Which plasma membrane component can be either found on its surface or embedded in the membrane structure?
carbohydrates
cholesterol
glycolipid
protein
protein
If a doctor injected a patient with what was labeled as an isotonic saline solution, but then the patient died, and an autopsy revealed that several of the patient's red blood cells had burst, such as in the image on the right, would it be true that the injected solution was really isotonic? Why or why not?
False, the solution was hypertonic.
False, the solution was osmotic.
False, the solution was hypotonic.
True, the solution was isotonic.
False, the solution was hypotonic.
Proteins that are fully translated in the cytosol
and lack a mitochondrial signal will end up in
_________
(a) the cytosol.
(b) the mitochondria.
(c) the interior of the nucleus.
(d) the nuclear membrane.
(a) the cytosol.
Malformation of which cytoskeletal structures may be linked to an inability to contract muscle?
Microfilaments
Keratin is a type of________
1) Actin filaments
2) Intermediate filaments
3) Microtubules
4) Lamins
2) Intermediate filaments
What happens to the membrane of a vesicle after exocytosis?
It leaves the cell.
It is disassembled by the cell.
It fuses with and becomes part of the plasma membrane.
It is used again in another exocytosis event.
It fuses with and becomes part of the plasma membrane.
Organisms that live in cold climates adapt to low
temperatures by doing which of the following?
• increasing the amounts of saturated fatty acids in their
membranes to help decrease the fluidity of their
membranes
• increasing the amounts of unsaturated fatty acids in
their membranes to help keep their membranes fluid
• increasing the amounts of saturated fatty acids in their
membranes to help keep their membranes fluid
• decreasing the amounts of unsaturated fatty acids in
their membranes to help keep their membranes fluid
increasing the amounts of unsaturated fatty acids in
their membranes to help keep their membranes fluid
Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system?
- mitochondrion
- Golgi apparatus
- endoplasmic reticulum
- lysosome
- mitochondrion
Imagine a cell can perform exocytosis, but only minimal endocytosis. What would happen to the cell?
- The cell would secrete all its intracellular proteins.
- The plasma membrane would increase in size over time.
- The cell would stop expressing integral receptor proteins in its plasma membrane.
- The cell would lyse.
- The plasma membrane would increase in size over time.
The ciliary action of the cells lining the lumen of fallopian tube are responsible for transporting an egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Which cytoskeleton structures are linked to this movement?
- Microtubules
Which characteristic of a phospholipid, shown here, increases the fluidity of the membrane?
cholesterol
its head
saturated fatty acid tail
double bonds in the fatty acid tail
double bonds in the fatty acid tail
According to the fluid mosaic model of the plasma cell membrane, what is the location of carbohydrates in the cell membranes?
Carbohydrates are in contact with the aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell.
Carbohydrates are present only on the interior surface of a membrane.
Carbohydrates are present only on the exterior surface of a membrane.
Carbohydates span only the interior of a membrane.
Carbohydrates are present only on the exterior surface of a membrane.
What will happen if you mutate RanGTP in the nucleus.
