Monomers & Polymers of Carbohydrates are called?
Monomers - Monosaccharides
Polymers - Polysaccharides
Monomers & Polymers of Lipids are called?
Monomers: Fatty Acids & Glycerol
Polymers: Lipids (Triglycerides)
Monomers & Polymers of Proteins are called?
Monomers: Amino Acids
Polymers: Polypeptides (multiple polypeptides make up a protein)
Monomers & Polymers of Nucleic Acids are called?
Monomers: Nucleotides
Polymers: Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA)
What is a Catalyst?
Why are enzymes considered biological catalysts?
Catalysts: molecules that speed up chemical reactions but are not consumed in the process!
Enzymes are considered biological catalysts because they are proteins (a biomolecule/macromolecule) and they speed up chemical reactions within the body!
How many stomachs does a cow have?
ONE! But it is split into four compartments:
The rumen, the reticulum, the omasum and the abomasum.
The basic structure of carbohydrate includes a ______ carbon sugar
(draw the basic structure of a carbohydrate molecule)
The basic structure of carbohydrate includes a six carbon sugar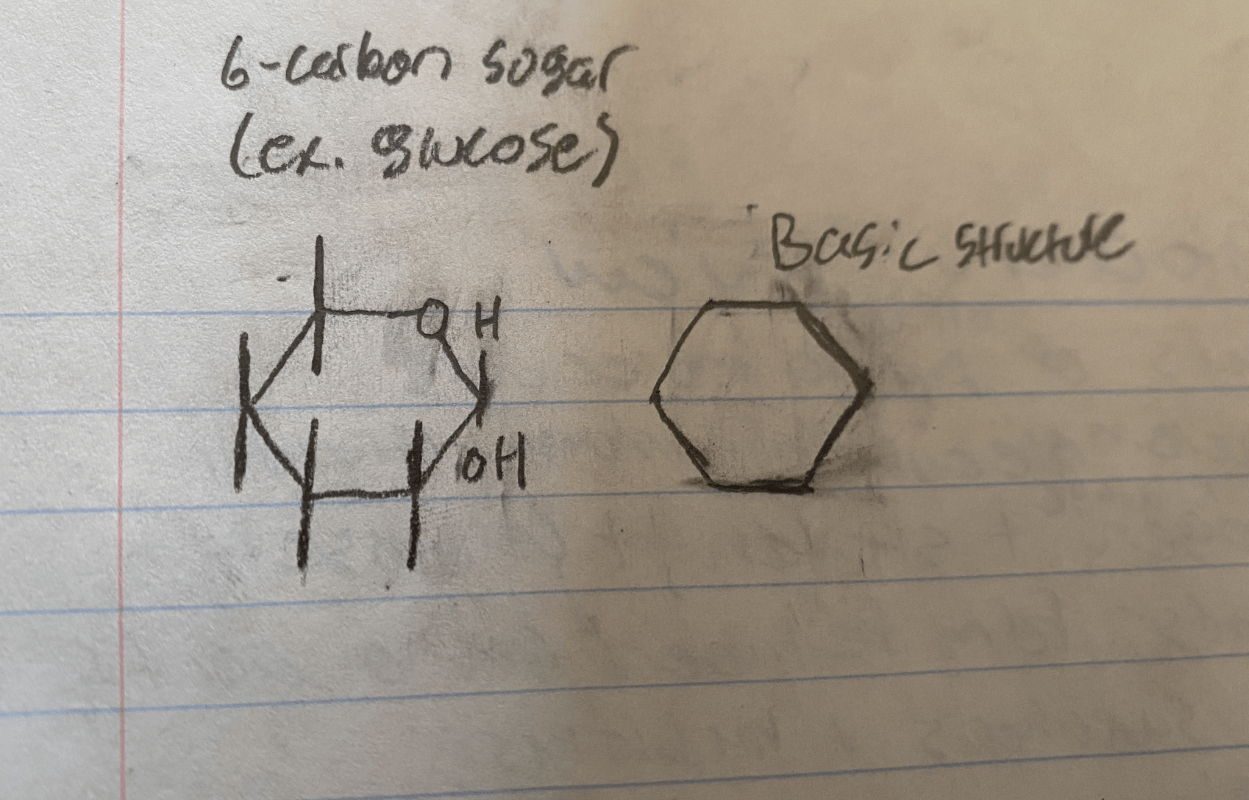
What is the bodies first choice of a molecule to "burn" for energy ? Second choice?
