Monomers covalently bonded to each other.
What is a polymer?
Large, organic molecules that do not dissolve in water.
What are lipids?
Contains information that determines the characteristics of an organism and directs its cell activities.
What is DNA?
What is a ionic bond?
In proteins, structure = ________
What is function
A competitive inhibitor interacts at this site on an enzyme.
When ______ has decreased to a minimum, a system is at thermodynamic equilibrium.
What is entropy?
Name for a simple sugar, like glucose and fructose.
What is a monosaccharide?
Monomers that link to form nucleic acids
What are nucleotides?
The cell membrane is made of this fatty acid, with two fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol.
What is a phospholipid?
A 3-nucleotide sequence that determines what amino acid will be incorporated into a polypeptide.
What is a codon?
This bond holds monosaccharides together in a polysaccharide.
What is a glycosidic bond?
In this stage/ structure of protein folding, multiple polypeptide sequences come together to form large protein complexes
What is quaternary structure
On water molecules the Hydrogen end is _____ and the Oxygen end is ______.
What is positive, what is negative.
This describes the tendency of water to minimize its contacts with non-polar molecules
What is the hydrophobic effect?
This type of catalysis is mediated by animo acids like Ser and Thr
What is nucleophilic/covalent catalysis?
This base is only found in RNA.
What is uracil?
Water is an example of this type of bond that shares electrons unevenly
What is Hydrogen (or polar covalent)?
This stage of protein folding is the sequence of amino acids
What is primary structure
The molecule that trees use as the substrate to generate their large size.
What is CO2?
Peptide bonds form between these two functional groups
What are the carboxyl and amino groups?
This form of nucleic acid is single stranded.
What is RNA?
When an ionic bond dissociates, it forms positive and negative ions known as
What are cations and anions
This amino acid disrupts the formation of secondary structures.
What is glycine
These 6 letters in the alphabet are not represented by the 20 biological amino acids.
What is B, J, O, U, X, Z
When this value is zero, it indicates that the reactions are at equilibrium.
What is ΔG?
The end result of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions.
What is lactate?
When carbohydrates are attached to a lipid, the resulting molecule is this.
What is a glycolipid.
The EXACT complete name of this molecule
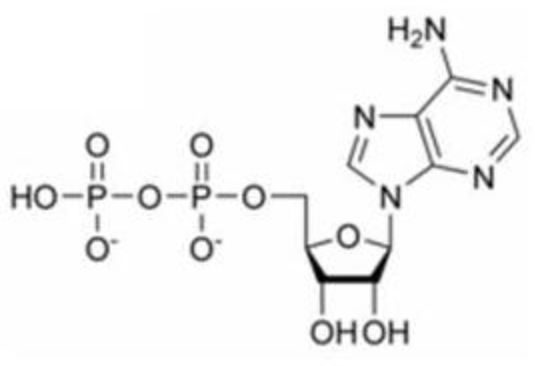
What is adenosine diphosphate
A nucleotide is made up of these 3 components.
What are nitrogenous bases, phosphate groups, and pentose sugar?
The type of bonds that hold the "backbone" of DNA together.
What are covalent bonds?
This structure or stage of folding forms beta sheets or alpha barrels
What is secondary structure
Dr. Defnet's daughter is named after a character in this show.
What is Gravity Falls