A student collects several plants and pebbles from a riverbank, places them in an aquarium, and records observations for 15 days. The sizes of the plants increase, while the sizes of the pebbles remain the same. The student classifies the pebbles as nonliving things.
Which criteria does the student use as the basis for the classification?
A. Ability to grow
B. Ability to reproduce
C. Ability to move
D. Ability to respond to stimuli
A. Ability to grow
The element _______is found in all of the organic compounds.
A. Iron
B. Carbon
C. Nitrogen
D. Oxygen
B. Carbon
Which statement describes differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Prokaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and mobile.
B. Prokaryotic cells have circular DNA inside a nucleus.
C. Eukaryotic cells are less complex with fewer organelles.
D. Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles.
D. Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles.
Examine the structures in the diagram.

What is shown in the area labeled Z?
A. Carrier proteins
B. Phospholipid bilayer
C. Phosphorous bilayer
D. Receptor proteins
B. Phospholipid bilayer
Which process must take place before mitosis can occur properly?
A. Active transport
B. Aerobic respiration
C. DNA replication
D. Protein synthesis
C. DNA replication
Robert Hooke observed cork tissue from a plant using a microscope and saw small, honeycomb-like structures, as shown in the image.
What contribution did Hooke make to biology based on his observations?
A. He named the small structures organelles.
B. He named the small structures cells.
C. He stated that all cells come from preexisting cells.
D. He stated that every living thing is made up of more than one cell.
B. He named the small structures cells.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
A. store genetic information
B. store energy (long-term)
C. store energy (short-term)
D. build skin, hair, nails, muscles
A. store genetic information
Which organism listed below is prokaryotic?
A. Bacteria
B. Cat
C. Fungi
D. Grass
A. Bacteria
DOUBLE POINTS!!!
The diagram shows the exchange of gases between the cells in the alveoli of the lungs and the red blood cells in the capillaries.

What process is taking place?
A. active transport
B. diffusion
C. facilitated diffusion
D. osmosis
B. diffusion
The process of mitosis occurs in all organisms, though the process can be slightly different among different species.
Based on observations of this image, in what type of organism is mitosis occurring?
A. Bacteria
B. Plant
C. Mammal
D. Reptile
B. Plant
Which sequence represents increasing complexity in humans?
A. ovary → egg cell → uterus
B. muscle cell → cardiac tissue → heart
C. stomach → liver → gall bladder
D. white blood cell → red blood cell → blood
B. muscle cell → cardiac tissue → heart
DOUBLE POINTS!!!
Which statement defines a function of carbohydrates in the human body?
A. They transport substances to different parts of the body.
B. They are the primary source of energy for cellular respiration.
C. They accelerate the speeds of chemical reactions in the body.
D. They compose hormones that regulate the sugar content in the body.
B. They are the primary source of energy for cellular respiration.
Which statement differentiates plant cells from animal cells?
A. Cytoplasm allows nutrients and raw materials to move throughout the cell.
B. Cell walls composed of cellulose provide structure and support.
C. Cell membranes maintain the shape and control the flow of materials into and out of the cell.
D. Ribosomes found on the ER function in the production of proteins for the cell.
B. Cell walls composed of cellulose provide structure and support.
Examine the diagram that shows a container divided into sections by a semi-permeable membrane.

Over time, the concentration of water molecules will balance on either side of the semi-permeable membrane. By what process will that happen?
A. active transport
B. cellular communication
C. osmosis
D. specialization
C. osmosis
A student observed onion cells in various stages of cell division. The results of two samples are shown in the table.

