anterior & posterior
what is situated or facing towards the front of the body or structure
and
what is situated or facing the back or rear part of the structure or body
coronal section
what is giving a frontal view
neurons
what is a basic unit of the nervous system
dendrites
what are the tree like structures coming off of the soma
chromosomes
what is DNA
receptors
what is the site of action of neurotransmitters, hormones, and drugs
local potentials
what are small localized, short-lived change in voltage across the cell membrane following the opening of ligand-gated channels
local potentials are generated on the dendrites and cell body
Acetylcholine (ACh)
what is the neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning, and memory.
(with Alzheimer's ACh- producing neurons deteriorate).
Which is the most common anticholinergic side-effect?
what is blurred vision
anticholinergic= blocks ACh in nervous system (treat COPD, overactive bladder, parkinson's)
a substance that stimulates or mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter is referred to as
what is agonistic
following a stroke involving the MCA (middle cerebral artery), an elderly man experiences weakness and loss of sensation in his left arm and leg. In addition, he exhibits
left visual field loss.
Wernicke's aphasia.
left-right disorientation.
finger agnosia.
what is (a) left field vision loss
because this man's symptoms involve the left side of his body, this indicates that the stroke affected the right side of his brain. Depending on the location of the brain damage, the man may also be experiencing left visual field loss, anosognosia (denial of deficits), and left-sided neglect. The symptoms listed in answers B, C, and D are caused by damage to the left side of the brain.
Following a stroke, a woman complains of numbness in her left hand and she does not respond to images presented to her left visual field. She most likely suffered damage where
what is the right postcentral gyrus
the postcentral gyrus includes the somatosensory cortex, and is located in the parietal lobe. Damage to the right postcentral gyrus could result in numbness in the left hand and contralateral neglect, which includes neglect of the left visual field. Broca's ("A") and Wernicke's ("B") areas are both located in the left hemisphere of the brain and only affect language. The precentral gyrus ("C") is responsible for motor functioning.
Side effects of propranolol (Inderol) are most likely to include:
tachycardia and mania
tachycardia and tremor
bradycardia and hypersomnia
bradycardia and depression
what is (4) bradycardia and depression
bradycardia= slow heart rate
Propranolol (Inderal) is a beta-blocker often used to treat hypertension, migraine, essential tremors and is also useful in reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety. Side effects of Inderal include bradycardia (slow heart rate), hypotension, fatigue, sexual dysfunction, and depression.
The areas of the brain associated with declarative memory include all of the following except the:
striatum
diencephalon
peripheral cortex
hippocampus
what is the (1) striatum
Declarative memory consists of both episodic memory, past and personally experienced events, and semantic memory, knowledge of the meaning of words and how to apply them. In general, declarative memory is associated with the hippocampus (d.) and temporal cortex. More specifically, declarative memory, primarily involves the diencephalon (b.). The diencephalon, comprised of the thalamus and hypothalamus, is located between the two hemispheres of the brain, sometimes referred to as the “between brain,” or the anterior to midbrain regions. The diencephalon contains important connections and relays for sensory, motor as well as limbic pathways that are involved with memory. Additional areas that are associated with declarative memory are the peripheral cortex (c.), the amygdala and the neocortex. In particular, this includes the right frontal & temporal lobes for the episodic component, and the temporal lobes for the semantic component. The striatum (a.) controls various muscular activities such as walking and balance.
A patient suffers damage to the spinal cord severe enough to cause numbness and tingling. However, the spinal cord is not severed. The patient is most likely experiencing what?
what is paresis
The term "paresis" means partial paralysis. Paresis can occur as a result of an injury to the spinal cord that does not result in its severation. If the spinal cord is severed, the result could be paraplegia (paralysis of the lower limbs), quadriplegia (paralysis of all four limbs), or hemiplegia (paralysis of one side of the body), depending on the location of the lesion. Note that the term paresis (or "general paresis") has been used to describe a syphilis-caused syndrome characterized by inflammation of cerebral tissue and mental and physical deterioration. However, the term's literal meaning is partial paralysis, and this is how it is often used as well.
dorsal and ventral
what is the back or posterior side of an organism
and
what is the front or anterior side of an organism
horizontal section
what is giving a dorsal view (top/arial view)
glial cells
what is a supporting cell of the nervous system
types
-astrocytes
-microglia
-schwann cells
-oligodendroglia
axons and terminal buttons
what is the tube that conducts electrical signals to the terminal buttons
genes
what are small portions of the DNA that code for the synthesis of a protein molecule
enzymes
what are proteins in the membrane that catalyze biochemical reactions in the cell
process of local potentials
what is an electrical current momentarily opens sodium channels to allow sodium ions to flow into the cell and the inside of the cell becomes more positive and closer to the threshold
Dopamine
what is the neurotransmitter responsible for influencing movement, learning, attention, and emotion.
