What is the smallest unit of life?
A Cell!
Monomers of carbohydrates are called:
Monosaccharides
Transport across the membrane using no energy
Passive Transport
What is the energy an object has due to its position or structure?
Potential Energy
According to Chargaff's rule, pair the following nitrogenous bases:
A, C, G, T
A-T
G-C
Many medical studies show that patients who receive a treatment feel better even if the treatment was an ineffective sugar pill. What is this phenomenon called?
Placebo
Water is the least dense when it is ________.
Frozen
Which organelle performs photosynthesis; converts sunlight to sugar
Chloroplasts
The pores on leaves where gas exchange occurs are called
Stoma/stomata
What are the two types of gametes?
Sperm and Egg
What is the first step of the scientific method?
Observation
Identify this process
Dehydration Synthesis
What is the high energy molecule that is a major product of cellular respiration
ATP
What is produced by your muscle cells when you can’t get oxygen to them quickly enough?
Lactic Acid
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
List the hierarchy of life, starting with the atom and proceeding to the biosphere.
(Atom), molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, (biosphere)
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
Lowering Activation energy
List the order of the organelles involved in the protein synthesis pathway
Nucleus
Ribosome
RER
Transport vesicle
Golgi
Transport Vesicle
Plasma Membrane
Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP by far?
Electron Transport Chain
Identify the phase of mitosis shown.
Metaphase
Name the 7 Properties of Living Things
1. Reproduction
2. Growth and development
3. Energy use
4. Order
5. Cell(s)
6. Response to the environment
7. Evolution
Identify this monomer, and state what macromolecule it forms.
Amino acid
Protein
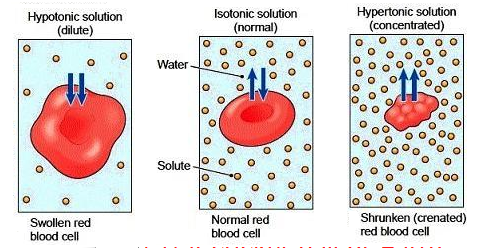
Draw an animal cell in a HYPERtonic solution. Indicate the relative concentrations of solute and water in the solution and in the cell, as well as the net flow of water.
Provide the balanced equation for photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Photo --> 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
CR --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Identify 2 major differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Mitosis: Involves one division, resulting in two daughter cells.
- Meiosis: Involves two divisions (Meiosis I and Meiosis II), resulting in four daughter cells.
- Mitosis: Maintains the chromosome number (diploid, 2n, 46 chromosomes).
- Meiosis: Reduces the chromosome number by half (haploid, n, 23 chromosomes).
- Mitosis: Produces genetically identical cells.
- Meiosis: Produces genetically diverse cells due to processes like crossing over and independent assortment.
- Mitosis: Occurs in somatic (body) cells.
- Meiosis: Occurs in germ cells to produce gametes.