Which statement best explains why more cells were seen in the interphase stage?
A. The onion cells in the sample were not dividing when cells were counted.
B. Interphase is the longest stage of the cell division process.
C. The onion cells were mutating instead of dividing.
D. The student did not count enough cells to find other stages of cell division.
B. Interphase is the longest stage of the cell division process.
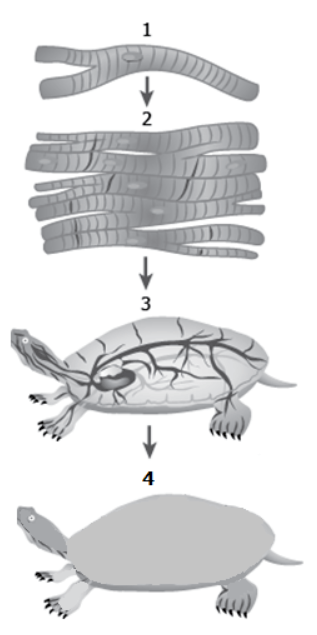 The image shows a model made to represent levels of cellular organization in a tortoise. A level of organization is missing in the model.
The image shows a model made to represent levels of cellular organization in a tortoise. A level of organization is missing in the model.
Which level of organization will complete the model?
A. Cellular level needs to be added before 1.
B. Tissue level needs to be added after 1.
C. Organ level needs to be added after 2.
D. System level needs to be added before 3.
C. Organ level needs to be added after 2.
Which compound is organic?
A. O2 is organic because it contains oxygen.
B. N2O3 is organic because it contains nitrogen.
C. H2O is organic because it contains hydrogen and oxygen.
D. C6H12O6 is organic because it contains hydrogen and carbon.
D. C6H12O6 is organic because it contains hydrogen and carbon.
With which cellular process are ribosomes directly involved?
A. doubling genetic material before cell division
B. producing cellular energy molecules from glucose
C. synthesizing structural and functional proteins
D. separating sister chromatids during cell division
C. synthesizing structural and functional proteins
A molecule is transported by both active and passive transport within a cell. The presence of which other molecule distinguishes active transport from passive transport?
A. ATP
B. Cellulose
C. Glucose
D. NaCl
A. ATP
The diagram shows the process of budding in yeast.
A student claims that budding is similar to mitosis. Which evidence supports the student’s claim?
A. The new cells are genetically identical to the parent cell.
B. The cytoplasm is divided equally in the new cells.
C. The DNA replicates at the end of both processes.
D. The processes increase genetic variation.
A. The new cells are genetically identical to the parent cell.
DOUBLE POINTS!!!!
Which organism could be considered nonliving because it cannot carry out all the functions of life on its own as described in the cell theory?
A. A virus
B. A multicellular algae
C. A unicellular algae
D. A prokaryote
A. A virus
What relationship exists between amino acids and proteins?
A. Amino acids are made up of proteins.
B. Proteins are made up of amino acids.
C. Proteins and amino acids bond to form polypeptides.
D. Proteins and amino acids are both inorganic compounds.
B. Proteins are made up of amino acids.
The organelle shown consists of a stack of flattened membranes.

What is the primary function of this organelle?
A. attaching amino acids to tRNA molecules
B. long-term storage of molecules in the cell
C. production of large and small ribosomal subunits
D. repackaging proteins for export from the cell
D. repackaging proteins for export from the cell
The diagram shows four types of transport.

Which process requires energy and is necessary for maintaining homeostasis?
A. J
B. K
C. L
D. M
D. M
The diagram shows a cell in different stages of mitosis.

