Define taxis and give one example in animals.
Taxis is a directional movement of an organism in response to a stimulus.
Ex. Worms move to darker areas
What is a biological rhythm?
A biological rhythm is a regular, cyclic pattern of behaviour or physiological activity controlled by an internal biological clock (endogenous) and influenced by external cues (exogenous).
What is mutualism? Give an example.
Mutualism is an interspecific relationship where both species benefit.
Ex. Cleaner fish remove parasites from larger fish (cleaner gains food, host fish reduces parasite load).
What is an intraspecific relationship?
An interaction between members of the same species, often linked to cooperation, competition, reproduction, or social organisation.
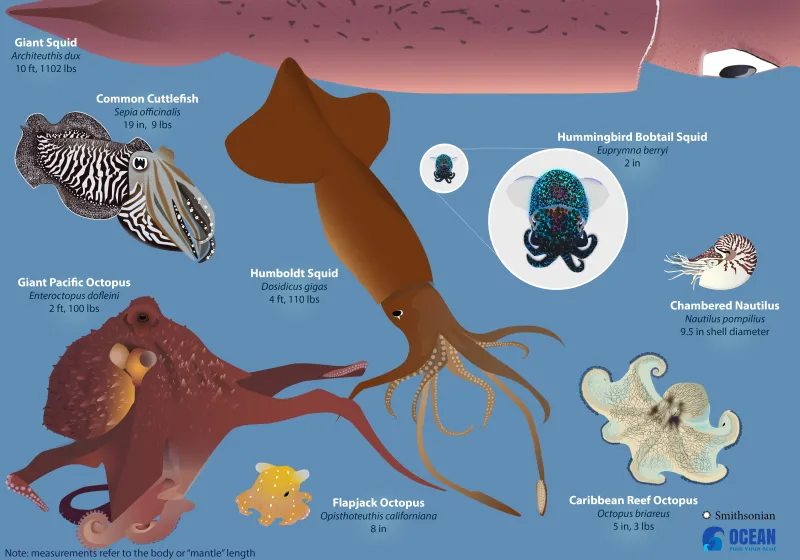
What is a cephalopod?
A predatory mollusc. Literally means 'head foot'.
Squids, octopuses, and cuttlefish
How does kinesis differ from taxis?
Kinesis is a non-directional response where the rate of movement changes depending on stimulus intensity.
Define circadian rhythm and give an example.
A circadian rhythm is an approximately 24-hour cycle in the behaviour or physiology of an organism. Example: Sleep–wake cycle in humans, or leaf opening and closing in bean plants.
How does mutualism provide an adaptive advantage to the species involved?
Mutualism increases survival and/or reproductive success by improving access to resources, protection, or reproduction.
What is an agonistic behaviour? Give an example.
Agonistic behaviour is a contest between members of the same species, usually involving threat displays rather than lethal fighting.
Ex. Red deer stags locking antlers during rutting season.
What is the scientific name of slaters?
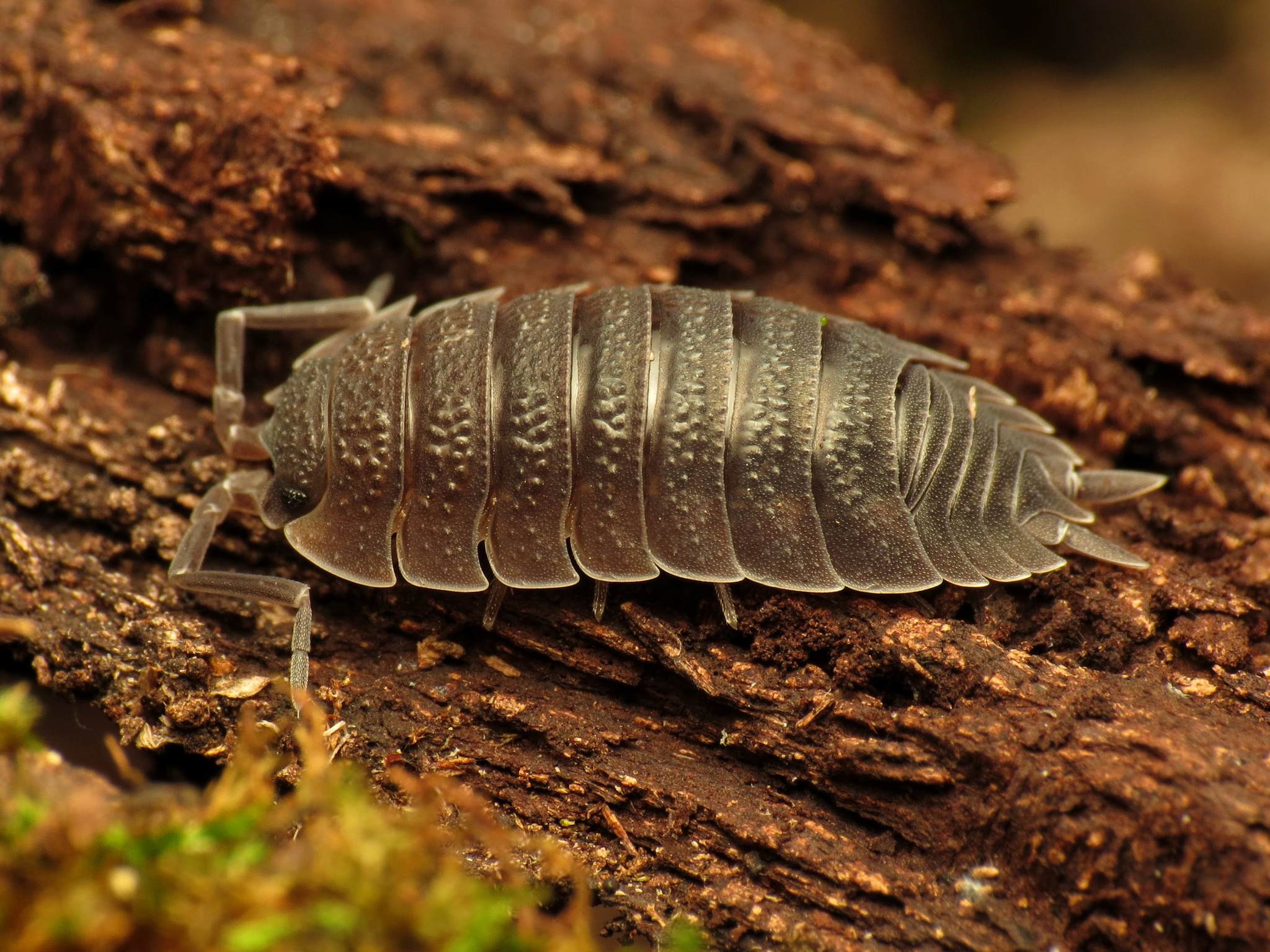