(excess dopamine receptor activity is linked to schizophrenia. Deficient dopamine- brain produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson's
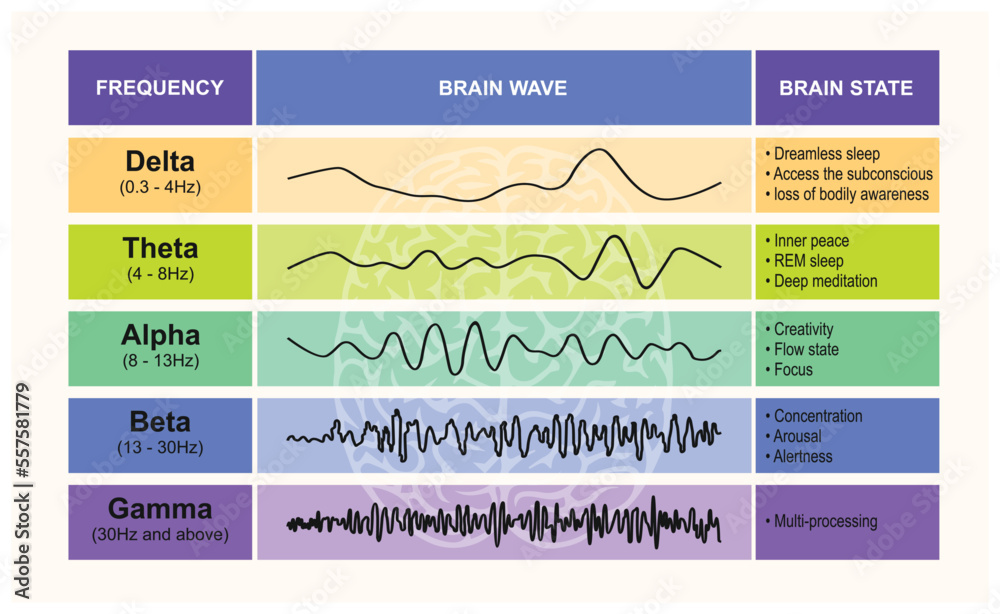
Which type of brain waves predominate when a person is awake, alert, and actively processing information?
what are beta waves
the part of the brain that is compromised in parkinson's
what is the substantia nigra
Depression and chronic pain are both associated with which neurotransmitters?
what is norepinephrine
The brain pathways that process pain signals use some of the same neurotransmitters that are involved in the regulation of mood, notably norepinephrine and serotonin. Pain, as well as anxiety, sadness, and hopelessness, are intensified when regulation fails and both chronic pain and chronic depression can alter the nervous system functioning and perpetuate itself. Antidepressants, especially tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), have proved to be effective in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia, chronic low back pain, chronic headache and postherpetic neuralgia. Tricyclics heighten the activity of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin; SSRIs act more selectively on serotonin. Amitriptyline (Elavil), a tricyclic, is one of the antidepressants most often recommended as an analgesic, partly because its sedative qualities.
Brain damage to the _____________ frequently results in loss of social inhibitions and ignoring rules of polite conduct.
what is the prefrontal cortex
typically, the onset of the SSRIs antidepressant effect begins within a few
what is a few weeks
urrent clinical practice indicates that at least 2 to 3 weeks of continuous SSRI use are necessary for the antidepressant effects to manifest in patients. The results of a meta-analysis conducted by Posternak & Zimmerman (2005), of 47 double-blind, placebo-controlled trials conducted between 1981 and 2000, found most of the antidepressant effects occurred during the first 2 weeks.
