What invention led to the discovery of Cell Theory?
The Microscope
Where is DNA stored in Eukaryotic Cells? (The Brain/White House of the cell.)
The Nucleus
Prokaryotes do not have which MAJOR organelle? (PRO=NO)
Nucleus
Meiosis results in...
Somatic Cells or Gametes?
Gametes.
2 genetically identical somatic cells or 4 genetically different gametes.
2 genetically identical somatic cells
What process causes cells to develop a specialized form and function?
Differentiation
The smallest unit of life (and can carry out all activities associated with life) is...
The cell.
If a toxic chemical destroys a cell ribosomes, which macromolecule could would that cell not be able to produce?
Protein
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotic Plant cells share a unique organelle that protects the cell and provides structure. What organelle is this?
Cell Wall
Meiosis results in...
4 genetically different haploid cells or 2 genetically identical diploid cells
4 genetically different haploid cells
The cell cycle is broken into 2 general parts: Interphase (G1, S, G2) & M-Phase. What are the 4 phases of M-Phase.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Which cells in the human body are considered diploid?
Somatic Cells
What are the two general types of cells and which appeared first on Earth?
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic. Prokaryotes evolved first.
Animal Cells and Plant Cells both have vacuoles. What is the difference between vacuoles in animal cells and plant cells?
Animals - Many small vacuoles. Plants - One large central vacuole.
Which organelle is composed to two layers of phospholipids associated with proteins that control what comes in and out of the cell?
Cell Membrane
If a diploid cell with 28 chromosomes goes through meiosis, how many chromosome would the resulting daughter cells have?
14
If a daughter cell has 16 chromosomes after Mitosis, how many chromosomes did the parent cell have?
16
Groups of cells that carry out a similar function are called?
Tissues
Place the following terms in the correct order of complexity in living things.
Organ, Tissue, Cell, Organ System, Organism
Cell > Tissue > Organ > Organ System > Organism
Animal cells are not able to perform photosynthesis. Which organelle do animal cells lack?
Chloroplasts.
What process is shown in the picture below?
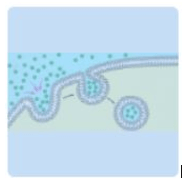
Endcytosis.
What 2 processes lead to genetic variation in meiosis?
Crossing Over & Independent Assortment.
Right after mitosis, the cytoplasm splits to create two identical cells. What is that process called?
Cytokinesis.
Where are totipotent stem cells found? This leads to ethical issues in stem cell research.
Embryos
What are the three parts of Cell Theory?
2. Cells are the basic unit of life.
3. Cells can only come from pre-existing cells.
Liver cells have a high metabolic rate - meaning they need a lot of energy to operate. Which organelle do Liver cells need a lot of?
Mitochondria
Which of the following organelles that help prokaryotic cells move around? Must select all!
Cytoplasm, Lysosomes, Pili, Flagella, Cytoskeleton, Endoplasmic Reticulum
Pili & Flagella
How is Metaphase I in meiosis different from Metaphase in mitosis?
Chromosomes align in pairs during metaphase I in Meiosis.
Chromosome align in a single file line during metaphase in Mitosis.
Perform the hand signals for Mitosis we reviewed in class.
PMAT > Cytokinesis
What are the 3 types of stem cells?
Totipotent = Can turn into all cells.
Pluripotent = Can turn into most cells.
Multipotent = Can turn into some cells.