What is deamination vs depurination?
Deamination is when an amine group (NH3) is removed by mistake, and depurination is when a purine is removed (adenine/guanine)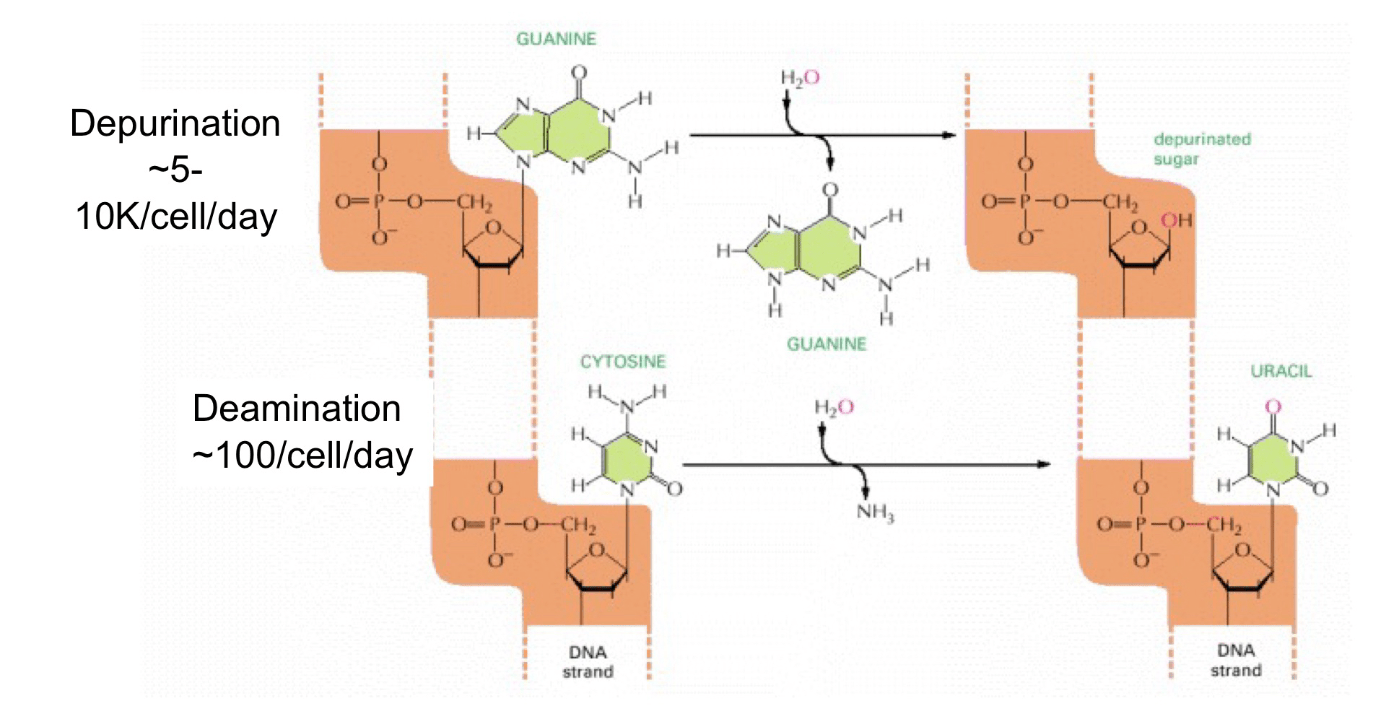
_____ are mRNA segments that are expressed while _____ are mRNA segments that are cut out.
Exons, Introns
mRNA is read from the ____ end to the ____ end
5' to 3'
Repressor protein is allosterically ________ (inhibited or activated) by ________
inhibited, lactose
If none of our e.coli colonies took in our plasmid, and were spread onto a plate that that had just LB, what would we see on the plate
Lawn, because there's no kanamycin to kill anything off
Draw out DNA polymerase III in e.coli.
Why is alternative splicing beneficial?
