What is a nucleoside?
Nitrogenous bases and monosaccharide (sugar)
What is denaturing and what is an example of a denatured protein?
A change in the protein structure that eliminates the protein function. Heat can break H-bonds in protein structures. An example of this would be the denaturing of eggs when heat is added.
What kind of polysaccharide cannot be digested by human beings?
A. cellulose
B. glucose
C. starch
D. sucrose
cellulose
Name the polymer for lipids
N/A
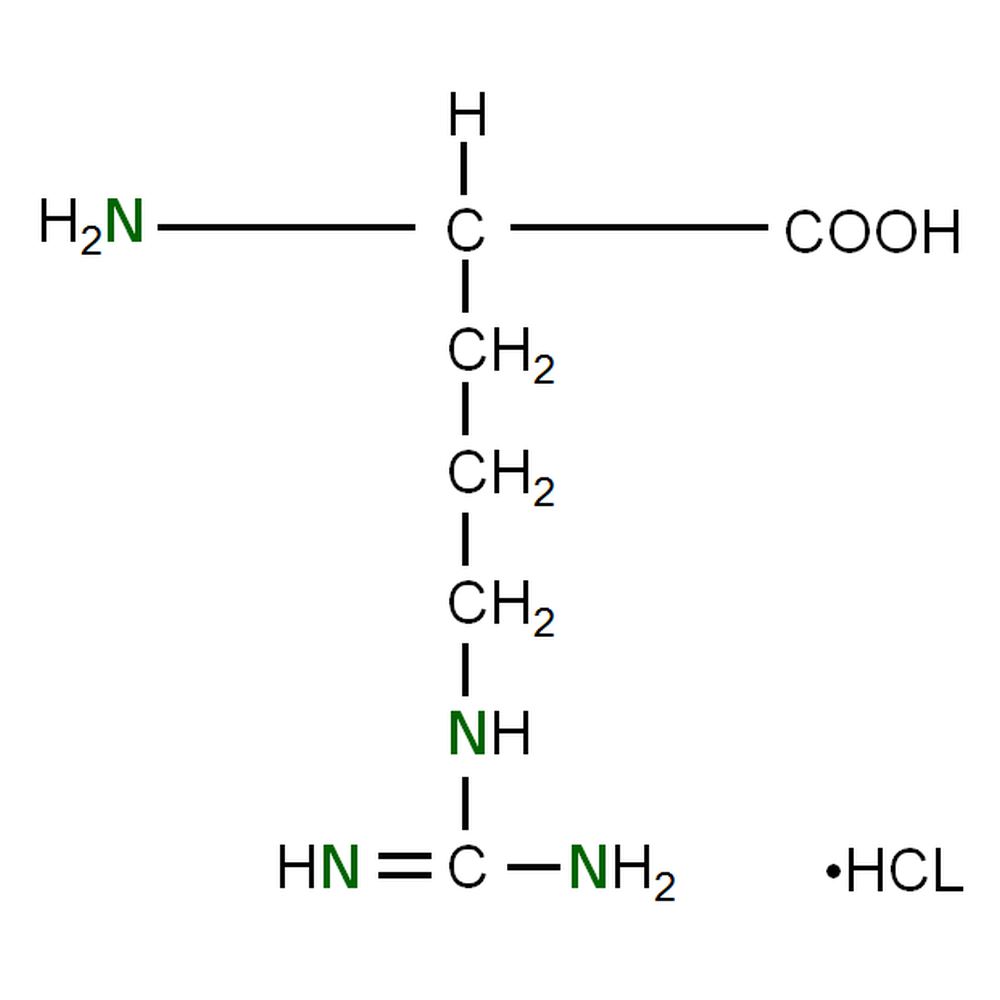
Identify the R-Group
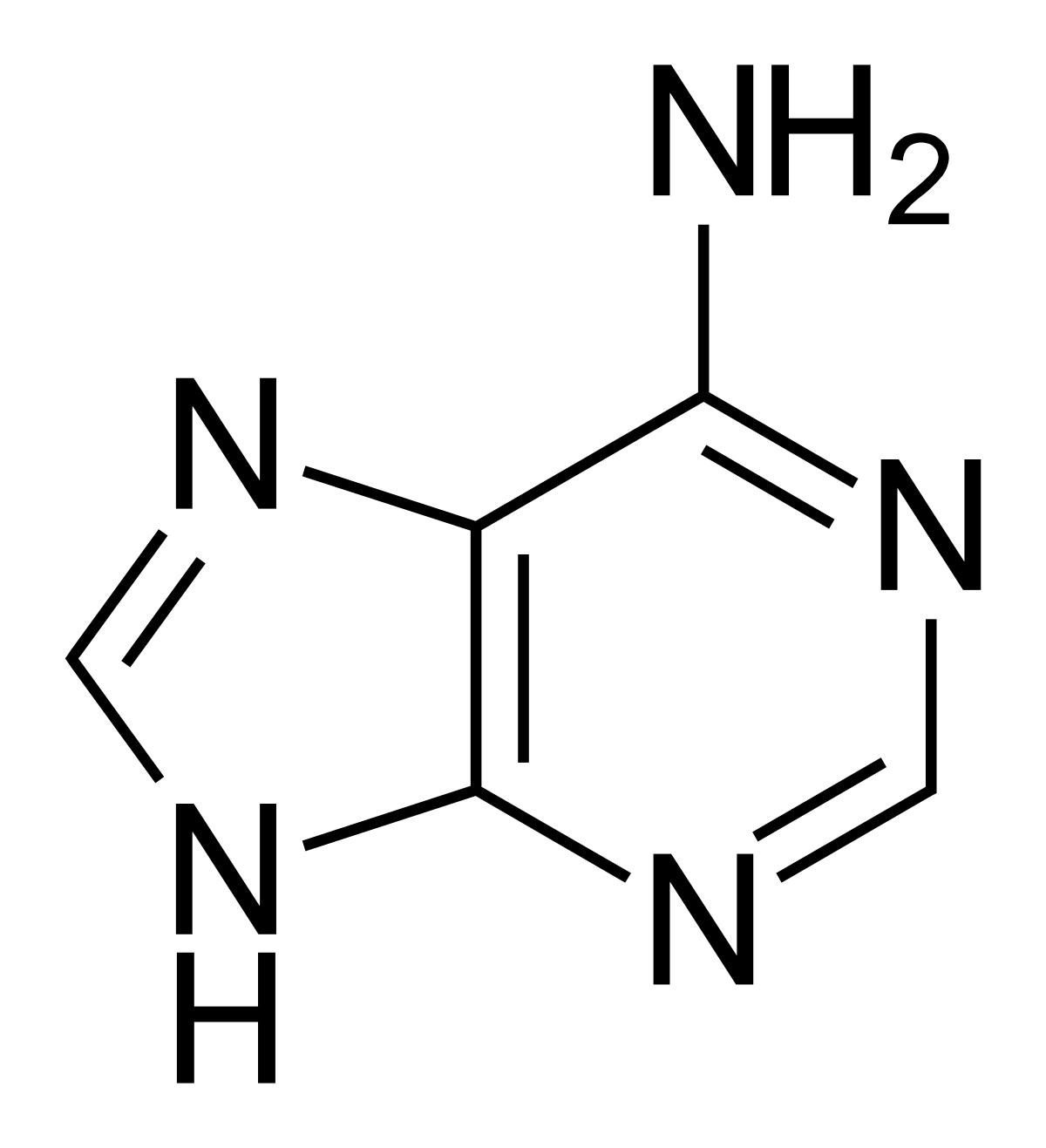
State the purines and pyrimidines and how they are different?
Cytosine, Thymine (DNA), and Uracil (RNA) – pyrimidines, single ring
Adenine, guanine – purines, double ring
Proteins do all of the following things in the body except which one of the following?
A. Carry genetic information
B. Speed up chemical reactions
C. Digest food
D. Carry oxygen in blood
E. Defend against microorganis
Carry genetic information
What type of reaction is this and what kind of bond is formed?
Condensation reaction and glycosidic bond
Describe an amphipathic molecule and what is an example of one.
A molecule that can be a hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecule. ex: phospholipid
Write the complimentary RNA strand for the given DNA strand below.
ATT GTG CGC TTG
UAA CAC GCG AAC
Explain transcription and translation.
Transcription is DNA to RNA. Translation is RNA to DNA
Describe how amino acids form peptide bonds.
Peptide bonds form through a condensation reaction between a nitrogen atom and a oxygen atom
Which one of the following is a monosaccharide?
A. fructose
B. glycogen
C. lactose
D. sucrose
fructose
Fats like lard and butter are solid at room temperature. What is it about the structures of their fatty acids that would support this trend?
Saturated fatty acid
What is the amount of monosaccharide in oligosaccharides and what type of bond is used?
3-10 monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds
Which property is found in nucleosides and nucleotides?
A. Both contain a nitrogenous base, a pentose, and at least one phosphate group.
