What is the common process used to form and break down bonds to make carbs, lipids, and proteins?
2 reactions!
Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis
What is the function of a carbohydrate?
supply your body and brain with energy
What are the building blocks of fats?
glyceride = 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Proteins are made up of...
amino acids!
What is the name of the enzyme model that requires an exact match with it's substrate?
Lock and key model
Drawing molecules... an amino acid

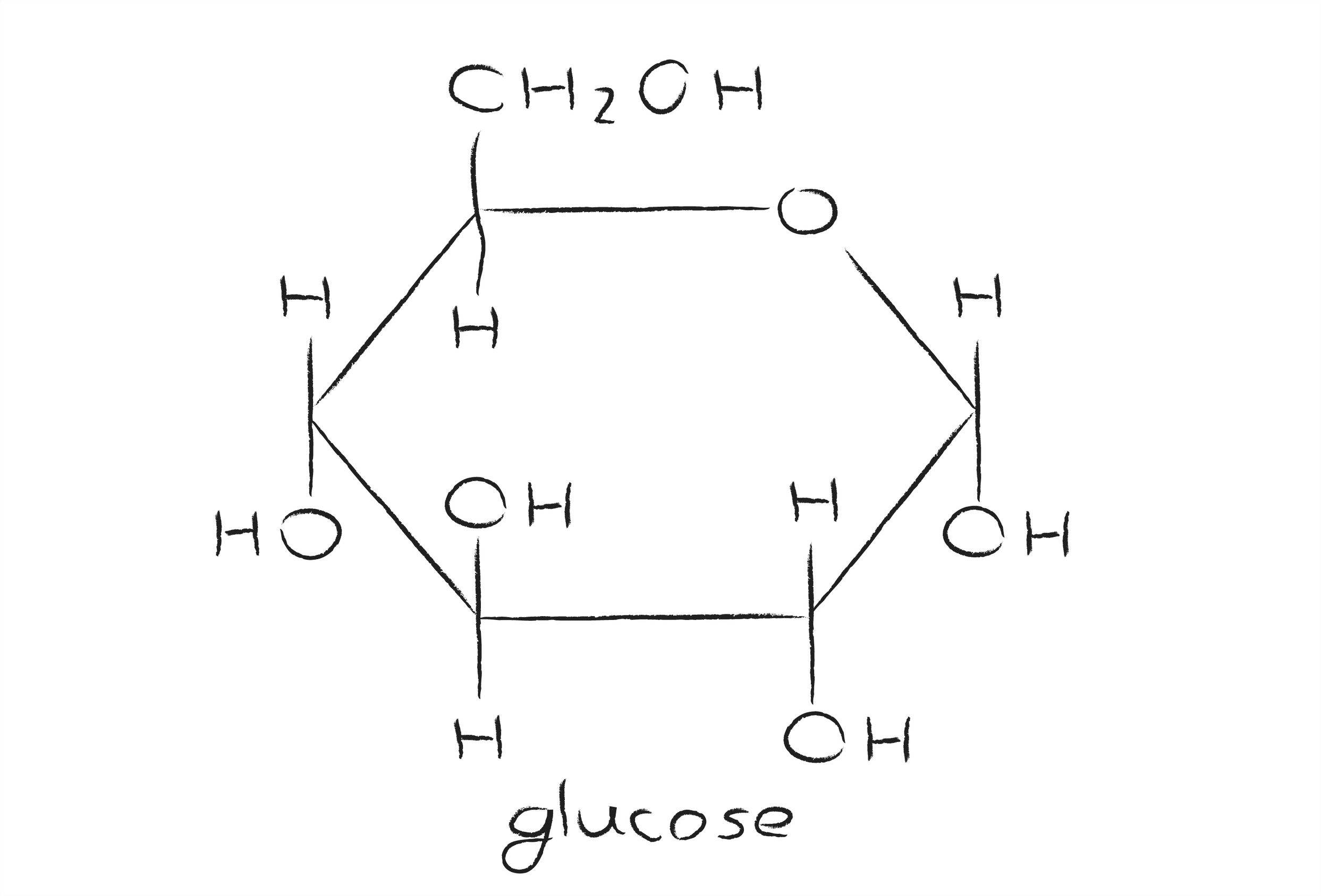
Drawing molecules... a glucose molecule
Where can lipids be found?
oils, fats, nuts, meats, pb, etc
What is the function of proteins?
Source of energy – used when carbohydrate levels are low. Structure – build muscles, bone, cartilage, skin and hair tissues
Enzymes are made up of...
amino acids!