Damage to the hippocampus would most likely result in deficits in
what is long-term memory
According to the catecholamine hypothesis, depression is due to a deficiency in what
what is norepinephrine
medial & lateral
what is the direction towards the middle or midline of the body
and
what is the side of the body/ body part that is farthest from the midline or center of the body
sagittal section
what is giving medial view, lengthwise
sensory neurons
what is the neuron that detect environmental stimuli and turn messages into electrical signals
soma
what is the cell body, which is responsible for the neurons metabolism, growth, and maintence
transcription factors
what are nuclear proteins that direct protein production
(bind to promoter regions of the gene and modify rates of transcription
ion channels structural characteristics
what are carries potassium, sodium, chloride, and calcium across the channel
what is a water filled pore that ions can pass through
depolarization and hyperpolarization
hyper- what is an inhibitory action. when negative ions flow into the cell making the inside more negative
serotonin
what is the neurotransmitter responsible for mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
undersupply is linked to depression. Some anti depressants (Prozac) raise serotonin levels.
Possible side effects of the benzodiazepines include all of the following, EXCEPT:
drowsiness
short-term memory dysfunction
impaired psychomotor functioning
impaired concept formation
what is impaired concept formation
cells in the premotor cortex that are activated when one executes object-directed actions; when one sees someone else preforming actions of the same type
what are mirror neurons
Repetitive exercise and hypnosis are therapeutic techniques used to establish the “relaxation response” which involves ____________________________ activity.
decreased parasympathetic nervous system
decreased sympathetic nervous system
increased somatic nervous system
increased autonomic nervous system
what is (2) decreased sympathetic nervous system
Damage to the orbitofrontal cortex is most likely to result in
what is altered emotional behaviors
A person whose corpus callosum has been severed will be able to do all of the following except
name an object he cannot see but has felt with his left hand.
say "spoon" when a picture of a spoon is flashed to his right visual field at the same time that a picture of a plate is flashed to his left visual field.
use his left hand to find and match an object that appears in his left visual field.
repeat a sentence that has been whispered into his right ear.
what is (1) name an object he cannot see but has felt with his left hand
Remember, the left side of the brain controls the functions of the right side of the body and, in most people, language.
Which of the following devices measures cerebral blood flow with a color scale?
X-Ray
CT
MRI
SPECT
what is (4) the SPECT
The SPECT (single proton emission computed tomography) (as well as the PET or positron emission tomography) is used to measure blood flow in the brain using radioactive isotopes. It is, therefore, used to assess brain functioning (rather than structure). You can remember that this device uses color scale imaging since the acronym "SPECT " can also be thought of as an abbreviation for "spectrum." The other imaging devices (X-Ray, CT, and MRI) are used for identifying structures.
Which of the following is a non-stimulant medication that alleviates inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms in AD/HD?
methylphenidate
atomoxetine
pemoline
dextroamphetamine
what is (2) atomoxetine (strattera)
In November 2002, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new medication called atomoxetine (Strattera) specifically for AD/HD. This medication is neither a stimulant nor an antidepressant. It alleviates inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms of AD/HD by affecting specific aspects of the norepinephrine system. This medication is a reuptake inhibitor that acts on the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (which affects blood pressure and blood flow) in the same way that antidepressants act on the neurotransmitter seratonin, allowing the natural chemical to remain longer in the brain before being drawn back up. Because it is a non-stimulant, it may be less objectionable to some families. Nevertheless, it has similar side effects as other medications used for AD/HD. It is a prescription medication, but it is not a controlled substance like a stimulant.
contralateral, bilateral, & ipsilateral
what is relating to or on the opposite side of the body
and
what is structures or conditions that occur on both sides of the body
and
what is structures or conditions that occur on the same side of the body as the reference point
peripheral nervous system
what is made up of somatic nervous system (sense organs & voluntary organs), sensory nervous system (afferent, sensory input), and motor nervous system (efferent, motor output).