B. Both contain a covalent phosphodiester bond.
C. Both contain a carbon atom that is part of a glycosidic bond.
D. Both contain two sugar groups.
Both contain a carbon atom that is part of a glycosidic bond.
Describe the relationship between protein, amino acids and polypeptide.
Many anime acids joined by peptide bond make a polypeptide chain and one or more polypeptides make a protein.
Cell recognition signals are what type of carbohydrate?
Oligosaccharides
State 3 ways lipids are used.
Energy storage (in fats and oils)
Membranes (phospholipid ones)
Organ protection (e.g. layers of fat as cushion)
Thermal regulation (e.g. blubber)
Prevent water loss in plants (in waxy coating on leaves)
Steroids like cholesterol (important for membranes) and estrogen (hormone, signaling)
What is cholesterol specifically classified as?
- a lipid
- a phospholipid
- a steroid
- a wax
C
Using base pairing rules, why can’t Guanine bind with Adenine?

Remember partial charges for base pairing.
NH = +
N = -
O = -
State the four levels of protein structures and describe how each level contributes to the construction of higher-level structures.
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. All higher structures are made from lower structures. Secondary structures rely on H-bonds to achieve the alpha helix and beta-sheet structures while tertiary structures rely on R-group interactions. Quaternary structures are a culmination of tertiary structure proteins.
Explain the difference in the structure of cellulose, starch, and glycogen
Cellulose = linear molecules form H-bonds
Starch = branching limits H-bonds
glycogen = high amount of branching
Related the structure properties of fatty acids in different temperatures.
Saturated = no double bonds, can be tightly stacked
Since saturated fatty can be tightly stacked, can withstand higher temperatures
Unsaturated = double bonds, loosely stacked
Unsaturated fatty acids are loosely stacked and are liquid at room temperature.
Comparing the effects of two diets of different nutritional values on the growth of mice is what type of experiment?
Controlled