What is DNA?
The genetic material that organisms have inherited from their parent.
What is the Cell Cycle?
The name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells.
The sequence of Interphase.
G1 --> S --> G2
(Gap 1 --> Synthesis --> Gap 2)
Two well-known steps of the M-Phase.
Mitosis and Cytokinesis.
Meiosis is...
...cell division that reduces the parent chromosome number by half to produce gametes (Eggs and sperm).
The monomer for DNA.

Nucleotides.
The importance of the Cell Cycle.
Growth and repair (healing).
The stage where the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles.
Gap 1 - (G1).
What is Mitosis?
A series of events where the (nucleus) DNA splits into two identical sets.
The amount of divisions completed in Meiosis.
Two divisions. (Meiosis I and Meiosis II)
Label the parts.
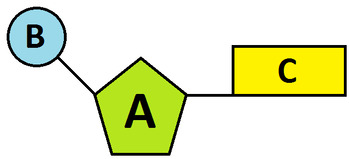
A. Deoxyribose (Sugar)
B. Phosphate Group
C. Nitrogenous Base (Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine, Thymine)
The two phases of the cell cycle.
1. Interphase
2. M-Phase
The stage where a genetic copy is made with information of a cell.
Synthesis - (S).
What is Cytokinesis?
The separation of the cytoplasm and organelles into two new cells.
When eggs and sperm fuse.

Fertilization.
The Complementary Base Pair Rule for DNA.

Guanine must pair with Cytosine. (G - C)
Adenine must pair with Thymine. (A - T)
Which section does Cell Division take place?
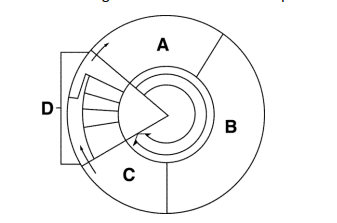
Section D.
What happens during the three stages of Interphase?
The cell grows rapidly, replicates DNA to form an identical copy, and prepares for division.
Describe the cells produced after Mitosis.
Two diploid daughter cells that are identical.
Why is Meiosis important?
Sexual reproduction provides genetic variation in the offspring, which allows resistance and adaption to environments.
How does the structure of DNA relates to its function?

Complementary Base Pairing allows DNA to be copied correctly. The enzyme that replicates DNA adds a nucleotide to the growing stand that is complementary to the other strand.
Which section does DNA Replication take place?

Section B.
Interphase prepares for...
...division during Mitosis with all the nutrients used for growth and replicating itself.
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis is cell division for somatic cells and for the asexual reproduction of unicellular eukaryotic cells, whereas Meiosis is cell division for gamete (reproductive) cells.
Describe the terms Crossing Over and Independent Assortment in Meiosis.
1. Crossing over is when homologous (one each from both parents) chromosomes pair up to increase genetic variation.
2. Independent Assortment is when homologous pairs randomly line up with different assortments from the homologous chromosomes. It is the end product of Meiosis which is four unique haploid gamete cells.