1) Why do viruses like SARS-CoV2 produce variants so quickly?
They reproduce quickly, which allows mutations to form more rapidly in the copied DNA.
4) What are the 5 major points of Darwin’s theory?
- Variations exist within populations.
- Some variations are more favorable than others.
- More offspring are produced than survive.
- Individuals with greater fitness have a higher chance of survival (natural selection).
- Populations change over time.
8) How does genetic evidence point to natural selection?
Organisms have similar genes, which provides evidence that they are likely related by a common ancestor (ex: similarities can be seen in the Cytochrome C protein)
19) What are the 4 types of isolation that can cause speciation?
Geographical isolation, mechanical isolation, temporal isolation, or behavioral isolation.
24) What is the difference between a prezygotic barrier and a postzygotic barrier that causes speciation?
The prezygotic barrier prevents mating, while the postzygotic barrier occurs after mating because the zygote is not viable.
10) Explain why dark peppered moths had a greater survival rate during the industrial revolution. What phenomenon is this an example of?
There was a mutated gene that caused peppered moths to have the dark color. Because dark color helped the organisms camouflage and survive on the soot covered trees during the industrial revolution, they had greater survival rates. This is an example of natural selection.
6) Explain why bacteria continue to evolve & how this relates to a large number of antibiotics being on the market today.
Bacteria reproduce quickly and can easily swap genetic material through plasmids during conjugation. Mutated bacteria continue to reproduce and often have fitness against certain antibiotics. New antibiotics are needed to treat infections as the previous ones are not working.
15) A population with HIGH or LOW genetic diversity is better able to withstand environmental changes. What causes genetic diversity in a population?
High - Mutation creates a new phenotype; gene flow: passing of genes from a different population; sexual reproduction: genes are shuffled during meiosis
7) What does the similarity between these structures show about these organisms? What are these structures called?
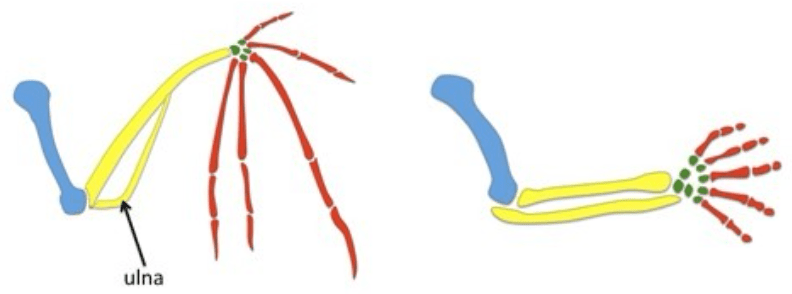
The similarity between the structures in these two organisms shows that the likely evolved from a common ancestor. They are called homologous structures.
22) Are all Great White Sharks part of the same gene pool? Why or why not?
Even though these sharks are of the same species, gene pools come from specific populations of sharks and populations are species found at a certain time in a certain place.
3) According to Darwin, what would cause finches to have different beak shapes?
Food sources available
21) Give an example of how a farmer would use and benefit from artificial selection.
A farmer could replant seeds from the tomato plants that grew the biggest tomatoes. This may help ensure that bigger tomatoes are grown in future crops
JUST FOR FUN: Darwin is known for his theory of evolution. This image shows the evolution of something we do every day in school; what is it?
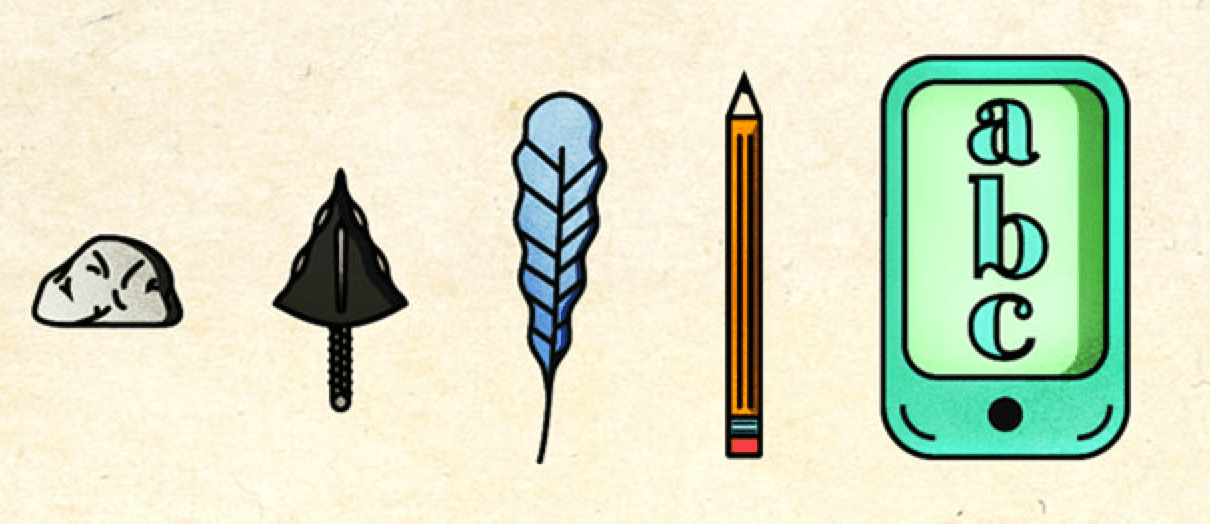

Writing!
14) Does natural selection act on genotypes or
phenotypes? Explain why.
Natural selection acts on phenotypes because they cause individuals to be suited to their environments with higher or lower fitness.
23) Why doesn’t a simple dominant trait (like free or attached earlobes) in a population show a normal distribution in a bell curve?
Because it does not have a range of phenotypes- it only has two. Normal distributions are caused by polygenic traits.
13) What is a gene pool?
A set of all the alleles within a population
5) Amoxicillin is a medicine prescribed for many different types of infections. What type of antibiotic is it?
Broad-spectrum antibiotic
16) Sketch a graph that shows how the bell curve changes for each of the following types of natural selection on polygenic traits:
Directional selection
Stabilizing selection
Disruptive selection
- Directional selection: the graph should shift to the left or the right as one extreme phenotype becomes better suited for the environment
- Stabilizing selection: the graph should be higher in the middle as the intermediate phenotype shows the best fitness
- Disruptive selection: the graph should decrease in the middle as the intermediate phenotype is the least fit
9) You have 5 solid cats (homozygous dominant) and 5 calico cats (heterozygous).
What is the allele frequency for the recessive allele?
Dominant allele?
20 total alleles, 5 are “c”, 15 are “C”.
5 “c” / 20 total alleles = .25
2) Explain the ideas that influenced Darwin from 2 of the following scientists:
• Malthus
• Hutton & Lyell
• Lamarck
- Malthus - populations outgrow their environments, causing some individuals to die, not all can survive
- Hutton & Lyell - uniformitarianism, changes on the earth's surface are the result of small changes over long periods of time
- Lamarck - traits an individual picked up during its lifetime could be passed onto offspring (failed theory)