Which stage represents the events taking place during anaphase of mitosis?
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
B. Stage 2
Which statement best explains why viruses are considered to be nonliving?
A. They are only able to be viewed with a microscope.
B. They are unable to reproduce independently.
C. They lack genetic material.
D. They have different types of proteins.
B. They are unable to reproduce independently.
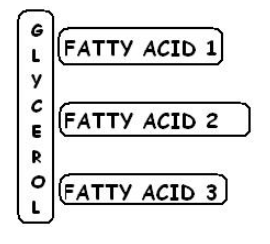 What is a function of this molecule in animals?
What is a function of this molecule in animals?
A. DNA nucleotide component
B. control insulin production
C. long-term energy storage
D. regulate gene expression
C. long-term energy storage
DOUBLE POINTS!!
The diagram shows an animal cell.
If the structure labeled X were to stop functioning properly, how would that immediately impact the cell?
A. The cell would not be able to produce ATP to meet its energy needs.
B. The cell would not be able to produce the proteins necessary for life.
C. The cell would not be able to get oxygen and nutrients from its environment.
D. The cell would not be able to transport mRNA from the nucleus to the ribosome.
C. The cell would not be able to get oxygen and nutrients from its environment.
What is the advantage of homeostasis?
A. It allows organisms to live in a range of environments.
B. It allows organisms to avoid a variety of predators.
C. It allows organisms to blend into their environment.
D. allows organisms to reproduce at a faster rate.
A. It allows organisms to live in a range of environments.
The diagram shows a microscopic view of a cell undergoing division.
Which statement is correct about the cell shown?
A. A plant cell is in cytokinesis with a cell plate forming.
B. An animal cell is in cytokinesis with a cell plate forming.
C. A plant cell is in anaphase with sister chromatids moving to opposite ends of the cell.
D. An animal cell is in anaphase with sister chromatids moving to opposite ends of the cell.
A. A plant cell is in cytokinesis with a cell plate forming.
Research provides evidence that the HIV virus requires a host to carry out its metabolic activities. Which evidence supports that the HIV virus is nonliving?
A. It has complicated DNA.
B. It has complicated structures.
C. It lacks food-producing or energy-producing cell organelles.
D. It lacks the genetic material needed to create more viruses.
C. It lacks food-producing or energy-producing cell organelles.
The breakdown of complex carbohydrates into glucose is completed in the small intestine during digestion. What protein acts as a catalyst to speed up the reaction?
A. cellulose
B. enzyme
C. hormone
D. steroid
B. enzyme
A cell biologist analyzed four different cells that had varying numbers of each type of organelle.
Based on the numbers of the four types of organelles listed in the table, which cell should the cell biologist hypothesize is most likely to produce the highest number of proteins for export from the cell?
A. Cell 1
B. Cell 2
C. Cell 3
D. Cell 4
A. Cell 1
Examine the movement of particles across the cell membrane.
What is the name for this type of transport of materials?
A. Facilitated diffusion
B. Pinocytosis
C. Phagocytosis
D. Simple diffusion
A. Facilitated diffusion
The diagram shows the relative length of each phase of the cell cycle in sequence beginning with the letter W.

Which phase of this diagram corresponds to mitosis?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
A. W
Hydra are small, multicellular organisms that live attached to the bottom of small ponds and slow-moving streams. They have the ability to respond slowly to their environments using a collection of nerve cells that work together to form a simple nerve net.
What level of organization best describes a hydra’s nerve net?
A. Cell
B. Organ
C. Organ system
D. Tissue
D. Tissue
Examine the pH data in Tables 1 and 2.
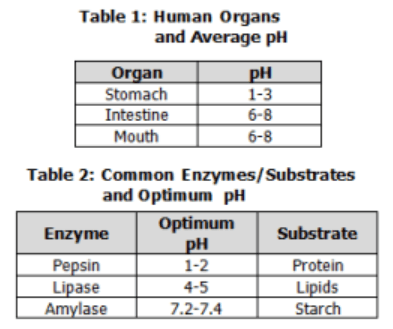
What can be inferred about the effectiveness of enzymes?
A. Enzymes have specific substrates and work best in any pH.
B. Enzymes do not have specific substrates and work best in any pH.
C. Enzymes have specific substrates, so they work best within a small range of pH.
D. Enzymes do not have specific substrates, so they work best within a small range of pH.
C. Enzymes have specific substrates, so they work best within a small range of pH.
The table shows the structures found in an unknown cell and the percent of the total cell mass each structure comprises.
Based on the information provided, what can be concluded about the unknown cell?
A. Since the cell lacks a cell wall, it must be a plant cell.
B. Since the cell lacks chloroplasts, it cannot be a prokaryotic cell.
C. Since the cell has mitochondria and DNA, it must be a eukaryotic cell.
D. Since the cell has a cell membrane and DNA, it cannot be an animal cell.
C. Since the cell has mitochondria and DNA, it must be a eukaryotic cell.
Cells use a variety of methods to move essential materials across biological membranes.
What process helps to move the molecules shown in the diagram across the membrane?
A. Facilitated diffusion
B. Active transport
C. Osmosis
D. Simple diffusion
B. Active transport
The table shows the lengths of the cell cycle for different types of cells in the human body.
Which type of cell is most likely lost at the fastest rate in the human body?
A. Trachea
B. Taste buds
C. Red blood
D. Stomach
D. Stomach
Why do multicellular eukaryotes need to regulate the genes that are expressed at any given time?
A. If they all expressed everything, they would not have enough mRNA.
B. It allows the cells to specialize and form more complex tissues.
C. That is the only way they can determine what DNA has been damaged.
D. There is a limited amount of protein that can fit in a cell at a time.
B. It allows the cells to specialize and form more complex tissues.
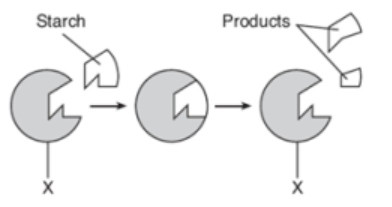 Use the diagram to answer the question.
Use the diagram to answer the question.
Molecule X is most likely what type of compound?
A. carbohydrate
B. lipid
C. nucleic acid
D. protein
D. protein
A student lists several characteristics of viruses in a table.
Which characteristic(s) differentiate(s) viruses from cells?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 4
D. 2 and 4
The image shows three samples of red blood cells placed in different solutions. Sample Q shows the cells in their normal blood plasma solution.
Which statement must be true about the cells?
A. Sample P was placed in a concentrated salt water solution, and sample S was placed in a concentrated sugar solution.
B. Sample P was placed in a concentrated salt water solution, and sample S was placed in distilled water.
C. Sample S was placed in a concentrated salt water solution, and sample P was placed in distilled water.
D. Sample S was placed in a concentrated salt solution, and sample P was placed in a concentrated sugar solution.
B. Sample P was placed in a concentrated salt water solution, and sample S was placed in distilled water.
DOUBLE POINTS!!
The diagram shows the chromosome number during mitosis.