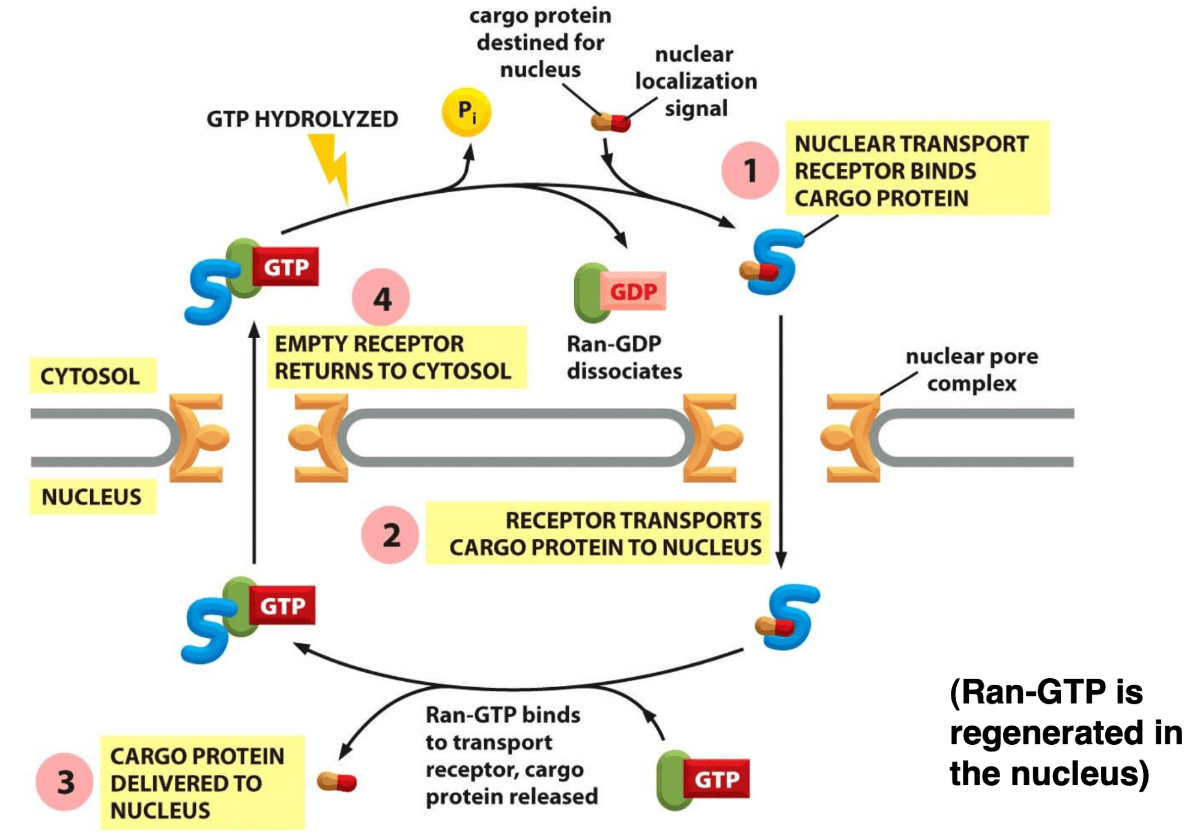
Defects and diseases
Which type of cytoskeletal element is described as a tough, ropelike fibers composed of a variety of related proteins like keratin?
a. Microfilaments
b. Microtubules
c. Intermediate filaments
d. Macrofilaments
c. Intermediate filaments
Which cytoskeletal structure is linked with the movements of a macrophage?
- Cilia and flagella
- Glycocalyx
- Microtubules
- Microfilaments
Microfilaments
What do double bonds in phospholipid fatty acid tails contribute to?
the fluidity of membranes
the hydrophobic nature of membranes
the hydrophilic nature of membranes
preventing high temperatures from increasing fluidity of membranes
the fluidity of membranes
In what important way does receptor-mediated endocytosis differ from phagocytosis?
It transports only small amounts of fluid.
It does not involve the pinching off of membrane.
It brings in only a specifically targeted substance.
It brings substances into the cell, while phagocytosis removes substances.
It brings in only a specifically targeted substance.
Many viruses enter host cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. What is an advantage of this entry strategy?
- The virus directly enters the cytoplasm of the cell.
- The virus is protected from recognition by white blood cells.
- The virus only enters its target host cell type.
- The virus can directly inject its genome into the cell’s nucleus.
- The virus only enters its target host cell type.
What is your conclusion about this graph?
