What is the Purpose of Photosynthesis?
For plants to trap & convert radiant energy, water & carbon dioxide into:
1. CPE (glucose) for the plant to use
2. Oxygen which is released as a byproduct (respired by other living organisms)
What is an Antenna Complex?
Where is the energy from a photon of light sent inside the antenna complex?
The antenna complex in a photosystem includes all of the pigment molecules and the electron acceptor molecule!
- The energy from the photon of light is sent to the reaction centre
Why is it called the light-independent RXN?
How many carbons does the starter molecule being regenerated in the Calvin Cycle have?
Because it can occur during the day or the night time, the dark RXN is driven by the presence of CO2 as opposed to light!
5 carbons!
What is the main difference between Harmless & Harmful Electromagnetic Waves
It has to do with their wavelength!
Harmful Waves: Short Wavelength (λ<400nm)
Harmless Waves: Long Wavelength (λ>700nm)
In order, who were the top 5 artists on Mr. Taylor's Spotify Wrapped?
1. Kendrick
2. Drake
3. J Cole
4. Jack Harlow
5. Cordae
Provide the Full Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Including States

What happens to an electron that allows it to be picked up by an electron acceptor after exiting a photosystem?
It becomes excited due to the energy transferred from photons of light, this causes the electron to rise to higher energy orbital. Then the electron acceptor molecules are able to "steal" the electron before it loses energy and falls back to it's original energy orbital!
What is the ultimate fate of PGAL?
Two PGAL molecules are chemically bonded to produce a glucose molecule!
If the solvent front (b) is 160 nm, and the pigment that travelled (a) is 77 nm, what is the retention factor of this sample of leaf goo?
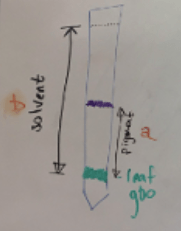
Rf = How far pigment travelled ÷ how far solvent travelled
Rf = 77nm ÷ 160nm = 0.48125 --> ~0.48 is the retention factor of this sample of leaf goo!
The assassination of which archduke was the catalyst for WWI?
Franz Ferdinand
Where is chlorophyll located within the chloroplast?
Why is a dark RXN required if plants create ATP during the (light RXN) of photosynthesis?
Because there are times that there is no light (winter = no leaves or nighttime!)
→ Plants would die during these times if they did not have ATP, so they use the dark reaction to make glucose which they can burn during CR in times of crisis to produce the ATP needed to live!
Draw a diagram of a chloroplast that indicates the relationship between the light & dark RXN's of photosynthesis
What pigments did we learn about during the PS unit?
Chlorophyll (a & b)
Carotenoids
Betalains
Anthocyanins
Name as many digits of Pi as you can, bonus 100 points if you get past 20 digits!
3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937510582097494459230781640628620899862803482534211706798214808651328230664709384460955058223172535940812848111745028410270193852
What molecules do autotrophs contain that trap & convert energy from the sun into glucose?
Draw a cross-section of the molecule and label it's components pieces
Plants & other autotrophs contain molecules called chloroplasts that trap & convert solar energy into glucose. However, this process also takes place within the thylakoids of the chloroplast!
Draw & annotate a chemical flowchart for the process of Photolysis
1. Water & Light combine which splits the water molecule in a process called photolysis
2. This produces 2 H+ ions, 1/2 O2 & 2e-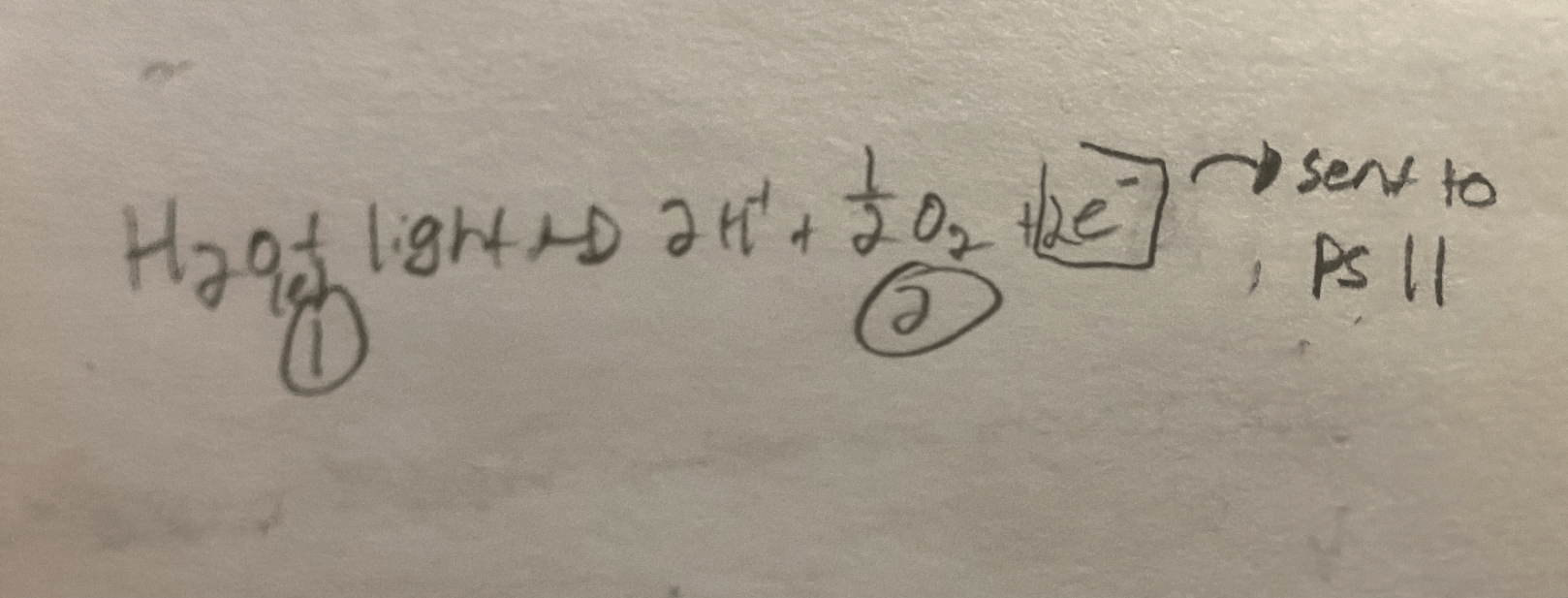
How many PGAL are produced per Calvin cycle?