-Ganglia (large, well-defined groups of cell bodies
-Nerves (large collections of axon that enter and leave the CNS
interneurons
what is a neuron that forms neural circuits and are responsible for conscious sensations, recognition, memory, decision making, and cognition
lipid-rich, insulating layer that surrounds the axons of many nerve cells. Produced by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system
what is the myelin sheath

transcription
what is when DNA unravels, mRNA makes complementary strand for translation (occurs in the nucleus)
ligand-gated ion channels
what is when a drug, hormone, or neurotransmitter binds to a receptor causing the channel to change shape and open for passage in and out of the cell
characteristics of local potentials
what is
graded: the larger the stimulus, the greater the magnitude of the potential
Decremental: the potential decays as it travels along the cell membrane
norepinephrine
what is the neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal
under supply can depress mood
he statement "I am sad because I cry" is most consistent with the
what is the james lang theory of emotion
damage to the prefrontal cortex is most likely to cause
what is impaired memory and attention
Perseverating is an indication of damage in
what is the frontal lobe
Difficulty in interpreting feedback from the environment is one of the most common characteristics of frontal lobe damage. Perseverating or uncontrollable repetition of a particular response, risk taking, lack of social consciousness and non-compliance with rules are examples of this type of deficit.
Decreased amounts of GABA are most associated with
what is huntington's disease
Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Low levels of GABA have been linked to several disorders, including Huntington's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and anxiety disorders.
Memory impairment is to Alzheimer's disease as _____________ is to Parkinson's disease:
bradykinesia/akinesia
dyspraxia
hyperkinesia
hypophonia
what is (1) bradykinesia/akinesia
bradykinesia=slowed movements. delayed or slowed
akinesia= lack of movements. absence of voluntary movement
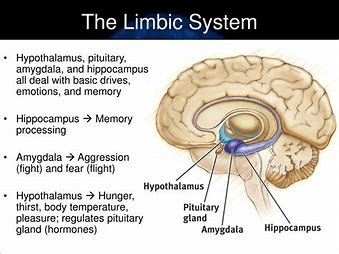
What forebrain structures are located around the brain stem and are important for motivated and emotional behavior?
what is the limbic system
The limbic system is a set of structures controlling motivated and emotional behaviors such as eating, drinking, sexual behavior and aggression. Main structures of the limbic system include the olfactory bulb, the hypothalamus which regulates motivational behaviors, the pituitary gland which controls the timing and amount of hormone release, and the hippocampus which is associated with learning and memory. The basal ganglia (a.) codes and relays information associated with the control of voluntary movement. The tegmentum (c.) is one of two regions of the “midbrain” and contains the substantia nigra which is part of the brain’s sensorimotor system. The reticular formation (d.) is a group of nerve fibers located inside the brainstem which controls sleep, arousal, and attention.
The condition describing a side-effect of antipsychotic medication that is incorrectly matched with its symptoms is:
akathisia — inability to sit, constantly pacing, restlessness
dysarthia — imperfect articulation of speech
akinesia — appears to be slow moving, indifferent to stimuli, emotionally constricted
opisthotonus — spasms in the lower extremities
what is (4) opisthotonus
Opisthotonus (d.) refers to whole body spasm, oculogyric crisis refers to rapid eye movements and
dysarthia (b.) refers to imperfect articulation of speech. These are some of the symptoms of dystonia and dyskinesia.
Akathisia (a.) is most common after about a week of treatment and characterized by constant pacing or an inability to sit still.
Akinesia (c.) is one of the side effects associated with Parkinsonism, a neurologic side effect of typical antipsychotic medication.
All four terms describe possible short-term side effects of antipsychotic medications, especially the older antipsychotics associated with extrapyramidal syndrome (EPS) which include Parkinsonism, acute dystonia, dyskinesia and akathisia.
proximal & distal / afferent & efferent
what is closer to the bodies center point of attachment
what is farther away from the center point of attachment
what is moving towards the brain
what is moving away from the brain
central nervous system
what is made up of autonomic nervous system (internal organs & glands), sympathetic (arousing), and parasympathetic (calming).
