The type of receptor that is embedded in the plasma membrane and interacts with hydrophilic ligands
What is a transmembrane receptor?
This step of mitosis is represented below.
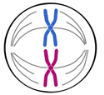
What is metaphase?
The process by which oxygen is transported to cells and carbon dioxide is transported from cells.
What is gas exchange?
Properties that exist when the sum of all parts creates features that do not exist within individual components
What are emergent properties?
Has nucleic acid and a protein coat but cannot be treated with antibiotics
What is a virus?
Chemical messengers used in quorum sensing
What are Autoinducers?
A cell of a living organism OTHER than the reproductive cells. This includes but is not limited to nerve cells, skin cells, heart cells, lung cells, etc.
What is somatic?
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart under high pressure, have thick, muscular, and elastic walls to withstand the pressure and maintain blood flow
What are arteries?
The two voluntary actions in the digestive system and the involuntary action.
Voluntary: Swallowing, Egestion
Involuntary: Peristalsis
Can only be reproduced in human cells, attacks Helper T Cells
What is HIV?
Two of the four functional categories of signaling chemicals in animals
What are hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, or calcium ions
A single set of chromosomes
What is haploid?
The adaptations of the alveolus to do gas exchange.
What is highly irrigated and have a large SA:V ratio
The general pathway of a reflex arc
What is Receptor cells or direct nerve endings -->Sensory neuron --> Synapse -->Relay neuron in CNS (decision making station) --> Synapse --> Motor neuron --> Effector
Produced by the immune system that attach onto the virus to slow it down and mark which cells the Killer T Cells should attack
What is an antibody?
The largest class of cell surface receptors in humans?
What are GPCRs (G protein coupled-receptors)?
The exchange of genetic material in prophase 1 between homologous chromosomes is called this
What is crossing over?
The adaptations of plants to conserve water in dry environments (name at least 2)
What are thick leaves, deep roots, and reduced number of stomata?
The structure of a myelinated neuron and why the action potential is faster compared to unmyelinated axons.
What is myelinated neurons have Schwann cells wrapped around their axons, forming an insulating layer. In myelinated axons, action potentials jump between nodes, allowing faster signal transmission.
Parts of the first line of defense (4)
What is cillia, mucus, stomach acid, and skin?
This type of feedback amplifies signal transduction. The second type dampens the response to maintain homeostasis.
Unregulated cellular division can lead to this health diagnosis
What is cancer?
The relationship between humidity and rate of transpiration
What is high humidity slows down transpiration due to a smaller vapor pressure gradient, while low humidity speeds it up by creating a larger gradient for water to evaporate from the plant. (inverse relationship)
How the sleep cycle is controlled (explain)
What is melatonin secretion by the pineal gland follows a diurnal pattern where melatonin levels rise in the evening (promoting sleep) and fall in the morning (promoting wakefulness)?
Cell in the third line of defense that aids in a faster secondary response due to its ability to remember
What is a Memory B Cell?