What is asexual reproduction?
One cell, called the parent cell, divides into two identical daughter cells. The offspring are genetically identical to the parent cell. There is no fusing (joining) of cells.
Budding results in equal division of
the _____(1)______ and unequal division of the _____(2)______.
1. nucleus
2. cytoplasm
What is regeneration?
The development of a new organism from a part of the parent organism.
stock
the part of a graft that is rooted in the ground.
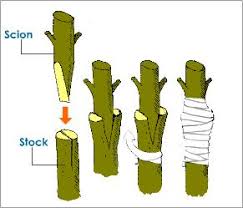
Commercial growers use ______ rather than seeds when they want to be sure the offspring are identical to the parent.
vegetative propagation
Asexual reproduction is more common in _____(1)_______ animals than in ______(2)______
animals.
1. invertebrate
2. vertebrate
A one celled organism that reproduces by budding is ____________.
yeast (others)
Name two animals that reproduce by regeneration.
Starfish and planaria
scion
the part of a graft that is attached to the main body.

The ____ or ____ can reproduce by regeneration.
starfish or planaria
Name three types of asexual reproduction.
extra 300 pts. if you can name all five
1. binary fission
2. budding
3. sporulation
4. regeneration
5. vegetative propagation
__________ is a multicellular organism that reproduces by budding.
hydra (others)
What is vegetative propagation?
A form of asexual plant reproduction. In vegetative propagation, a part of a plant, like a root, stem or leaf, grows into a new plant. The new plant is exactly the same as the parent plant.
bulbs
(and not the kind you screw into a light fixture)
A type of vegetative propagation in which an underground stem, that is specialized for food storage, develops into a new plant.
an onion for example
Reproduction involving one parent cell is called _________ reproduction.
asexual
Describe binary fission.
The simplest type of asexual reproduction. During binary fission a one celled organism divides by mitosis to form two daughter cells of equal size. Both the nucleus and the cytoplasm divide equally. The chromosomes of the offspring are identical to that of the parent.
What is a spore
Spores are specialized asexual reproductive cells that contain a nucleus and a small amount of cytoplasm.
Name three plants that reproduce by vegetative propagation.
extra 500 pts. if you can name all six
1. runners
2. bulbs
3. tubers
4. rhizomes
5. cuttings
6. grafting
runners
(and not someone who runs a marathon)
A type of vegetative propagation in which stems, called runners, grow out over the surface of the soil from the existing stem, where new plants grow.

strawberries reproduce asexually by _________
runners
Name two organisms that divide by binary fission.
extra 200 pts. if you can name all three
1. amebas
2. paramecia
3. bacteria
State one advantage of spore formation.
Spores are surrounded by tough protective coats that enable them to survive unfavorable conditions.
In one type of propagation, you can sometimes cut a piece of a plant and put it into water to grow roots. What would this be called?
cuttings
rhizomes
A type of vegetative propagation in which long modified stems, that grow horizontally under the soil, produce plants a nodes along the stem. example: grass.
The eyes on potatoes are actually___________

buds or little plants