-layers of nuclei(clusters)- large, well-defined groups of cell bodies
-tracts (fiber pathways)- large collections of axons projecting toward or away from a nucleus or layer in the CNS
motor neurons
what is the specialized brain cells that transit signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, enabling movement and other bodily functions
type of glial cell that is responsible for forming the myelin sheath around the neurons of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and supplying nutrients to individual axons.
what is Schwann cell

OUTSIDE : translation
what is when mRNA attaches to ribosomes, which decodes the mRNA and makes the amino acid sequences to form proteins
voltage-gated ion channels
what are opened by the application of a small electrical change to the membrane
integration
what is when a small depolarization or hyperpolarization add up together to create larger changes
the integration of EPSPs and IPSPs occur in the axxon hillock and is responsible for the generation of the action potential if threshold is met
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) & Glutamate
what is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply is linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
what is a major excitatory neurotransmitter involved in memory. Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures (why some people avoid MSG, monosodium glutamate, in food)
An individual taking clozapine begins exhibiting symptoms of muscle rigidity, tachycardia, hyperthermia, altered consciousness, and autonomic dysfunction. In this case, the best course of action would be to:
reduce the dose gradually until the symptoms are alleviated
stop the drug immediately and administer electrolytes and fluids
switch to a traditional antipsychotic drug
check to see what other drugs the patient is taking since clozapine does not produce these symptoms
what is B (stop the drug immediately and administer electrolytes and fluids)
research on brain and ADHD suggest the degree of impusivity is associated with the
what is the size of the caudate nucleus
A whisper being audible in a library reading room, but not in a busy cafeteria is explained by:
the all-or-nothing principle
the “law of effect”
Weber’s law
the “law of proximity”
what is (3) the weber's law
Weber’s law is one of the psychophysical laws that explains the relationship between physical stimuli and their psychological effects. According to Weber, the “just noticeable difference” in the stimulus is proportional to the magnitude of the original stimulus, explaining why a whisper can be heard in a quiet room but not in a noisy one.
Which of the following types of epileptic seizures is commonly referred to as a grand-mal seizure?
simple partial
complex partial
absence
tonic-clonic
what is (4) tonic-clonic seziures
There are many different types of seizures, but they are classified into two general categories: Primary generalized seizures and partial seizures. Primary generalized seizures involve widespread electrical discharge occurring simultaneously in both sides of the brain; partial seizures begin with electrical discharge in a limited area of the brain. A tonic-clonic seizure, previously referred to as a grand-mal seizure, is an example of a primary generalized seizure. In the tonic phase of the seizure, the body's muscles stiffen up and the person loses consciousness and falls to the floor. The tongue or cheek may be bitten and the person may turn blue in the face. The clonic phase is characterized by repeated jerking--rapidly alternating muscle contraction and relaxation. Afterward, consciousness returns slowly and the person may be drowsy and confused. Regarding the other choices, a simple partial seizure is one in which electrical discharge takes place in a limited area of the brain, and the person remains alert and remembers what happens; the specific manifestation of the seizure can vary from case to case. In a complex partial seizure, electrical discharge begins in a small part of the brain's frontal or temporal lobes and quickly spreads to brain areas that affect alertness and awareness. The person will usually not remember the seizure and often not remember events occurring immediately before or immediately afterward. And an absence seizure, previously known as a petit mal seizure, is an example of a primary generalized seizure and is characterized by "blanking out"--the person just stares. They are sometimes accompanied by changes in muscle activity, most commonly eye blinking.
Clomipramine and fluoxetine alleviate the symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder by affecting levels of what
what is serotonin
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder are typically treated with lithium and/or any of the following medications EXCEPT:
phenelzine
carbamazepine
divalproex
valproic
what is (1) phenelzine
Currently, lithium and/or an anti-seizure medication is the drug treatment-of-choice for Bipolar Disorder. Unlike the others, phenelzine is not used for the treatment of Bipolar Disorder as it is an MAOI antidepressant.
Lesions in the prefrontal association cortex result in
what are impaired executive functions
a rapid and temporary change in the electrical potential of a neuron’s membrane, critical for transmitting signals along axons.
what is an action potential
The sensation of tingling, pricking, or numbness of an individual’s skin, more generally known as the feeling of “pins and needles” or a limb “falling asleep” is referred to as
what is paresthesia
paresthesia may be transient or chronic. Transient paresthesia of the hands and feet are common symptoms of hyperventilation syndrome, panic attacks or pressure on a nerve that inhibits or stimulates its function. Chronic paresthesia indicates a problem with the functioning of neurons which may be the result of poor circulation in the limbs, vitamin deficiency or malnutrition, metabolic disorders like diabetes and hypothyroidism, nerve irritation from tissue inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, muscle cramps as a result of anxiety or excessive stress, poor posture, heavy lifting, or physical trauma or direct damage to the nerves. Chronic paresthesia may also be symptomatic of serious conditions, such as autoimmune disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis or lupus erythematosus) and herpes zoster or shingles.
