1) A nucleotide consists of 3 parts. Name them.
A sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base.
15) tRNA carries an __________ on one side and an ____________ on the other.
anticodon; amino acid
5) What did Chargaff conclude from his experiments?
Chargaff concluded that the amount of adenine in a cell was equal to the amount of thymine and likewise for guanine and cytosine.
12) Name 3 differences between DNA and RNA.
DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded
DNA uses deoxyribose sugar, RNA uses ribose sugar
DNA uses thymine, RNA uses uracil.
4) Explain why DNA replication is considered semi-conservative.
One of the strands is “conserved” and used as a template to create another new strand.
18) Prokaryotic gene expression involves a ______________ and an operator, but eukaryotic gene expression involves several special proteins called __________________ ________________.
promoter; transcription factors
10) The process of forming an RNA strand from a DNA strand is called ___________. Where does it occur in the cell?
transcription; in the nucleus
JUST FOR FUN: Name this character from "The Amazing World of Gumball":

Darwin
14) A triplet of mRNA nucleotides is called a(n) _____________ and on tRNA is called a(n) _____________.
codon; anticodon
20) This segment of DNA (TGCAATGGC) needs to be transcribed. What is the resulting mRNA sequence?
ACGUUACCG
8) When cells copy their DNA before division, this process is called ______________. Where in the cell does it occur?
DNA replication. Occurs in the nucleus.
24) Give 2 examples of mutagens.
UV radiation, tobacco, chemicals, etc.
7) Why were Franklin’s, Avery’s and Hershey & Chase’s experiments important?
(From your Webquest)
Avery’s and Hershey and Chase’s experiments were important because they verified that DNA, not protein, carried the genetic information.
22) What type of chromosomal mutation is shown below?
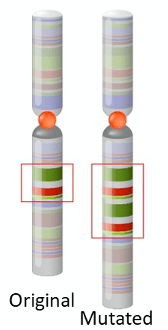
- Duplication
9) Examine this DNA strand:
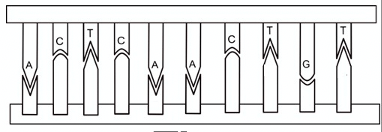
The complementary strand to this is:
TGAGTTGACA
21) Which is likely to cause greater disruption in the resulting protein: point mutations or frameshift mutations? Explain.
Frameshift- Rather than disrupting just one amino acid, it can disrupt a whole chain of them.
17) If a repressor is attached to the operator, will the gene be transcribed or not? Why or why not?
No because the repressor will block the RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter.
23) What type of chromosomal mutation is shown below?
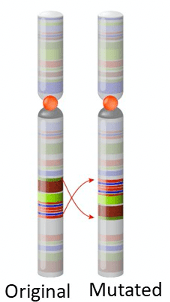
Inversion
11) List the 3 types of RNA and the job of each.
mRNA- carries a copy of the DNA to the ribosome
tRNA- plays matchmaker with mRNA codons and correct amino acids
rRNA- makes up ribosomes where translation occurs
19) In order for RNA polymerase to bind to eukaryotic DNA, what must the transcription factors do?
They must remove the coils in the DNA and cause it to relax.
3) List the function of each of these enzymes:
-DNA polymerase
-Helicase
DNA polymerase adds nitrogen bases during DNA replication.
Helicase unwinds the parent DNA strands during DNA replication.
13) The process of creating an amino acid chain from an mRNA strand is called _____________.
Where in the cell does this occur?
translation; in the ribosomes
6) How did Franklin, Watson, & Crick contribute to the structure of DNA?
Franklin determined that DNA was helical and Watson & Crick made the final double helix model with bases on the inside.
16) How do introns and exons differ?
Introns are removed during the final processing of the mRNA,
but exons remain to be used in protein synthesis.
2) What is the purpose of histones?
Histones allow long strands of DNA to be wrapped and organized into chromosomes without tangling.