and why is it important?
A durable polymer that covers exposed zygotes of charophyte algae and forms the walls of plant spores, preventing them from drying out.
What are monocots? How about dicots? Provide an example of each.
Monocots: one leaf inside of the seed that emerges when the angiosperms stars to grow
ex: grasses, palms, orchids
Dicots: 2 leaves emerge from the seed
ex: flowering trees
What type of information could be used to form a phylogenetic tree?
morphological, genetic, and biochemical
Name at least 4 differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
What does it mean to be colonial as a protist, and how does this differ from being multicellular and unicellular?
When individuals work together towards a common goal, but they are still their own organisms.
Compared to charophytes, plants have a few additional traits. What are they?
Alternation of generations
Walled spores produced in sporangia
Apical meristems (stem cells for plants)
Possession of cuticles and stomata
What is the difference between angiosperms, bryophytes, gymnosperms, and seedless vascular plants?
What are 4 ways that horizontal gene transfer can occur between domains? Provide a brief description of what that means.
Compare and contrast gram positive and gram negative bacterial cells.
What are two key roles protists play in their habitats?
What is the mycorrhizal relationship? How does each member of this relationship benefit?
A mutualistic relationship between plant roots and fungus.
Fungus = sugar
Plant = Increased S.A. for nutrients and water
Draw a biologically accurate picture of a flower, and include the following terms:
anther, carpel, filament, ovary, ovule, petal, sepal, stamen, style
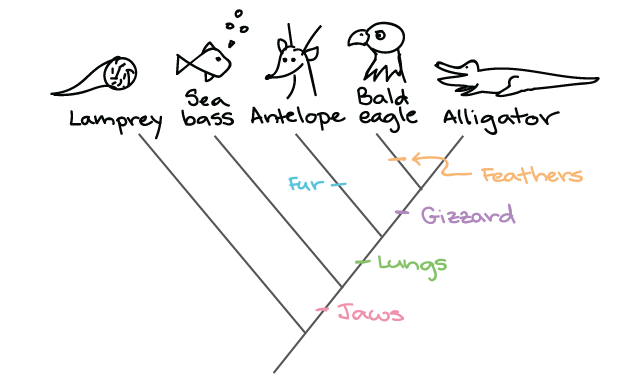
This table shows presence (+) or absence (0) of various features:
Feature Lungs Jaws Feathers Gizzard Fur
Lamprey 0 0 0 0 0
Antelope + + 0 0 +
Bald Eagle + + + + +
Alligator + + 0 + 0
Sea bass 0 + 0 0 0
Draw a phylogenetic tree based on these traits!
Part one: What is the difference between conjugation, transformation, and transduction?
Part two: What structures are involved in conjugation, and what is being passed between cells?
In transformation, a bacterium takes up a piece of DNA floating in its environment. In transduction, DNA is accidentally moved from one bacterium to another by a virus. In conjugation, DNA is transferred between bacteria through a tube between cells.
part 2: pilus, and plasmids
What are our 4 major supergroups of protists? What are the major groups inside each of these? What are their distinguishing features?
excavata (diplomonads and parabasalids), SAR (stramenopiles, alveolates, rhizians) , archaeaplastida (green and red algae), and unikonta (amoebozoans and opisthokots).
Draw the life cycle of a fern!
Draw the life-cycle of an angiosperm!