How many CO2, NADPH & ATP are required for one cycle of the Calvin Cycle
6 PGAL are produced in total but only 1 is sent to make glucose, so 1 PGAL is produced per cycle!
Per Calvin Cycle:
- 3 Carbon Dioxide
- 6 NADPH
- 9 ATP
What does a high Rf value indicate? a low one?
High Rf = pigments travelled further through the solution and are higher up on the chromatography strip (0.8 or higher)
Low Rf = pigments travelled a shorter distance through the solution and are lower down on the chromatography strip (0.3 or lower)
Name as many Christopher Nolan Movies as you can (bonus 50 points for every movie after 6)
- Following (1998)
- Memento (2000)
- Insomnia (2002)
- Batman Begins (2005)
- The Prestige (2006)
- The Dark Knight (2008)
- Inception (2010)
- The Dark Knight Rises (2012)
- Interstellar (2014)
- Dunkirk (2017)
- Tenet (2020)
- Oppenheimer (2023)
What is the process of chromatography?
Chromatography: process of separating pigments to see what pigments are present in leaf samples/molecules
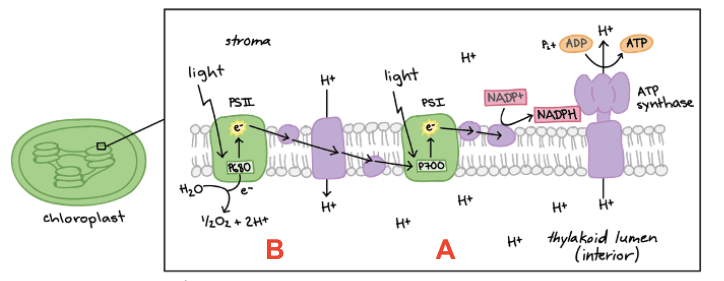
Draw & annotate stages A & B of the light-dependent RXN
Stage A: (actually occurs second) → Photosystem I
- PS I absorbs light (photons) which excites electrons
- Ferredoxin (an e- transport protein) steals the electron
- NADP Reductase steals the e- and passes it to the final electron acceptor → NADP+ which is reduced to NADPH (which will be used to make glucose later!)
- H+ ions floating in the stroma are also gained by NADP+
Photosystem I did not get the electron it passed to NADP+ back, so it cannot absorb any more light! = PROBLEM
Stage B: (actually occurs first) → Photosystem II: we have only made NADPH so far
- PSII absorbs photons which excites e-
- These electrons are accepted by the PEA and passed down a row of proteins called the ETC (electron transport chain)
- Each time the e- “falls down the stairs”, it releases a small bit of energy that is used to pump H+ ions from the stroma → thylakoid lumen
- This creates a hydrogen ion gradient!
- H+ ions flow back to stroma through ATP synthase which couples the flow of ions to the production of ATP (phosphorylation)
- the e- from the ETC goes to PSI so it can create NADPH (needed to make glucose)
- Creates a problem! PSII needs its e- back to absorb more light! --> Photolysis of water provides the electrons to PSII
Annotate & Draw the three stages of the Calvin Cycle
Carbon Fixation (Stage A)
CO2 is chemically bonded to 5C molecule called RuBP (Ribulose Bisphosphate)
The RUBISCO (Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase) enzyme catalyzes the bonding of CO2 to RuBP
The result of this bonding is an unstable 6C compound that immediately breaks into two 3C compounds.
Reduction (Stage B)
The 3C compounds are low energy, to convert to a high energy state they are activated by ATP and reduced by NADPH
The results of these processes are two 3C sugar molecules called PGAL/G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)
Some PGAL molecules will be used to make glucose, others will stay in the calvin cycle (they move on to Stage C)
Replacing RuBP/Regeneration (Stage C)
Energy from ATP molecules are used to break and reform bonds to regenerate RuBP from PGAL molecules.
Key point: the calvin cycle needs to happen six times to synthesize one molecule of glucose!
Of the 12 PGAL (3C) molecules produced in the two calvin cycles
10 PGAL are used to regenerate RuBP = 30 C
2 PGAL are used to form a glucose molecule = 6C
What wavelengths of light do chlorophyll a, b & carotenoids absorb & reflect according to this graph? (colours & nm)
Chlorophyll a:
Absorbs Violet/Blue/Orange & Red Light (~400 -~500nm & ~625-~700nm)
Reflects: Green Light (~500-625nm)
Chlorophyll b:
Absorbs Violet/Blue/Orange & Red Light (~400 -~500nm & ~625-~675nm)
Reflects: Green Light (~500-~625nm)
Carotenoid:
Absorbs Violet/Blue/Turquoise(Blue-green) Light (~400 -~535nm)
Reflects: Yellow, Orange & Red Light (~575-~700nm)
What can run but never walks, Has a mouth but never talks, Has a bed but never sleeps, Has a head but never weeps?
A river