How is mitosis important in the reproduction of organisms?
A. Mitosis ensures the chromosome number of the daughter cells is identical to the parent cells, allowing unicellular organisms to reproduce identical offspring sexually.
B. Mitosis ensures the chromosome number of the daughter cells is half that of the parent cells, allowing unicellular organisms to reproduce more diverse offspring sexually.
C. Mitosis ensures the chromosome number of the daughter cells is identical to the parent cells, allowing unicellular organisms to reproduce identical offspring asexually.
D. Mitosis ensures the chromosome number of the daughter cells is half that of the parent cells, allowing unicellular organisms to reproduce more diverse offspring asexually.
C. Mitosis ensures the chromosome number of the daughter cells is identical to the parent cells, allowing unicellular organisms to reproduce identical offspring asexually.
 When a human egg is fertilized by a sperm, the resulting zygote begins the process of cell division that eventually results in an organism with trillions of cells. The image shows a mass of human cells at the eight-cell stage, shortly after fertilization.
When a human egg is fertilized by a sperm, the resulting zygote begins the process of cell division that eventually results in an organism with trillions of cells. The image shows a mass of human cells at the eight-cell stage, shortly after fertilization.
What properties do these eight cells have?
A. They are already differentiated cells, each containing the same DNA but with only certain parts activated depending on the cell’s ultimate fate.
B. They are already differentiated cells, each containing slightly different combinations of DNA but with the potential to become any cell type in the body.
C. They are undifferentiated cells, each containing the same DNA having the potential to become any cell type in the body.
D. They are undifferentiated cells, each containing slightly different combinations of DNA depending on their ultimate fate in the body.
C. They are undifferentiated cells, each containing the same DNA having the potential to become any cell type in the body.
What determines the specific reaction that an enzyme will catalyze?
A. the sequence of amino acids and the shape of the protein
B. the sequence of amino acids and the shape of the lipid
C. the sequence of fatty acids and the shape of the lipid
D. the sequence of fatty acids and the shape of the protein
A. the sequence of amino acids and the shape of the protein
A student is studying a cell under a microscope using Gram stain and fuchsin stain. The table shows the color that each stain gives to the cell parts.

The student observes that the cell is stained purple and has no trace of magenta. The student concludes that the cell is a prokaryotic cell.
What scientific knowledge supports the conclusion made by the student?
A. Prokaryotic cells absorb stains quickly.
B. Only prokaryotic cells have a cell wall.
C. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles.
D. Only prokaryotic cells intake energy from the outside environment.
C. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles.
Analyze the table to answer the question.
In which of the solutions in the table would a cell with a composition of 50% solute and 50% solvent experience the greatest movement of water into the cell?
A. W
B. X
C. Y
D. Z
A. W
The table describes the events of mitosis out of sequence.

Which sequence accurately summarizes the process of mitosis from beginning to end?
A. Y W Z X
B. Y Z W X
C. X Y W Z
D. X W Z Y
B. Y Z W X