A unilateral throbbing headache that is aggravated by light, sound, or any movement is characterized as a
cluster headache
migraine headache
tension headache
sinus headache
what is (2) a migraine headache
Use of benzodiazepines is associated with a “rebound effect.” If an individual is experiencing “rebound anxiety,” this refers to:
an initial paradoxical increase in anxiety
anxiety persisting even after increasing dosage
anxiety re-appearing after long-term usage of the drug
an increase in severity of anxiety temporarily following the discontinuation of the drug
what is (4) an increase in severity of anxiety temporarily following the discontinuation of the drug
The mesencephalon (midbrain)is made of up of
what is
The area of the brain referred to as the “midbrain” is also known as the mesencephalon and is divided into two regions: the tectum and the tegmentum. The substantia nigra (a.) is located in the tegmentum and is part of the brain’s sensorimotor system. The inferior colliculus (c.) is part of the tectum and is involved in audition. The superior colliculus (d.) is also part of the tectum and mediates vision. The hypothalamus is located in the diencephalon. The diencephalon and the telencephalon make up the forebrain.
Cortisol is frequently used as measure of
what is stress
Cortisol is a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex, which is located near the kidneys. It stimulates the liver to convert fat and protein into glucose for energy. Under stress, cortisol level rises to provide the energy needed to cope with the stress. However, chronic stress results in chronically elevated levels of cortisol which is believed to cause several health consequences.
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) is a term used:
for clinical diagnosis of prenatal alcohol exposure
to describe the differentiation of effects between fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol effects
to describe the range of effects from prenatal alcohol exposure for conditions that have some but not all of the clinical signs of fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
to describe the range of effects from prenatal alcohol exposure
what is (4) to describe the range of effects from prenatal alcohol exposure
A patient who has recently suffered a stroke speaks only with great effort and uses two word sentences such as "eat dinner" to indicate he would like to eat his dinner. He is able to comprehend the speech of others well if they speak in simple sentences. He has weakness on the right side of the body and displays occasional outbursts of anger. The patient is most likely suffering from
what is bronca's aphasia
Broca's aphasia is caused by damage to an area of the left frontal lobe of the brain called Broca's area. It plays a role in the production of language
The ______ of the action potential from the axon hillock down the axon and to the presynaptic terminal results in release of chemical neurotransmitters that communicate with a postsynaptic neuron.
what is the propagation
Ultrasound techniques are least effective for detecting which type of traumatic brain injury?
shearing
tissue bruising
swelling
inter-cranial pressure (ICP)
what is (1) shearing
raumatic (physical) brain injuries are generally divided into three main types. The two more dangerous types are tissue bruising (b) and swelling (c), which cause tissues to swell and become compressed within the skull resulting in intercranial pressure (ICP). Shearing, or nerve fiber tearing, occurs from sudden impact of the brain with an object. Unlike tissue bruising and brain swelling, brain injury from nerve tearing is difficult to detect with ultrasound techniques such as x-rays, CT scans and MRIs which are most frequently used in traumatic brain injury cases. A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is more effective in the detection of nerve tearing injuries.
he neurotransmitter most directly related to voluntary muscle movement is
what is acetylcholine
Which of the following medications would MOST likely cause confusion?
fluoxetine
amitriptyline
sertraline
paroxetine
what is (2) amitriptyline
Compared to the SSRIs, the tricyclics are much more likely to cause anticholinergic effects. Confusion is one of several possible anticholinergic effects. Other anticholinergic effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention and tachycardia.
Tricyclics are a class of antidepressants used to treat mood disorders such as bipolar disorder, dysthymia, and major depressive disorder.
a rapid depolarization followed by the overshoot, when the membrane potential becomes positive
a rapid repolarization followed by the undershoot, when the membrane potential hyperpolarizes past rest
what is the rising phase and the falling phase

a time when a second action potential cannot be fired under any circumstances regardless of the strength of the stimulus. The voltage-gated sodium channels are either open (during the rising phase) or inactivated (during the falling phase).
what is the absolute refractory period