DIFF mature mRNAs can come from different primary mRNA transcripts
Missense = codes for wrong AA
Nonsense = codes for nothing instead
High glucose concentration leads to _____ transcription of the lac operon
Low
What are ddNTPs and dNTPS, and what do they do?
ddNTPs: missing an -OH so they end DNA synthesis (since DNA polymerase attached itself to that -OH group)
dNTPs: have an -OH group, so DNA can keep synthesizing
What are telomeres and why are they important?
Telomeres are synthesized by telomerase, theyre "nonsenese DNA" added to the ends of our DNA during fetal development to protect against end replication problem (where the very ends of DNA can't be replicated)
What does AAUAAA sequence do?
Cleavage factors recognize the AAUAAA sequence and hop off CTD and onto mRNA, so the mRNA is cut from RNA sequence, and poly A Polymerase can bind and add the poly A tail
t-RNA enters at the ____ site, is catalytically attached to the growing polypeptide at the ____ site, and exits from the ____ site
A, P, E
How is CAP binding affected by present glucose?
What was the synthetic strategy used in the kinetics lab and why did we use it?
-pNPG
-because when cleaves, the anionic version is light absorbing, so we could use spectrophotometry to measure course of the enzymatic rxn
What are the common features of general DNA Excision Repair Pathways?
-Defect Recognition
-Damaged protein excised
-new DNA synthesized - phosphodiester backbone sealed w ligase
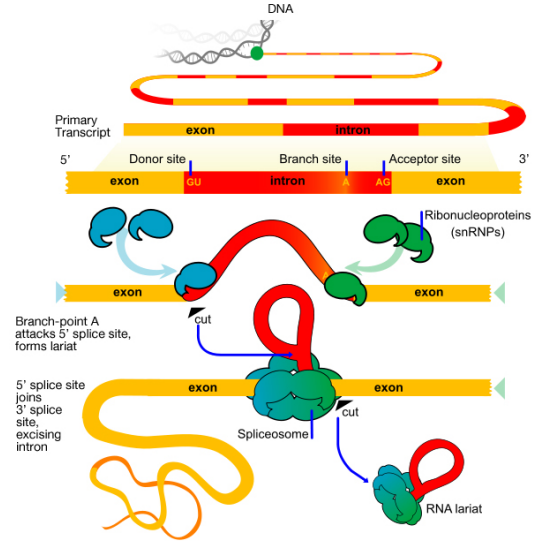
How does splicing occur?
Once AA's on tRNA are positioned on P and A sites, what catalyzes peptide bond formation?
Histone Acetylation by HATs modifies histone tails to _______ transcription. HDACs do the opposite.
promote
How does the computer in Sanger Sequencing determine what base is what?
The ddNTPs are colored, based on that color, the computer can decide what base is there
Draw out the process of how the lagging and leading strand is synthesized in e.coli DNA replication.
Describe step-by-step transcription initiation event:
TBP recognizes promoter sequence, it binds and bends DNA to make it more accessible, TFIIH-2's helicase unwinds double-stranded DNA, TFIID sits on top of promoters and recruits other transcription factors, RNA polymerase II comes and positions itself instead, TFIIH-2' kinase phosphorylates RNA POLY II CTD which allows RNA polymerase II to start moving
Translation is initiated by ___________ which attract the ________ ribosomal subunit which begins to scan the mRNA for the ______ codon with the sequence ____. Translation is stopped when it reaches the stop codon which causes ____________ to release the ribosomal subunits, newly formed protein, and mRNA
Initiation Factors, 30S or small, start, AUG. Release
How can gene regulation occur through changes in chromatin structure? What is it called when genes are permanently silenced?
-addition of methyl groups onto DNA nucleotides
-heterochromatic state
What was the point of the agarose nickel beads when the BglB protein was being purified?
The BglB protein formed bonds with the Ni in the agarose beads, so the remaining proteins and DNA can get washed off the columns.