A scientist observes an organism under the microscope that has no nucleus, but performs all life functions within one cell. What type of cell is it?
What is a prokaryote/prokaryotic?
Explain why sunlight, though nonliving, is essential to ecosystems.
Sunlight provides energy for photosynthesis, which drives energy flow in ecosystems.
What two levels of classification make up an organism’s scientific name?
What is genus and species?
Define autotroph and heterotroph, and give one example of each.
Autotroph = makes its own food (e.g., plants). Heterotroph = eats other organisms (e.g., animals).
Which kingdom contains organisms that are multicellular, autotrophic, and have cell walls made of cellulose?
Plantae — multicellular, autotrophic, cell walls made of cellulose.
Compare how a multicellular organism and a unicellular organism perform life functions. (Answer must explain organization differences.)
What is multicellular organisms have different cells for different functions that work together. While unicellular performs all functions in one cell.
A student argues that “rocks don’t affect living things.” Give a counterargument with evidence.
Rocks affect organisms by providing shelter, habitats, or minerals needed for survival.
Classify a mystery organism that moves, consumes other organisms, and is multicellular. Which kingdom does it belong to?
Animalia — it is multicellular, heterotrophic, and can move.
Compare sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of genetic diversity.
Sexual reproduction creates genetic diversity; asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring.
Contrast fungi and plants in terms of how they obtain food.
Plants make food through photosynthesis; fungi absorb nutrients from decaying material or hosts.
A student claims that all eukaryotes are multicellular. Use evidence to evaluate if the claim is correct.
The claim is incorrect — some eukaryotes (like protists such as Euglena or Amoeba) are single-celled.
Classify the following as biotic or abiotic: mushrooms, wind, water, bacteria. Then explain how two of them interact.
Mushrooms = biotic, wind = abiotic, water = abiotic, bacteria = biotic.
Example: Water (abiotic) is needed by bacteria (biotic) to survive.
Use a dichotomous key: An organism is single-celled, has a nucleus, and can move using cilia. Which kingdom is it?

Protista — single-celled, eukaryotic, and moves with cilia.
Evaluate why sexual reproduction might be beneficial for species survival in changing environments.
Sexual reproduction increases variation, which helps populations adapt to changing environments.
Some protists are autotrophic while others are heterotrophic. Explain how this makes classification challenging.
Protists are diverse — some act like plants (autotrophs) and others act like animals/fungi (heterotrophs), which makes them hard to classify.
Given a diagram of two cells, identify which is prokaryotic and which is eukaryotic, and explain the reasoning.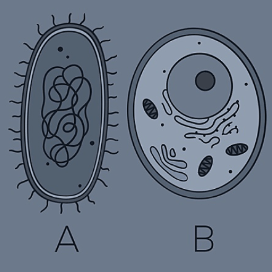
The cell with a nucleus and organelles is eukaryotic (B); the cell without a nucleus is prokaryotic (A).
Predict what would happen in a pond ecosystem if the abiotic factor of sunlight was drastically reduced.
Reduced sunlight means less photosynthesis, fewer biotic factors like plants, and less energy available for the entire food web.
Compare Linnaeus’ original 2-kingdom that only included plants and animals with the modern 6-kingdom system.(Name the newer 4 kingdoms)
Today’s six-kingdom system recognizes more diversity (fungi, protists, eubacteria, archaebacteria).
A fungus absorbs nutrients from its host. Explain why this energy strategy is different from autotrophs.
Fungi absorb nutrients externally from what they live on, while autotrophs (like plants) make their own food through photosynthesis.
Compare archaebacteria and eubacteria, giving one similarity and one difference.
Both archaebacteria and eubacteria are prokaryotic and unicellular, but archaebacteria live in extreme environments and have unique genetic/chemical differences.
Predict how damage to one type of cell in a multicellular organism might affect the survival of the organism compared to damage in a unicellular organism.
In multicellular organisms, one cell’s damage may not kill the organism because other cells perform different functions; in unicellular organisms, damage to the single cell can kill the entire organism.
Justify why scientists consider abiotic factors equally important as biotic ones for survival of ecosystems.
Abiotic factors like water, sunlight, and soil set the conditions that living organisms depend on for survival.
A student misclassified a plant as a protist when using a dichotomous key. Propose how they might have made that error and explain the correction.

The student may have confused photosynthetic protists (like algae) with plants. Correction: Plants are multicellular with specialized tissues; protists can be single-celled.
A bacterium divides rapidly through binary fission. How does this strategy affect its ability to adapt compared to sexual reproduction?
Binary fission produces identical offspring quickly, allowing rapid population growth, but less genetic diversity than sexual reproduction.
A student classifies a dog and a mushroom in the same kingdom because both are heterotrophic. Explain the error and correct it.
A mushroom is not an animal; fungi have cell walls and absorb nutrients, while dogs (animals) eat food and lack cell walls.
Correct classification: Mushroom = Fungi, Dog = Animalia.