Adult plants carry a pair of factors that govern the inheritance of each character.
What is Mendel's First Hypothesis?
The mechanism by which information encoded in DNA is made into a complementary RNA copy.
What is Transcription?
A small, circular DNA molecule separate from the cell’s main chromosome and can replicate independently.
What is a Plasmid?
The definition of ENERGY.
What is the capacity to do work or to be transferred as heat?
The collection of metabolic reactions within cells that breaks down food molecules to produce ATP
What is Cellular Respiration?
PP, Pp, pp
What is a Genotype?
Nucleotide information that specifies the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
What is the Genetic Code?
The two names for the enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences in restriction sites.
What are Endonucleases / Restriction Enzymes?
This term is defined as the study of energy and its transformations
What is THERMODYNAMICS?
The partial or full gain of electrons to a substance.
What is REDUCTION?
If an individual’s pair of genes consists of different alleles, one allele is dominant over the other, recessive allele.
What is Mendel's Second Hypothesis
Each codon specifies the same amino acids in all living organisms, and also in viruses.
What is the Genetic Code being Universal?
The name of the biotechnology that is used to distinguish between individuals using PCR at multiple loci within the genome.
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
Energy can be transformed from one form into another or transferred from one place to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
What is the 1st Law of Thermodynamics?
These are the three stages of Cellular Respiration.
What is:
Glycolysis,
Pyruvate Oxidation & the Citric Acid (Krebs) Cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Two alleles of a gene segregate (separate) and enter gametes singly, with half of the gametes carrying one allele and half carrying the other allele (haploid)
What is Law of Segregation (Mendel's Third Hypothesis)
A way to read a sequence of nucleotides as a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets (codons) that code for amino acids.
What is a Reading Frame?
The knocking out, replacement, or addition of a gene in a genome.
What is Gene Targeting?
Thermodynamic transformations that result in a system taking up heat from its surroundings
What are ENDOTHERMIC reactions?
This is the site of Photosynthesis in plant cells.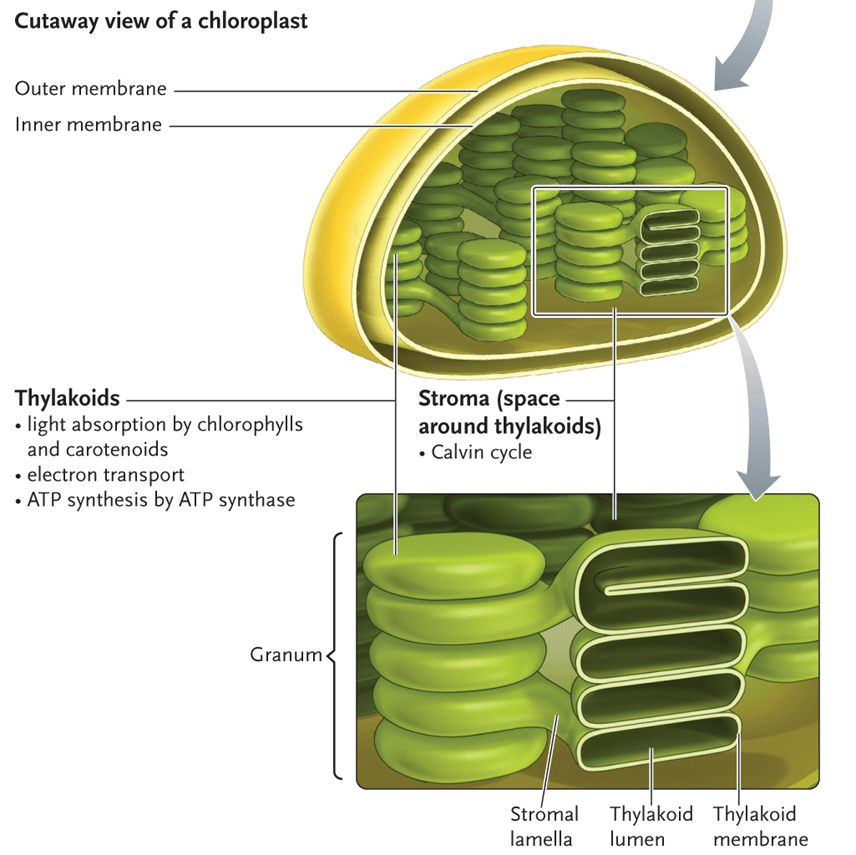
What is a Chloroplast?
Alleles of two genes that govern two different characters segregate INDEPENDENTLY during the formation of gametes.
What is Mendel's Fourth Hypothesis?
These small particals bind to introns, loop introns out of the pre-mRNA, clip the intron at each exon boundary, and then join adjacent exons together.
What are snRNPs?
A Programmable RNA-Guided Genome Editing System
What is CRISPR?
The Metabolic process in which energy is consumed to build complicated molecules from simpler ones.
What is the ANABOLIC pathway?
These are the 2 stages of Photosynthesis
What are LIGHT REACTIONS and the CALVIN CYCLE?