What is the main structure of the cell membrane called?
The phospholipid bilayer
Movement of molecules without energy is called what?
Passive Transport
What type of solution is the highlighted cell in?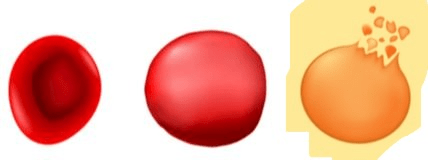
Hypotonic Solution
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
To regulate what enters and leaves the cell, maintaining homeostasis
The cell membrane is often compared to what in real life?
A security gate or selective barrier
Which is the hydrophilic part and hydrophobic part?
Hydrophilic = heads, Hydrophobic = tails
Is this active or passive transport?
Passive transport (facilitated diffusion)
What type of solution are these highlighted cells in?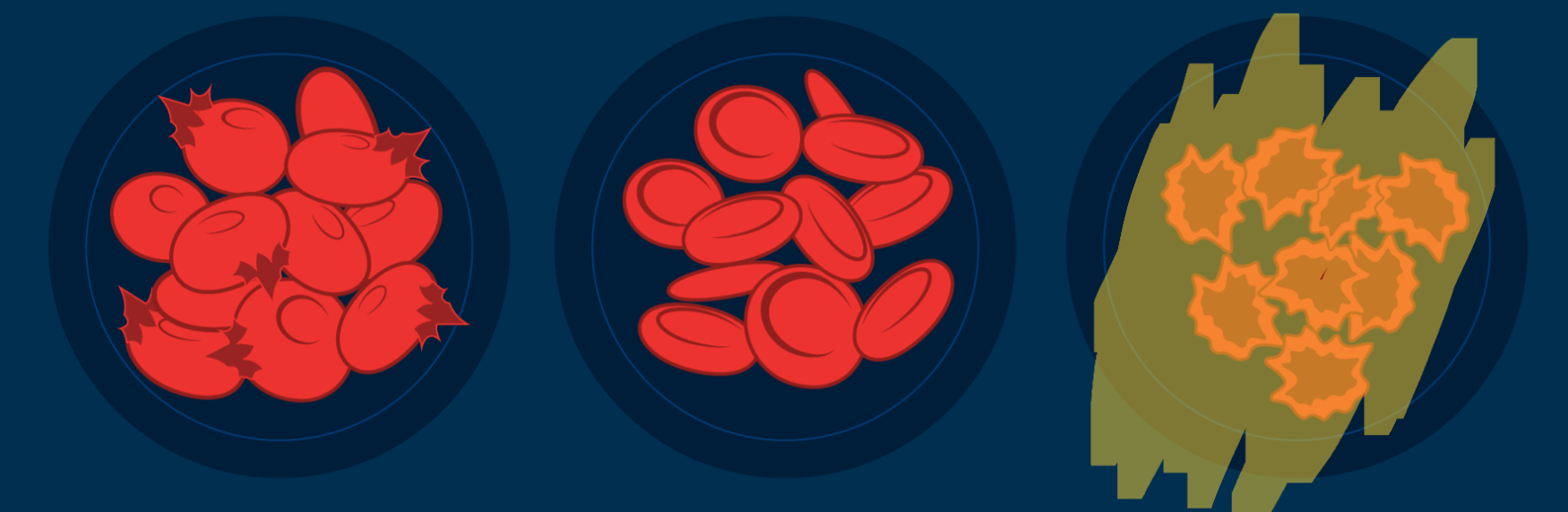
Hypertonic Solution
What characteristic of life does the image represent in the cell?
The balance of internal conditions (homeostasis)
What process is being shown?
Exocytosis
Which type of molecule helps stabilize the membrane’s flexibility?
Cholesterol
Movement of water across a membrane is called what?
Osmosis
A cell placed in a solution with equal solute inside and out will…?
Stay the same size (isotonic)
Give an example of how cells maintain balance in solute concentrations.
Using active transport or osmosis to adjust levels inside and outside the cell
Q: What might happen if all cell membranes became fully permeable?
The cell would lose control of balance and die
WHat type of protein is below?
What type of transport is this? 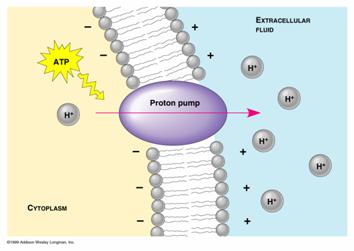
Active Transport
Why does water move toward a hypertonic solution?
Because there is a higher solute concentration there; water moves to balance it out.
What happens if a cell cannot regulate transport correctly?
It may swell, shrink, or die (loss of homeostasis)
How does the sodium-potassium pump move ions (directions & energy use)?
Pumps sodium out and potassium in, using ATP energy
Explain the “fluid mosaic model” of the cell membrane.
The membrane is flexible, with proteins and lipids floating and moving within it like a mosaic.
What is the difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport?
Facilitated diffusion uses proteins but no energy; active transport uses proteins and energy (ATP).
Which way do sodium and potassium ions move in the sodium-potassium pump?
3 sodium ions move out, 2 potassium ions move in (using ATP).
How does active transport help maintain homeostasis?
It moves molecules against gradients to keep proper internal balance
What are all the colors you could get in a package of gummy bears?
Red,yellow,green,orange,clear