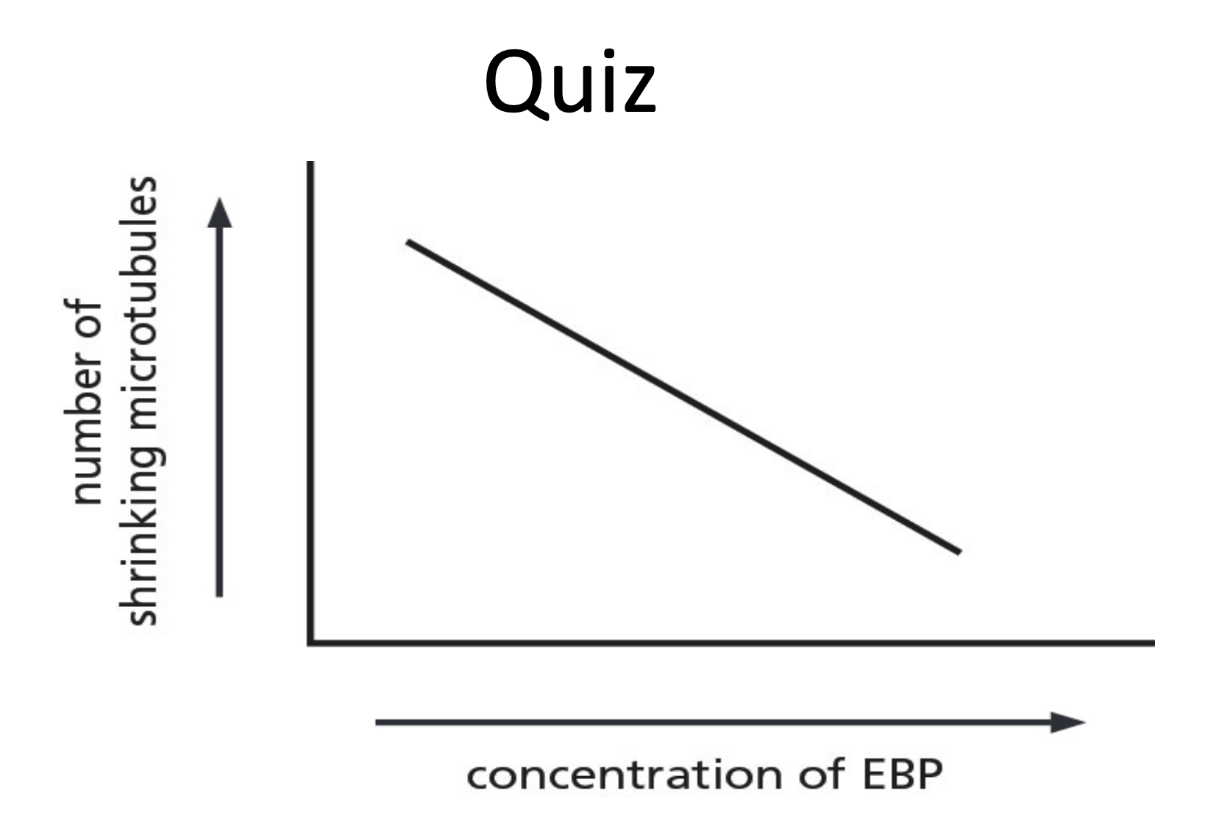
1) Addition of EBP leads to increase in microtubule shrinking
2) As the concentration of EBP increases, stability and length of microtubules increases.
3) Decrease in stability as concentration of EBP decreases
4) Decrease in stability of microtubules as EBP conc. increases
4) Decrease in stability of microtubules as EBP conc. increases
Which motor proteins are not linked to microtubules?
1) Dyenin
2) Kinesis
3) Myosin
Myosin
How is phosphatidylethanolamine found mainly in the
cytoplasmic monolayer?
• A. Phosphatidylethanolamine is synthesized and inserted
into the lumen monolayer of the ER and then flipped to the
cytoplasmic monolayer.
• B. A specific scramblase moves
phosphatidylethanolamine to the cytoplasmic monolayer.
• C. Phosphatidylethanolamine is synthesized and inserted
into the cytoplasmic monolayer of the plasma membrane
and is thus always in the cytoplasmic monolayer.
• D. A specific flippase moves phosphatidylethanolamine to
the cytoplasmic monolayer.
A specific flippase moves phosphatidylethanolamine to
the cytoplasmic monolayer.
.
