An organism's ability to maintain a balanced internal environment despite changes to the external environment is called:
homeostasis
This is organism is what most scientists believe is the smallest unit of life:
the cell
Most enzymes end with these three letters ______
-ase
Name the four biomolecules we examined in class:
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids
This molecule contains WAY too much energy for the cell to use all at once, so it is often one of the first to be broken down to generate ATP:
glucose
Aerobic Cellular Respiration occurs in what organelle ______
mitochondria
A ______________ feedback loop will AMPLIFY a change, while a _______________ feedback loop will COUNTERACT or DECREASE the change to bring an organism back to homeostasis.
positive
negative
This organelle is often referred to as "the bouncer" of the cell because it decides what gets to come in and out of the cell:
cell membrane
In a chemical reaction, _____ are on the left side of the equation and represent the "inputs" of a system, and _______ are on the right side of the equation and represent the "outputs" of an equation.
reactants and products
What are the three main elements every biomolecule contains?
CHO: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
6 CO2 + 6H20 --> C6H1206 + 6O2
This the equation for what major process:
photosynthesis
Blood clotting rapidly forms a clot at the site of blood vessel injuries. This amplification of the response ensures that the bleeding is quickly controlled and the wound is sealed.
What type of loop does the following diagram show?
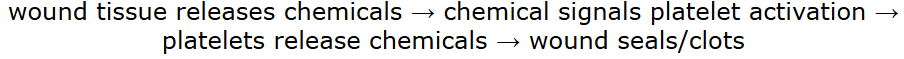
positive
Which cells lack a nucleus and have no membrane-bound organelles?
prokaryotes
The specific reactants upon which enzymes act are called _______. They fit the active sites of enzymes.
substrates
Name the monomers and polymers in carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides/simple sugars (glucose, candy, juices, etc)
Polysaccharides/complex sugars (starches, breads)
This pigment in chloroplasts absorbs all wavelengths of light EXCEPT green, which it reflects:
chlorophyll
Photosynthesis takes place in the ______ of cells.
chloroplasts
How do the respiratory system and cardiovascular system work together to maintain homeostasis in the body?
The cardiovascular system transports oxygen to the tissues and removes carbon dioxide, which the respiratory system then exchanges with the external environment.
This type of cell contains chloroplasts, has a rigid cell wall, and contains one large central vacuole responsible for containing water and other nutrients:
plant cell (eukaryote)
What two environmental factors can alter the shape (or denature) the active site of an enzyme?
heat and ph
The main function of this biomolecule is to store energy. Other important functions include providing insulation, making up cell membranes, and acting as chemical messengers that act as hormones
Lipids
In the ATP --> ADP cycle, these bonds are continuously broken (to release energy) and formed (to store energy):
phosphate bonds
Biomolecule that makes up the cell membrane, used for long term energy storage
Lipid
When body temperature rises, sweat glands release water to cool the body. What type of feedback loop is this?
negative
Unlike plant cells that contain chloroplasts, these cells cannot make their own food so cannot get energy from the sun. They instead have to get energy from food sources.
Animal cells
In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed - only rearranged, which demonstrates this major law of physics:
Law of conservation of matter
Enzymes are examples of this biomolecule ______. Enzymes act as catalysts that (slow down or speed up) chemical reactions.
-proteins
-speed up
The process of converting food energy into ATP in living cells is called: _______.
The chemical formula for aerobic respiration is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6H20 + _____ and ATP
6CO2
A chain of these make a protein
Amino acids
In childbirth, the hormone oxytocin causes stronger contractions, which release even more oxytocin. What kind of feedback is this?
Positive
reflected
The breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by the enzyme catalase produces water and oxygen gas. Catalase _________ the chemical reaction. (slows down, speeds up)
speeds up
After eating, which two systems coordinate to deliver nutrients and oxygen to muscle cells for energy?
digestive and circulatory
Endurance athletes rely on glycogen stored in this type of tissue to power long events.
muscle
During exercise, the respiratory system increases oxygen intake and the circulatory system speeds delivery. Is this an example of systems interactions that maintain homeostasis?
yes
Remember, according to a systems thinking perspective, homeostasis depends on communication between the receptors, the _____, and the effectors.
Name the body system responsible for detecting and processing sensory information from stimuli and activating bodily responses:
control center
nervous (central nervous system, peripheral nervous system)
Just like our body systems are made of organs, cells are made of _____________ like the nucleus, cell membrane, mitochondria, vacuole, etc.
organelles
In cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. What happens to the bonds during this process?
A. bonds are broken and rearranged to form new molecules
B. bonds add on additional molecules to grow bigger
A. bonds are broken and rearranged to form new molecules
When you eat tofu, your body breaks down proteins into these building blocks for repair and growth.
amino acids
During exercise, muscle cells break down glycogen into glucose. What form of energy does this reaction release?
ATP
True or False:Photosynthesis rates increases as the amount of light intensity and carbon dioxide increase (at least, up until a certain point).
true