What are the names of Structures A - G
Bonus 50 points if you can name the two structures not included in the bottom of the diagram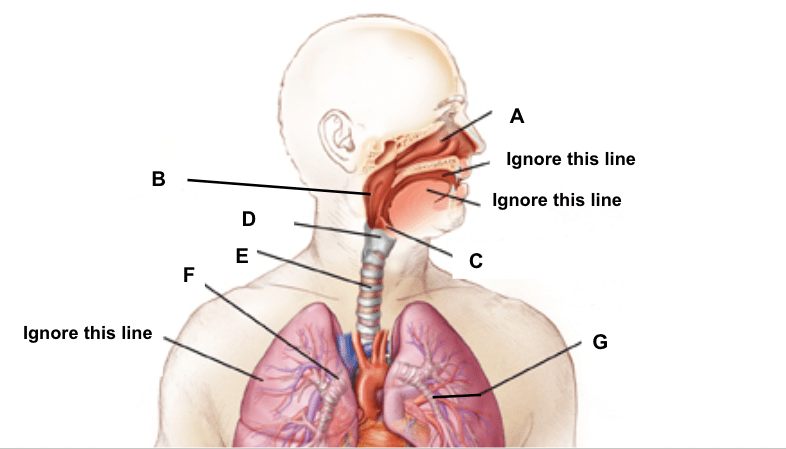
A. Nasal Passage
B. Pharynx
C. Epiglottis
D. Larynx (includes vocal chords)
E. Trachea
F. Bronchi/Bronchus
G. Bronchioles
- The Glottis, Alveoli and the Diaphragm are the three structures not labelled in the diagram
What phenomena (physics) is created when we inhale that causes air to be drawn into our lungs?
A vacuum
Respiration is two main stages, followed by a third stage. What are the names of these stages?
External Respiration: the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs (alveoli) and the blood (inside alveolar capillaries)
Internal respiration: the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood (inside alveolar capillaries) and the cells of our body
Cellular Respiration: the conversion of oxygen and glucose into carbon dioxide, water, heat and ATP (biological form of energy)
What is spirometer? What is it's function?
It is a tool that is used to measure lung capacity
If a Tree falls in the forest, and no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound.
NO --> Correct Answer
YES --> ALSO CORRECT BUT LESS CORRECT ANSWER
What are the functions of Structures:
A, D & G or B, C and E
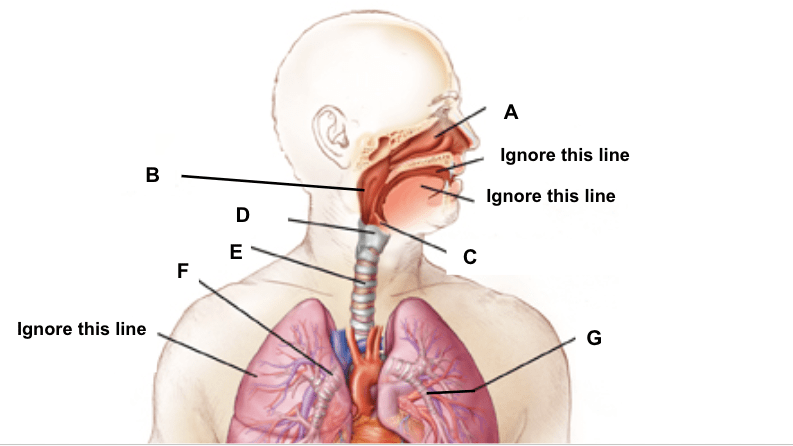
A. Nasal Passages: Moistens, warms and cleans incoming air!
- They moisten air by secreting mucus from mucus glands, they warm the air as it passes through as heat dissipates from blood vessels in the nasal passages. They are lined with ciliated cells which increase surface area, these ciliated cells clean the air by trapping and pushing the foreign particles back up into the nose & throat!
D. The Larynx is also known as the voice box as it contains the vocal cords. As air passes through the larynx it hits the vocal cords and causes them to vibrate which creates a sound. The larynx is made up of cartilage (firm connective tissue)
G. Bronchioles: passageway for air between the bronchi and the alveoli. They contain small pieces of cartilage to keep the airway open!
B. Pharynx: Passageway for air into the respiratory system, contains entryways to the eustachian tube in the ear, the mouth, and the nasal passages!
C. Epiglottis: small firm flap of cartilage. When breathing, the epiglottis is relaxed and in an upright position. When eating/drinking, the epiglottis covers the trachea!
E. Trachea (Windpipe) Passageway for air from the larynx and to the bronchi! Contains cartilaginous C-shaped rings to keep it from collapsing.
Describe the mechanical process of Inhalation
The intercostal (rib) muscles contract and draw the chest up and out.
The diaphragm contracts & flattens out, which draws the lungs down increasing their volume, but decreasing pulmonary pressure. This creates a vacuum which draws air into your lungs.
Pulmonary pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure
What is the name of this molecule? Explain the structure of the molecule and how it relates to the molecule's function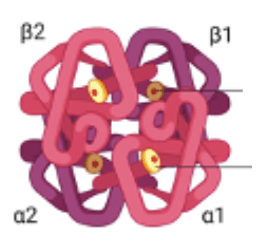
This is Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a quaternary protein (it has four sections). Each section of the molecule contains a heme group, and inside of the heme group is a molecule of Iron.
