smallest building block of life
cell
organelle that is the "powerhouse" of the cell
(stores energy as atp)
mitochondria
the part of the skeletal system that includes you skull, spine, and ribs. its function is to protect vital organs
axial skeletal system
thigh bone
femur
quadraceps
means closer to point of attachment
proximal
organelle that directs the cell by holding the "blueprints". represented by city hall
nucleus
this type of cell has a cell wall and one central large vacuole
plant cell
the part of the skeletal system that includes arms and legs. Its function is movement
appendicular skeletal system
finger and toe bones
phalanges
upper arm muscles that flex the arm
biceps
means farther from point of attachment
distal
The cell "highway" that contains ribosomes
rough endoplasmic reticulum
the structures on the rough ER (and scattered throughout the cell) that assemble proteins from the information brought to them by the mRNA
the "factories"
ribosomes
the hard, dense, smooth outer layer of bones that provides strength and protection
compact bone
collar bones
clavicles
upper arm muscles that extend the arm
triceps
front of body
ventral/anterior
storage areas of the cell
vacuoles
surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out of the cell. constructed of a 2 layers with a hydrophilic head and 2 hydrophobic tails.
cell membrane
a porous, lightweight bone tissue that provides strength and flexibility while reducing the weight of bones:
spongy bone
tail bone
coccyx
a large, triangular-shaped muscle located in the upper back and neck
trapezius
back of body
dorsal/posterior
the "waste disposal" area of a cell
lysosome
the dense structure within the nucleus that makes ribosomes
nucleolus
consists of bones or cartilage connected by a fibrous joint capsule and filled with fluid
synovial joint
shoulder blades
scapula
a broad, flat muscle located on the back
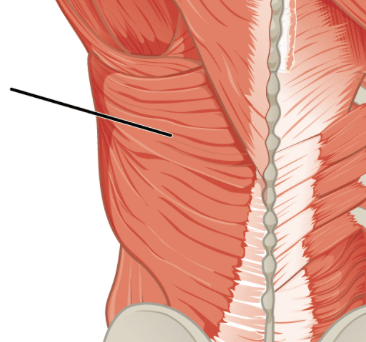
latissmus dorsi (lats)
brings closer to body
adduction