H2O is an example of an organic substance. True or False
Name the three disaccharides and what monosaccharides they are made from
lactose = galactose + glucose
sucrose = glucose + fructose
What is the chemical make up of lipids?
CHOPN!
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Nitrogen
peptide bond
What is a catalyst?
Speeds up chemical reactions
What does the brain use for it's primary source of energy?
carbohydrates!
What are the three polysaccharides? Where do they come from?
Cellulose = plants (cell wall of plants)
Starch = plants
Glycogen = animals (liver)
List three differences between saturated and unsaturated fats
Unsaturated - liquid at room temp, plant based fats, contains 1 C=C bond, bent
Saturated - solid at room temp, animal based fats, linear
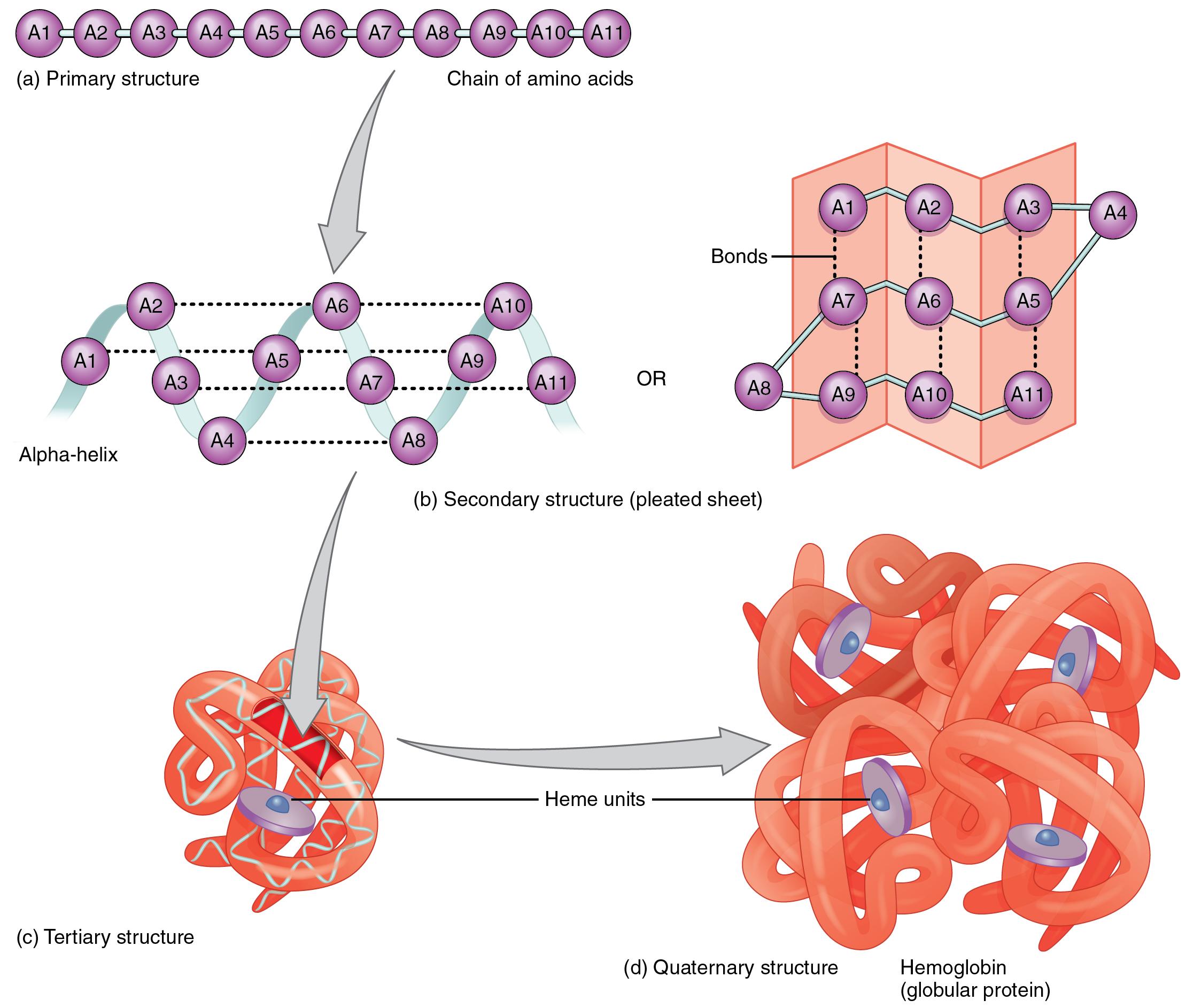
What are the four different structures of a protein? Describe the process
How do enzymes affect activation energy?