What is true about the amount of Ep stored in the bodies second choice of a molecule to "burn" for energy?
The bodies first choice of a molecule to burn for energy is a carbohydrate.
The bodies second choice is a lipid
Lipids contain two times the potential energy than carbohydrates do!
What is the macromolecule test used to ID proteins? Explain the positive & negative results of this test
Biuret Test: If peptide (protein) bonds are present, a colour change from blue (negative) to pink/violet/purple (positive) occurs.

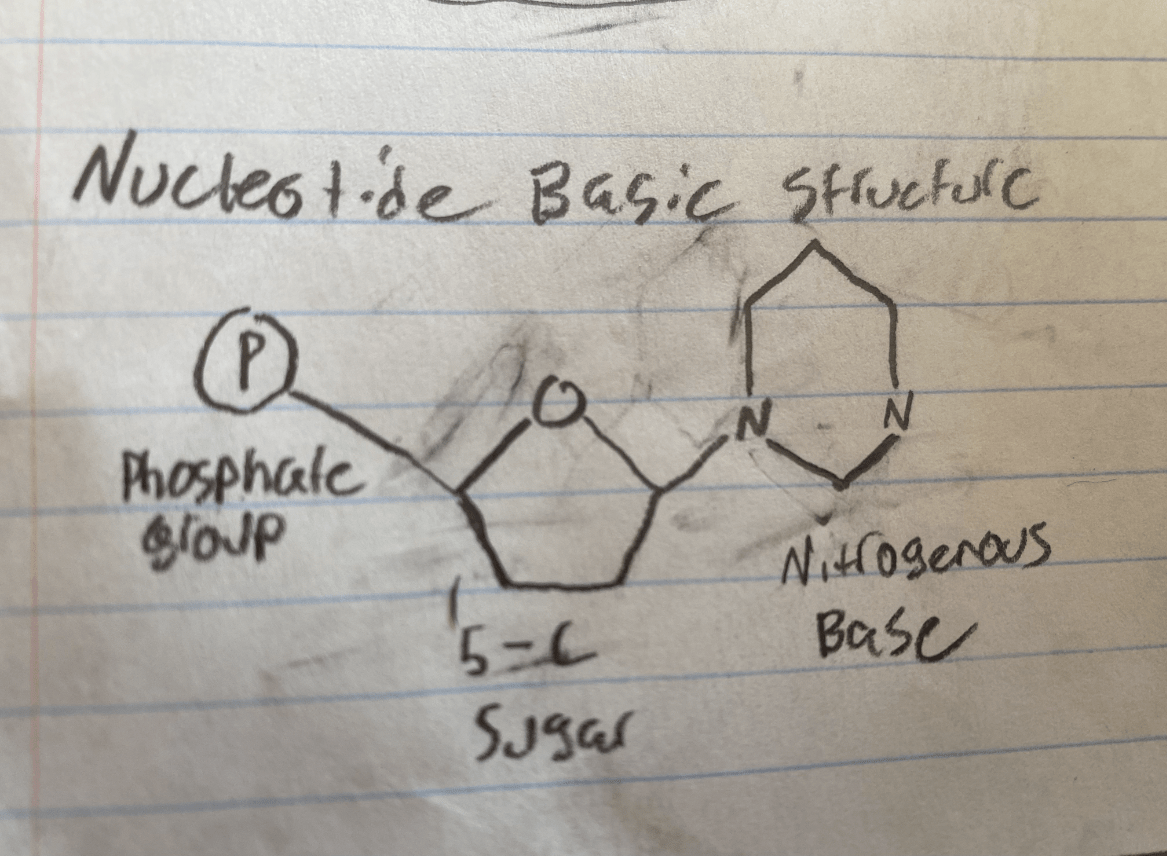
The basic structure of a nucleotide includes a ______ group, a ________ carbon sugar and a ________ base.
(draw the basic structure of a nucleotide molecule)
The basic structure of a nucleotide includes a phosphate group, a five carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base.
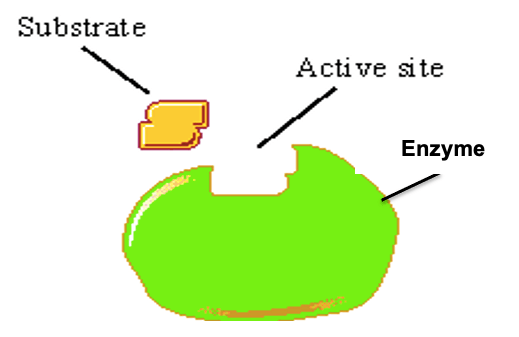
Label this Diagram
Why are flamingos pink?