Hemoglobin is the molecule that binds to Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen in the red blood cells. Its quaternary structures allows for the binding of multiple oxygen molecules at one time, and the iron group helps hemoglobin bind to oxygen as it has a high affinity for it.
What is a spirograph?
A visual representation of lung capacity. Spirographs show the amount of air that moves into and out of the lungs with each breath!
Finish the lyric: (100 bonus points for EFFORT AND PASSION)
She said do you love me?
I tell her only partly,
__ _____ ______ ________ _____ ___ ________ __ _________
Finish the lyric: (100 bonus points for EFFORT AND PASSION)
She said do you love me?
I tell her only partly,
I only love mahbed and my momma,
I'm sorry!
What is the name of the double-layered membrane that is attached to the outside of the lungs and the inner chest wall?
The Pleural Membrane: allows the lungs to move in response to the movement of the chest.
Describe the mechanical process of exhaling
The intercostal (rib) muscles relax and allow the chest to sink back downwards.
The diaphragm relaxes and returns to its original dome shape, this increases pulmonary pressure which causes air to rush out of out lungs.
Pulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure
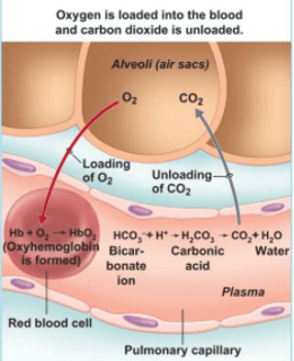
What causes the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide within the alveoli, capillaries & tissue cells.
Concentration gradients allow the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide, however, partial pressure gradients also allow for this diffusion!
How many litres of air does your body ventilate per day?
Your TV should be ~ ______ mL
Your ERV should be ~ _______ mL
and your VC should be ~ ______ mL
11,000L
Tidal volume: Less than 600mL
Expiratory Reserve Volume:~1000mL
Vital Capacity: ~3000-6000mL
In the Chinese Zodiac, which year is it (2025)?
The Year of the Snake!
What is the function of the Alveoli? How is the structure of the Alveoli related to their function?

The alveoli are the site of gas exchange in the respiratory system. In the alveoli, oxygen diffuses from the air into the blood (flowing in the alveolar capillaries), and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood (flowing in the alveolar capillaries) and into the alveoli to be exhaled!
Alveoli are made of spongy tissue, which allows them to expand and contract easily in response to breathing. The alveoli are also highly folded (membranous sacs), this increases the surface area in the lungs which increases the efficiency of gas exchange. The alveoli are one cell thick, which facilitates gas exchange. And finally, the alveoli are moist which helps with the diffusion of gases during gas exchange!