The fluid mosaic model described the plasma membrane, seen here, as a mosaic of components. Why is it advantageous for the plasma membrane to be fluid in nature?
Fluidity allows greater flexibility to the cell and motion of membrane components required for transport.
Fluidity helps only in transport of some materials, and does not contribute to the flexibility.
Fluidity helps in maintaining the pH of intracellular fluid, and helps in maintaining the physiological pH of the cell.
Fluidity helps in providing mechanical strength to the plasma membrane.
Fluidity allows greater flexibility to the cell and motion of membrane components required for transport.
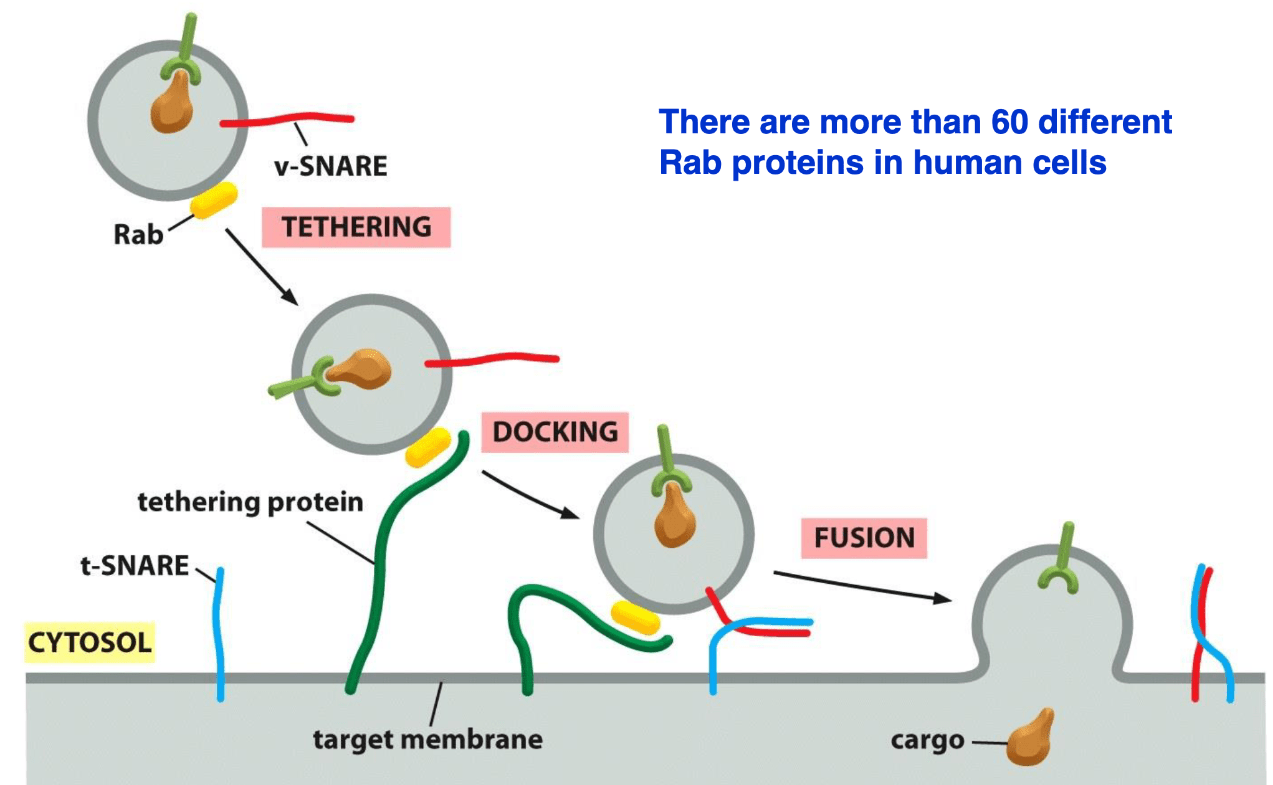 You are doing an experiment and see all the vesicles are accumulating on the membrane but not delivering the cargo to the cell. tSnare is working fine.
