The function of the Nucleic Acid biomolecules.
provide directions to build proteins
The monomer for carbohydrate.
What is monosaccharide?
The polymer for carbohydrate.
What is polysaccharide?
An example of nucleic acid.
What is RNA or DNA or ATP?
A and B are both...

monosaccharides
The function of Proteins
The monomer for lipid.
What is fatty acid chains and glycerol?
The polymer for lipid.
What is glycerol and fatty acid chains?
An example of a good lipid.
What is unsaturated fatty acids?
What is this and to what group of biomolecules does it belone?

triglyceride, lipids
The purpose of lipid biomolecules.
long-term energy storage, insulation
The monomer for protein.
What is amino acid?
The polymer for proteins.
What is polypeptides?
Name an example of a polysaccharide.
What is glycogen, starch, cellulose, or chitin?
What is this monomer and what group of biomolecules does it belong?

nucleotide, nucleic acids
The purpose of carbohydrate biomolecules.
quick, easily available energy
The monomer for nucleic acid.
What is nucleotide?
The polymer for nucleic acid?
What is DNA or RNA?
Name the type of protein responsible for speeding up chemical reactions protein.
What is enzyme?
Name this monomer and its polymer?
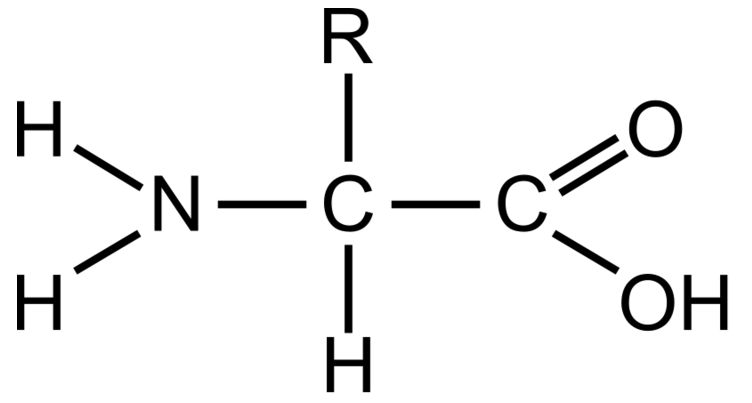
What is amino acid and protein?
What determines of a molecule is classified as organic?
at least one carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
The meaning of the prefix mono.
What is one?
The meaning of the prefix poly.
What is many?
A steroid is an example of what type of biomolecule?
What is a lipid?
What group of biomolecules would this belong to?

nucleic acid
CHONP