Porcellio scaber
What is positive chemotaxis and how can it be beneficial?
Positive chemotaxis is the movement towards a chemical stimulus- it can increase the chance of reproduction or finding food.
What is a zeitgeber and why is it important?
A zeitgeber is an external environmental cue (e.g., light, temperature, tides) that entrains or resets the biological clock to synchronise rhythms with the external environment.
Define exploitation and describe its three main forms.
Exploitation is an interspecific relationship where one species benefits at the expense of another.
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Herbivory
Explain these mating systems:
- monogamy
-polygyny
-polyandry
Monogamy- one mate
Polygyny- one male and many females
Polyandry- one female and many males
In Finding Nemo, Marlin and Dory get trapped inside the whale during a big feed. Why does a blue whale (the largest animal in existence) eat tiny krill?

Energy efficient! They can eat huge amounts of calories without having to 'hunt'.
Orthokinesis: change in speed of movement in relation to stimulus intensity (slaters moving faster in dry areas)
Klinokinesis: change in turning rate in relation to stimulus intensity (flatworms turning more often in bright light)
What is the difference between endogenous and exogenous control of rhythms?
Endogenous: driven by an internal biological clock, persists in constant conditions (e.g., free-running circadian rhythm in constant darkness).
Exogenous: controlled by external cues (zeitgebers) that reset/synchronise the internal clock.
Explain how predation can act as a selection pressure on prey populations.
Predation favours prey with better defences (camouflage, speed, toxins). Over time, these traits increase in frequency, leading to evolutionary change.
Give an example of communication within a species and explain its role.
Honeybees use the waggle dance to communicate food location to colony members. This ensures efficient resource gathering, benefiting colony survival.
What are the three main colours of algae?
Red, green, and brown
What is homing and what does an animal use to 'home'?
Homing is the ability to return to a specific location.
Animals can use landmarks, solar compasses, magnetic field, etc...
Define free-running rhythm and explain what it shows about biological clocks.
A free-running rhythm occurs when an organism is kept in constant conditions without zeitgebers, showing that rhythms are internally generated. It demonstrates the existence of an endogenous clock.
Give an example of a plant adaptation against herbivory and explain its advantage.
Lancewood have spiky leaves to deter moa from eating it. This helps the plant survive and reproduce successfully.
Define territory and explain its adaptive advantage.
A territory is an area actively defended by an individual or group against others of the same species. It reduces competition for resources (food, nesting sites, mates), ensuring sufficient resources for the defender’s survival and reproduction.
In Finding Nemo- Marlin cleans himself in a sea anemone. What type of relationship is this?
Mutualistic relationship.
Anemone- benefitting by eating the parasites.
Marlin- getting a good clean
How would an environmental cue trigger migration in animals?
Environmental cues like changes in day length, temperature, or food availability trigger hormonal changes that initiate migration.
How does photoperiodism affect flowering in plants?
Short-day plants flower when nights are longer than a critical length.
Long-day plants flower when nights are shorter than a critical length.
This ensures reproduction occurs in favourable seasons.
What is interspecific competition? Give an example.
Interspecific competition occurs when two species compete for the same limited resource.
Ex: Barnacles competing for space on rocky shores.
Contrast monogamous and polygamous mating systems and their adaptive advantages.
Monogamy: one male and one female pair bond, often where offspring need prolonged parental care (advantage = higher survival of young).
Polygamy: one individual mates with multiple partners, often where little parental care is needed (advantage = maximised reproductive output).
What is the main difference between a mammal and a marine mammal?
Marine mammals rely on the ocean for survival (food or habitat)
What is the difference between migration and homing?
Migration is a large-scale, seasonal, long distance movement, homing is returning to a home site.
Explain why photoperiods are a more reliable zeitgeber than temperature for plants.
Day length is consistent and predictable each year, whereas temperature varies unpredictably. Using photoperiods ensures that plants time flowering and seed production reliably with the seasons.
What is the competitive exclusion principle?
The competitive exclusion principle states that two species cannot occupy the same niche indefinitely.
One will outcompete the other, leading to extinction or niche differentiation.
How do dominance hierarchies reduce conflict within a group?
Hierarchies establish a ranking system where only the dominant individuals access resources first. Subordinates recognise signals of dominance, reducing the need for constant fighting and saving energy.
In Finding Nemo- Crush uses the East Australian Current to travel. What type of mass movement is this and why would Crush want to do it?