You are doing an experiment and see all the vesicles are accumulating on the membrane but not delivering the cargo to the cell. tSnare is working fine.
What is your hypothesis?
1) Rab protein is not working.
2) Snare protein is not working.
3) There is no cargo in these vesicles.
1) Rab protein is not working.
What will happen if Calcium is not present for muscle contraction?
1) Muscle will contract normally and actin myosin proteins will work normally
2) Muscle will be relaxed and no actin myosin binding
3) Muscle will be in locked position and both proteins will be locked.
4) ATP will bind to tropomyosin.
2) Muscle will be relaxed and no actin myosin binding
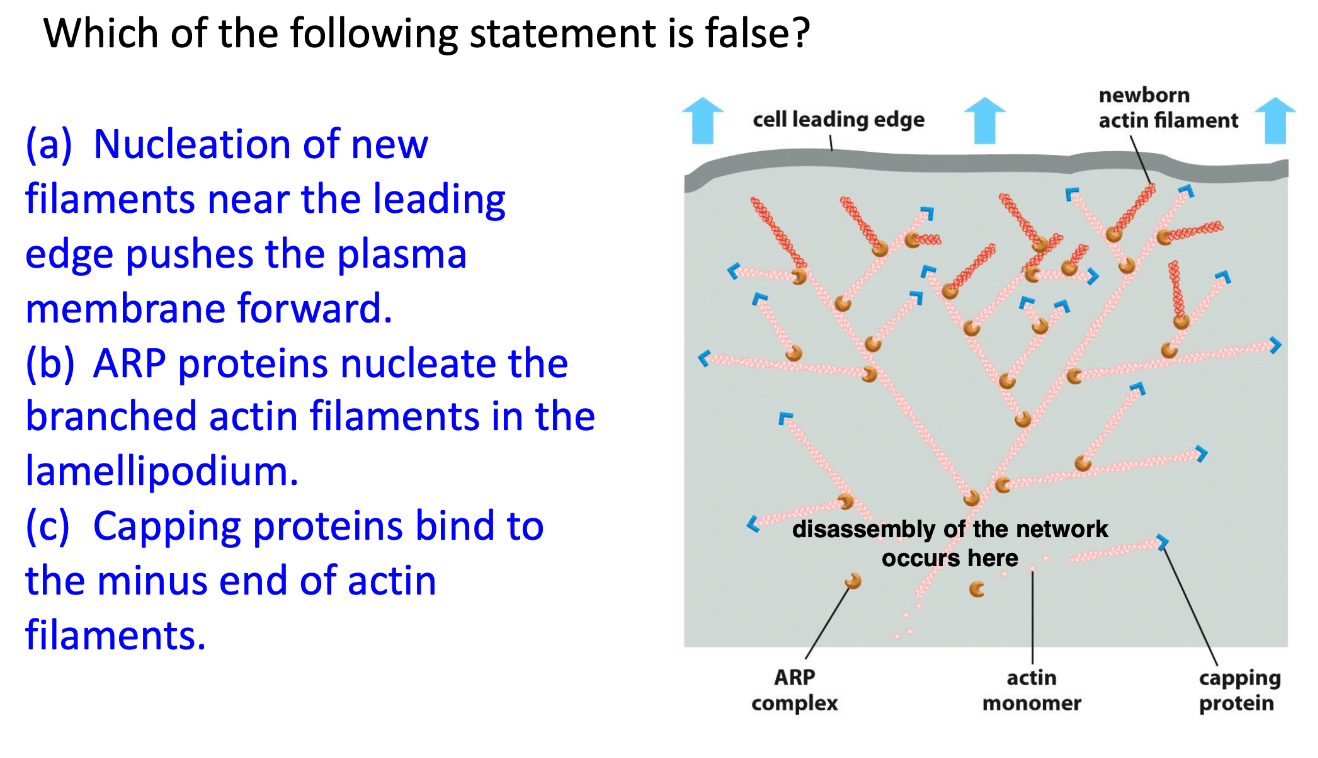
- Capping proteins bind to the minus end of actin filaments