What element being present determines if a molecule is classified as organic?
CARBON
at least one carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
What does Mono mean?
one
The meaning of the prefix poly.
What is many?
An example of nucleic acid.
What is RNA or DNA or ATP?
diffusion that takes no energy
passive diffusion
The function of the Nucleic Acid biomolecules.
provide directions to build proteins. Pass on genes
The monomer for carbohydrate.
What is monosaccharide?
The polymer for carbohydrate.
What is polysaccharide?
2 examples of a lipid.
What is fats, oils, or steroids?
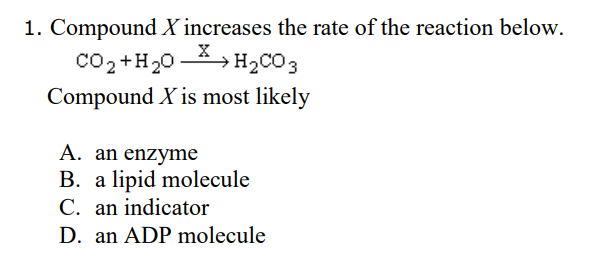
A enzyme
The purpose of carbohydrate biomolecules.
quick, easily available energy, fuels the brain, chitin, cellulose walls
What is fatty acid chain?
What is phospholipids?
Name an example of a polysaccharide.
What is glycogen, starch, cellulose, or chitin?
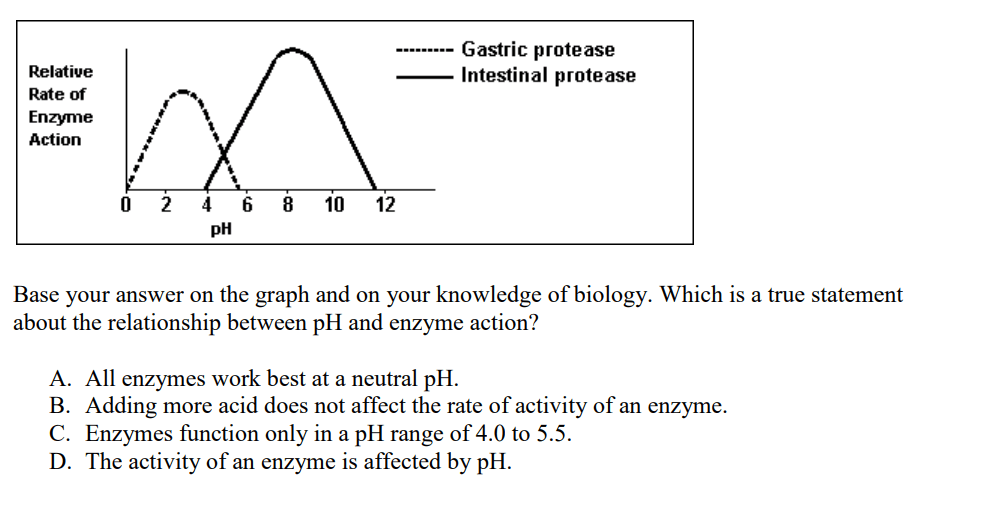
D
The purpose of lipid biomolecules.
long-term energy storage, insulation, steroids
The monomer for nucleic acid.
What is nucleotide?
The polymer for proteins. (can you draw it?)
What is polypeptides/ amino acid chains
Name the type of protein responsible for speeding up chemical reactions protein.
What is enzyme?
what is the energy molecule cells use for active transport?
ATP
The function of Proteins
cellular structure, speed up reactions, cellular communication etc
The monomer for protein.
What is amino acid?
The polymer for nucleic acid?
Nucleotide, Phosphate, sugar and nitrogen base
A steroid is an example of what type of biomolecule?
What is a lipid?
Give an example of Claim -> Evidence -> reasoning to solve a problem you had this morning
car wouldn't start, needed breakfast, wanted to get to school on time, etc.