Because flamingoes diet consists mainly of shrimp & algae which contain the pigment beta-carotene. This pigment is what gives the flamingoes/shrimp their pink colour!
Some examples of polymers in plants and animals are?
(Bonus 100 points if you can identify which are storage/structural polymers)
Glycogen (Animals) - Storage polymer: stored in the liver & muscles of vertebrates
Starch/Amylose (Plants) - Storage polymer (1000-6000 glucose units long)
Cellulose (Plants) - Structural polymer
- indigestible by humans, but needed for a healthy intestine. In tree bark, cell walls & plant fibres
What are the two possible macromolecule tests used to ID lipids? Explain the positive & negative results of these tests
Sudan IV test: a clear solution (negative) will dissolve in lipids, turning the solution red (positive)
Translucence tests: using unglazed paper, lipids will turn the paper translucent (positive), the absence of lipids will simply wet the paper temporarily (negative)

What types of bonds form between amino acids?
A peptide bond forms between amino acids, these amino acids bond together to form polypeptides. Multiple polypeptides form a protein.
Why are there no ID tests for Nucleic Acids when it comes to food?
Because all foods contain cells, all cells contain DNA/RNA (nucleic acids) which means all foods contain nucleic acids! Which means any food that was once alive would test positive, which would not help us identify much about the food!
What is the lock & key model? What does it have to do with enzymes
(a specific key word should be used during your answer!)
Substrates bind to enzymes according to the lock & key model. Only one key can open each lock, similarly enzymes are substrate specific. Each substrate can only bind to one type of enzyme!
What years did Mr. Taylor go to William Aberhart?
He went to Aberhart from 2015-2018!
1. Glucose & Fructose
2. Glucose & Glucose
3. Glucose & Galactose
1. Glucose + Fructose --> Sucrose
2. Glucose + Glucose --> Maltose
3. Glucose + Galactose --> Lactose
What is the reason that saturated fats are solid at room temperature but unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature?
It has to do with unsaturated fats (which are liquid at room temperature) having a double or a triple bond. This presence of a multiple bond causes unsaturated fats to solidify a much cooler temperature.
Saturated fats are only bonded through single bonds, this causes them to solidify at much warmer temperatures (ie. room temperature).
The basic structure of a protein includes an ______ group, a ________ group and an ________ group.
As well as a single hydrogen atom and a central carbon atom.
(draw the basic structure of a protein molecule)
The basic structure of a protein includes an R (side chain) group, a carboxyl group and an amino group.