Migration! North- warmer water for breeding. South- colder water, more nutrient rich for feeding.

List three navigational methods used in migration and provide examples for each.
Solar navigation (sun compass)- ex. monarch butterflies
Stellar navigation- birds using constellations at night
Magnetic navigation- turtles to locate nesting beaches
How do animals use circannual rhythms, and what is an adaptive advantage?
Circannual rhythms are yearly cycles (e.g., migration, hibernation, breeding seasons). They allow animals to prepare in advance for seasonal changes, ensuring survival and reproductive success.
Explain how interspecific competition can lead to evolutionary divergence.
To reduce competition, species may evolve different niches (resource partitioning).
Ex. Darwin’s finches evolved different beak sizes to exploit different food sources.
Explain the role of courtship behaviour in reproductive success.
Courtship allows individuals to recognise members of their own species, assess mate quality, and synchronise mating behaviour. This prevents wasted energy on unsuccessful or cross-species mating.
In Finding Nemo- the minnows all move together in a big group. How is this beneficial?

Safety in numbers, protection by being in a larger group.
Why is migration an adaptive advantage?
Migration allows organisms to exploit seasonal resources, avoid harsh climates, reduce competition, increase reproductive success, etc.
Kinesis is usually studied in spatial orientation, but how can it relate to time-based behaviours?
Kinesis can be influenced by rhythmic cycles in the environment. For example, woodlice may increase movement (orthokinesis) during dry periods of the day but reduce activity at night when humidity is higher.
Contrast the adaptive advantages of parasitism and mutualism from the parasite’s perspective.
Parasitism: Energy-efficient (parasite relies on host for food/shelter) but risks host death.
Mutualism: Stable, long-term relationship as both partners benefit, reducing risk of host extinction.
Why is dominance behaviour adaptive in a group?
It establishes clear roles, reducing conflict and injury, and ensures resources and mates go to the strongest individuals. This improves genetic quality and stability of the group.
In Finding Nemo- Bruce the shark is a 'vegetarian'. In reality, sharks are _________. If they were vegetarian, how would their teeth look different?
Carnivores.
Some of their teeth would be flat molars to grind plant material.
A bird species migrates annually from the Northern Hemisphere to the Southern Hemisphere. Explain how both innate behaviour and learning contribute to successful migration.
Innate behaviour provides the basic instinct to migrate and a general direction.
Learning/refinement through experience (e.g., using landmarks, improving flight routes) enhances efficiency and survival.
A researcher keeps birds in constant dim light. Their circadian activity pattern drifts later each day. What does this show?
This shows the birds have an endogenous circadian clock (free-running in absence of zeitgebers). Without light as a zeitgeber, their rhythm is not synchronised with the 24-hour day and drifts.
How can exploitation (predation or parasitism) increase biodiversity at the ecosystem level?
By controlling population sizes of prey/hosts, exploitation prevents one species from dominating resources, maintaining community balance and promoting biodiversity.
How can cooperative behaviour in rearing young increase survival rates?
Group members help care for offspring by guarding and feeding them. Shared parental investment increases the chances of young surviving to adulthood, benefiting group fitness.
In Finding Nemo- Nemo gets a ride to school on a manta ray. What type of relationship is this?

Commensalism- Nemo is benefitting by getting a free ride, the manta ray is not affected.