More enzymes will increase binding sites for substrate molecules and thus increase rate of reaction.
What is the bond that results when two amino acids join?
Ester linkage
State how the three polysaccharides differ in structure
Glycogen = branched chain
Starch = linear, one chain
Cellulose = cross-linked net, forms chain like structure (fence)
Where does the break down of lipids (fats) take place?
most fats get digested in the small intestine
What is an essential amino acid? How does your body retrieve them?
Essential amino acids are organic compounds that your body needs to function. You can get them from eating certain foods
Which graph shows an increase in substrate?
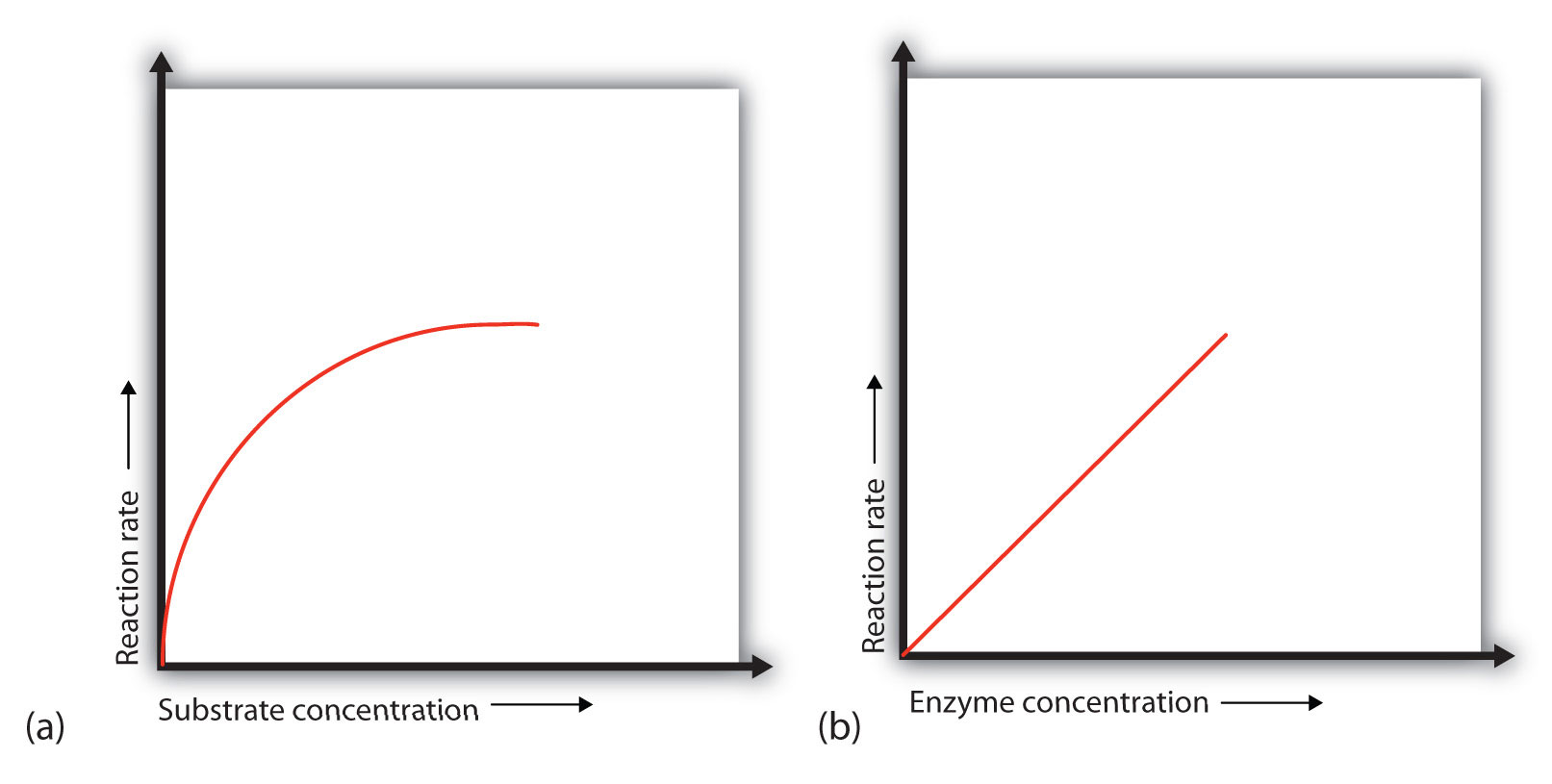
1st! A