As well as a single hydrogen atom and a central carbon atom.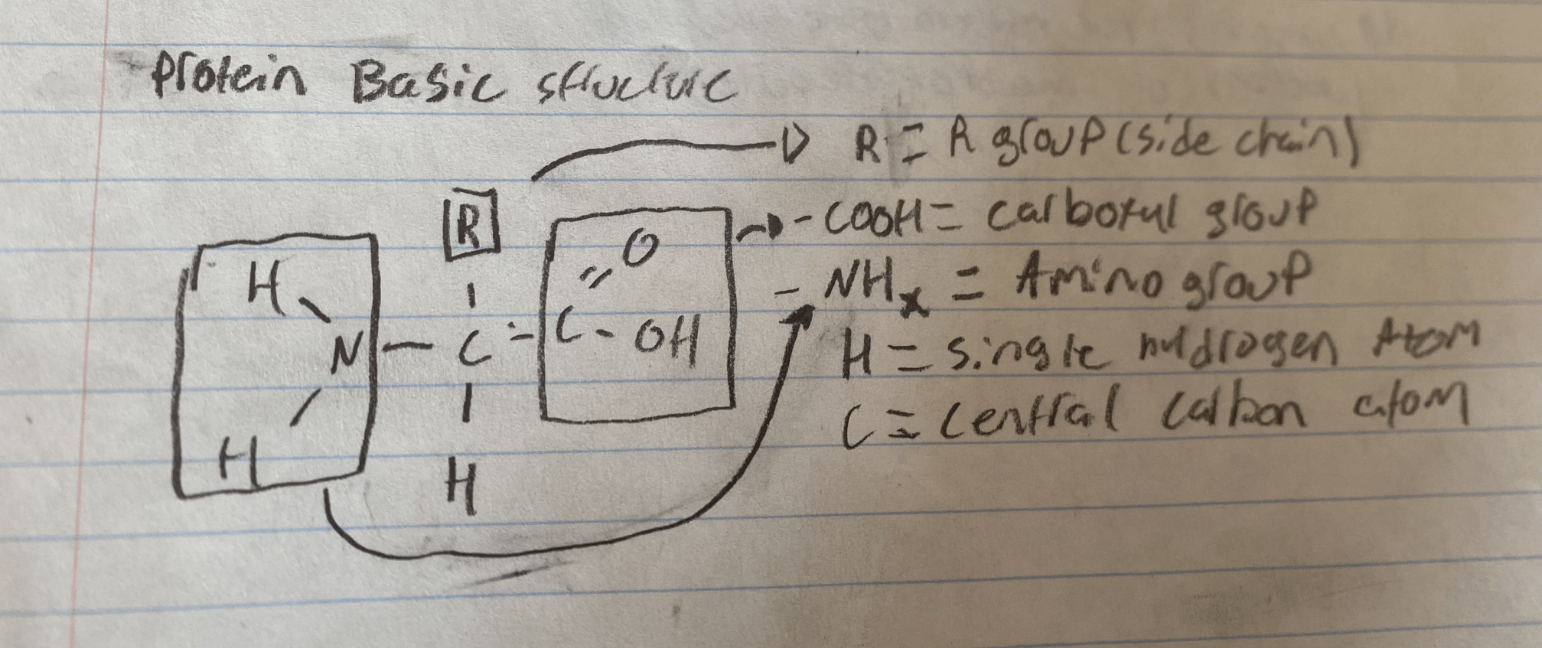
compare the structure and function of DNA & RNA
In DNA:
- Deoxyribose is the sugar & double stranded molecule
- Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine & Guanine are the nitrogenous bases
- DNA is the molecule of inheritance, it contains the genetic information required to build the cell (& guide growth/development)
In RNA:
- Ribose is the sugar & single stranded molecule
- Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine & Guanine are the nitrogenous bases
- during instances where RNA is required (like protein synthesis) these single stranded molecules contain the genetic information required to instruct the cell how to build proteins!
What factors can affect enzyme action/rate of reaction?
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions (ie. what is the enzyme actually doing )?
Factors affecting Enzyme action:
- pH, Temperature, [of Enzyme] & [of substrate] and well as inhibtors
Enzymes speed up the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the amount of activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur.
What is the second tallest mountain in the world?
K2 - (Pakistan/China)
K2 is 8,611 m (28,251 ft) tall!
What is the reason that Glucose, Fructose & Galactose all have the same chemical formula, but in reality they are completely different molecules?
Due to the chemical arrangement of the atoms. Although they all have the same formula (C6H12O6), they way the atoms are bonded in space and the order of the atoms are different! This difference in rearrangement causes each of the monosaccharides to have different chemical properties, and thus allow them to be completely different molecules. 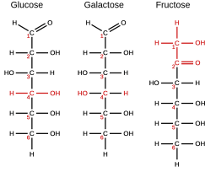
Are Trans Fats bad for you?
Explain how a Trans Fat is produced
Yes Trans Fats are bad for you. They are produced by chemically hydrogenating (adding hydrogens) unsaturated fats to break their double/triple bonds. The results of this are a single bonded lipid (saturated fat) and the "side effect" is the production of a Trans Fat!
How many amino acids are referred to as essential amino acids?
- why are they referred to as essential?
How many amino acids are there in total in the human body?
There are nine essential amino acids. They are called "essential" because the human body does not produce them and they need be consumed through the diet.
There are twenty amino acids in total in the human body!BONUS: When a mutation occurs in the DNA, what is actually happening? (ie. what part of the DNA molecule is being "mutated")
The Nucleotides in a DNA molecule bond in certain pairs, (A & T, C & G). One reason for a mutation is the mismatched bonding of nucleotides during DNA replication!
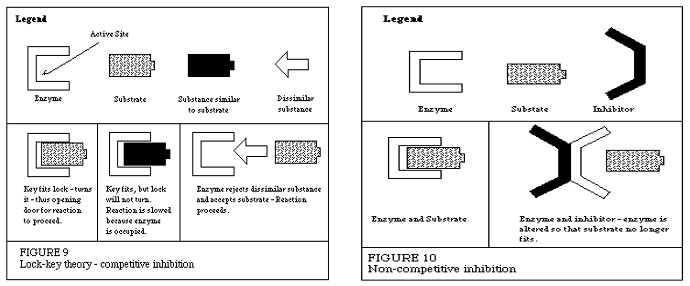
What are the difference between competitive & noncompetitive inhibitors?