Describe how this machine mimics the mechanics of breathing
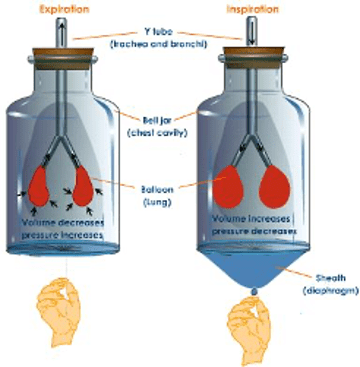
In the diagram, when you pull on the balloon it acts like the diaphragm increasing volume and decreasing pressure in the bell jar. This draws air into the tube causing the balloons to inflate, just like the lungs. (Inhalation)
When the balloon is released, it acts like the diaphragm decreasing volume and increasing pressure in the bell jar. This increase in pressure causes air to rush out of the balloons and through the tube just like the lungs. (Exhalation)
Describe the process of converting Carbon dioxide (in gas exchange) in the tissues and in the lungs (Groups take sections of the whiteboard)
In Tissues (Carbon dioxide diffuses into the Red Blood Cell)

At Lungs (between alveoli & lung capillaries)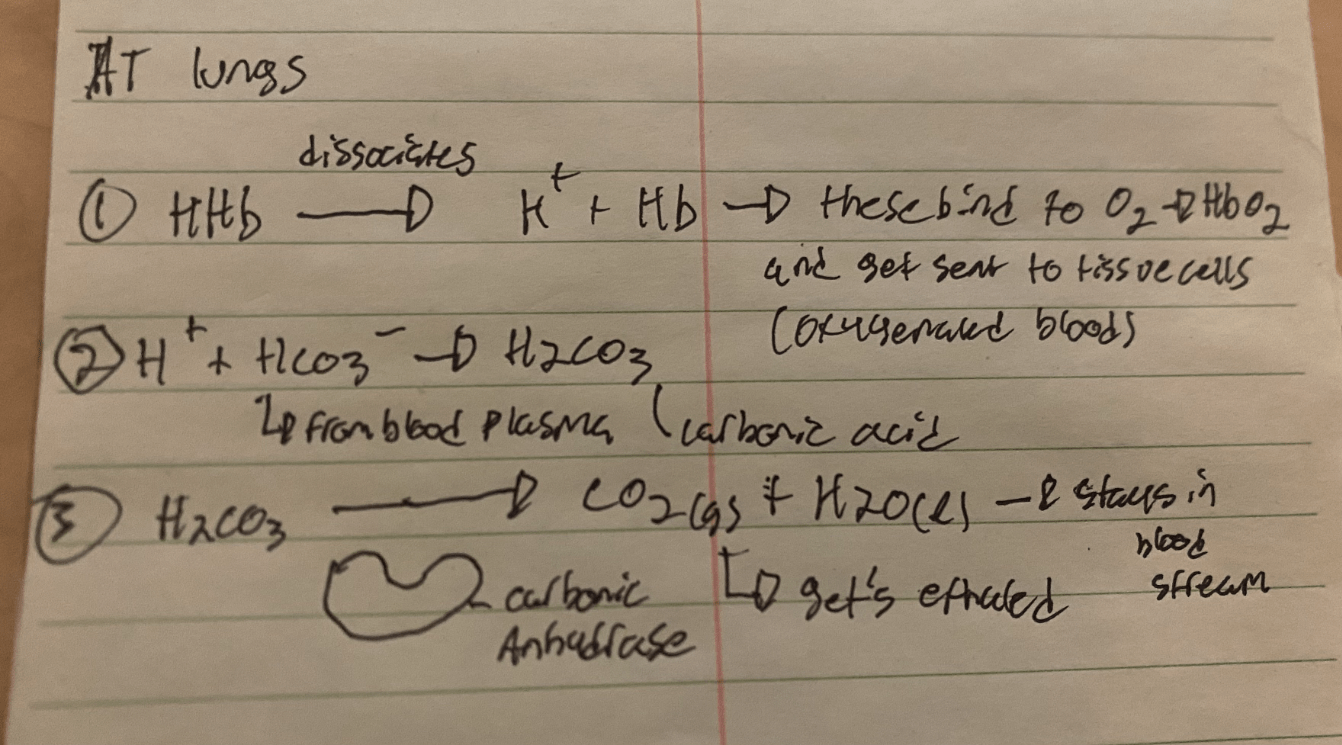
Which volumes/capacities do the Letter A-H represent on this spirograph?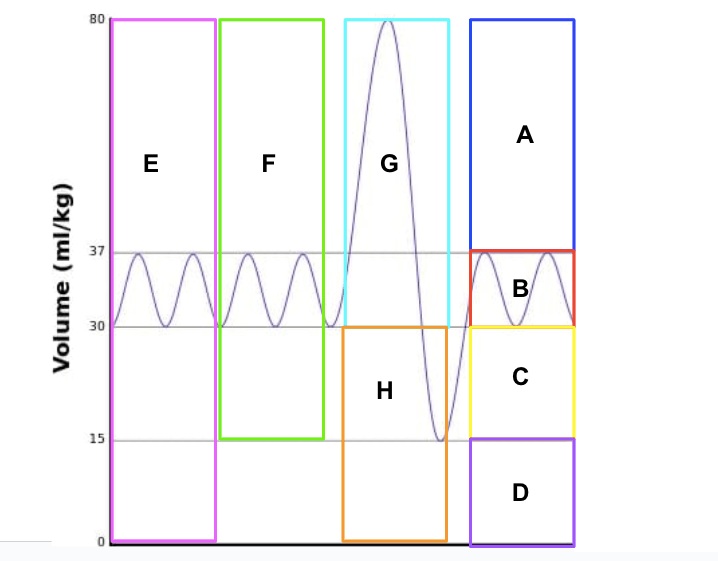
A = Inspiratory Reserve Volume
B = Tidal Volume
C = Expiratory Reserve Volume
D = Residual Volume
E = Total Lung Capacity
F = Vital Capacity
G = Inspiratory Capacity
H = Functional Residual Capacity
Which Canadian Prime Ministers daughter was a student at William Aberhart?
Stephen Harper's Daughter, Rachel Harper!
What is the function of the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a long thin muscle located below the lungs, it contracts and flattens during inhalation to increase lung volume. It relaxes and returns to its original dome shape and decreases lung volume (exhalation).
Explain everything you know about hiccoughs
What is physically happening when you get the wind knocked out of you?
Caused by a spasm of the diaphragm (what causes these spasms is unknown) --> Air hits vocal cords = "hic" sound
Getting hit in the stomach or the back can cause the diaphragm to spasm, which causes the muscle to tense and stop functioning properly. This is only temporary, taking regular breaths in and out will help reset the diaphragm.
Describe the process of exchanging oxygen & carbon dioxide in the capillaries/in the lungs (Groups take sections of the whiteboard)

What is the IRV, TV, and RV of this spirograph?
Inspiratory Reserve Volume:
80 ml/kg - 37 ml/kg = 43 ml/kg
Tidal Volume:
37 ml/kg - 30 ml/kg = 7 ml/kg
Reserve/Residual Volume =
15 ml/kg - 0 ml/kg = 15 ml/kg
How many songs does Taylor Swift Have? (Closest #)
According to my research, she has 274 songs! (As of April 2024)