Competitive Inhibitors directly bind to the enzyme at the active site. The inhibitor and the substrate compete to bind to the enzyme (left side of photo)
Non- Competitive Inhibitors bind elsewhere on the enzyme (called the allosteric site) which changes the shape of the enzyme (and its active site) which prevents binding of substrate to the enzyme!
Name 5 countries in the Middle East:
Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Bahrain
Cyprus
Egypt
Iran
Iraq
Israel
Jordan
Kuwait
Lebanon
Oman
Palestine
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
Syria
Turkey
United Arab Emirates
Illustrate & explain a hydrolysis or a dehydration synthesis reaction for a disaccharide (ie. maltose)
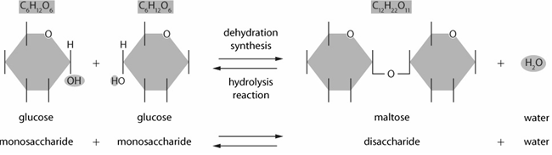
Dehydration synthesis
1. the hydroxyl (OH) group from one glucose molecule combines with a hydrogen (h) from the hydroxyl group of the second glucose molecule to form a molecule of water (Dehydration)
2. this removal of water allows for both glucose molecules to bond forming our disaccharide/maltose (Synthesis)
Hydrolysis
1. Water is added to a disaccharide/maltose (Hydro)
2. This addition of a water molecule breaks the bond in maltose (Lysis). A hydrogen (H) molecule attaches to the oxygen on one monosaccharide forming a hydroxyl (OH) group. The other hydroxyl group attaches to the second monosaccharide molecule.
3. The end products are two molecules of glucose.
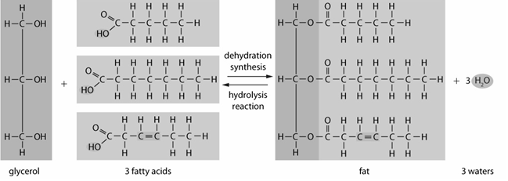
The basic structure of lipid includes a ______ molecule and 3 ________ _________ molecules
(draw the basic structure of a lipid molecule)
The basic structure of lipid includes a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid molecules
What are the function of cofactors & coenzymes?
which is a protein? which is an inorganic mineral?
Cofactors & Coenzymes bind to substrates. When they bind to a substrate, it tightens the fit between the substrate and the enzyme!
Cofactors are inorganic minerals (ie magnesium, zinc)
Coenzymes are proteins (ie. NAD+, Coenzyme A )
Protein Question:
Explain the four types of protein structure.
Bonus 100 points: Why do proteins form these structure?
Primary (1º) protein structure: the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
Secondary (2º) protein structure: coiling or folding of the polypeptide chain (alpha helix, beta pleated sheet)
Tertiary (3º) protein structure: more bending due to hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions in the polypeptide
Quaternary (4º) protein structure: interactions of multiple polypeptide chains to form the overall protein structure → Hemoglobin
Bonus: Proteins form structures in relation to their biological environment (ie. temp, pH, amount of water etc.)
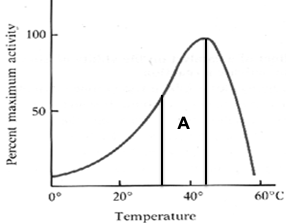
1. What can you infer about the optimal temperature range (A) of the following enzyme?
2. What can you infer about the difference between optimal pH of Trypsin & Pepsin in this graph? 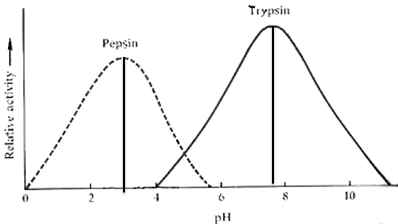
1. by looking at section A, we can infer that the optimal temperature range for the following enzyme is between ~32-44ºC
2. by looking at the straight line placed at the apex of each section of the graph, we can infer:
- Pepsin has an optimal pH that is acidic (~ pH of 3)
- Trypsin has an optimal pH that is relatively neutral (~7.4-7.8)
It is the beginning of eternity, the end of time and space.
It is the start of every end, the end of every place.
What is it?
The letter E!