Explain the difference between anatomy and physiology
Anatomy is the study of the structure/ form, while Physiology is the study of the function of the body parts.
What subatomic particle is located in the valence shell and has a negative charge?
Electron
Name the 3 major cell regions
Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Plasma Membrane
Name all of the body systems :
- Integumentary system
-Muscular System
- Skeletal System
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
- Cardiovasular System
- Immune System
- Repiratory System
- Digestive System
- Urinary System
-Reproductive System
Draw out the Anatomical Position

What is the correct level of organization from smallest to largest?
-Chemical- Cells - Tissue- Organ-Organ System- Organ
What is an isotope?
Element that has a same number of protons abut different number of neutrons
Explain the difference between passive and active transport?
Passive transport does not require cellular energy and moves substances down their concentration gradient (from high to low concentration), while active transport requires cellular energy, typically ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration)
Explain the different types of macromolecules and what they function as:
Carbohydrates provide quick energy and structural support.
Lipids are for long-term energy storage, cell membranes, and insulation.
Proteins catalyze reactions, provide structure, and perform a wide range of cellular work.
Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information to direct cell functions.
Draw out ionic bond and covalent bond
* Look up ionic and covalent bond diagram*
Which of the following body systems function by:
- provides support and protection
- Site of hemopoiesis
- Stores calcium and phosphorus
A. Skeletal System
B. Muscular System
C. Nervous System
D. Integumentary System
A
Explain the difference between polar and nonpolar compounds and what makes a substance something polar or nonpolar:
Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electrons, creating a slight positive end and a slight negative end, while nonpolar molecules have an even distribution of electrons, resulting in no net charge separation
Electronegativity
If a red blood cell is in a hypertonic solution, what will happen to that red blood cell?
Shrinks ( Crenation)
Explain the process of transcription and translation:
a two-step process where the genetic information in DNA is used to synthesize proteins. Transcription is the process of copying a gene's DNA sequence into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Translation is the subsequent process where the cell "reads" the mRNA sequence and uses it as a template to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide, which then folds into a protein
Draw out potential and kinetic energy and explain what the difference is:
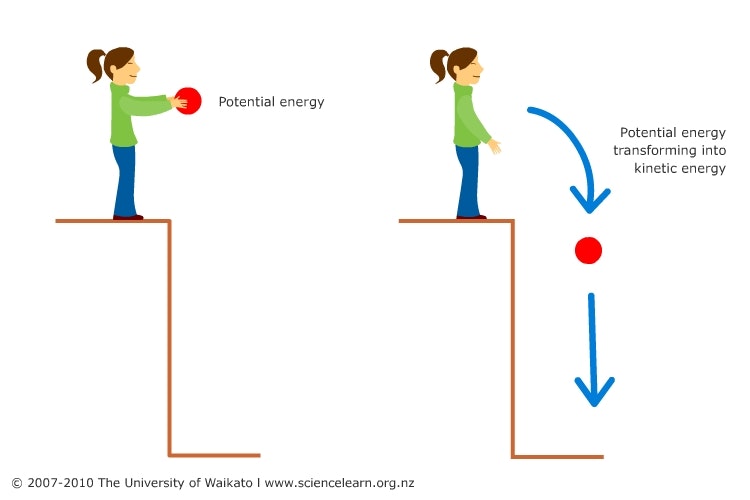
Potential energy is stored energy based on an object's position or state, like a ball held above the ground, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion, possessed by a moving object
Why is homeostasis important in the human body and how does it work?
it maintains the stable internal conditions necessary for enzymes and other proteins to function, preventing illness and allowing the body to survive and thrive.
A solutin has a pH of 8. Is this an acidic or basic solution and explain what acid or base are:
Basic
They are H+ acceptors
Define membrane potential, and explain how the resting membrane potential is established and maintained:
The RMP is established and maintained by the unequal distribution of ions (especially sodium and potassium) across the membrane, the selective permeability of the membrane to these ions via leak channels, and the action of the sodium-potassium pump, which actively transports ions to maintain the necessary concentration gradients and contribute to the negative charge inside the cell
Explain the different types of protein structures:
Primary (amino acid sequence)
Secondary (local folds like alpha-helices and beta-sheets)
Tertiary (overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain)
Quaternary (arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains)
Draw out and label ATP and where the energy is:
* Look up ATP Structure*
Explain the difference between negative feedback and positive feedback and give one example of each one:
Negative feedback opposes a change to maintain stability, working towards a set point, while positive feedback amplifies a change, pushing the system away from its starting state. Positive feedback, less common and often used for rapid completion, amplifies its stimulus, such as in childbirth contractions or blood clotting.
Positive Feedback: Birth, Blood Clotting
Negative Feedback: Temp. Regulation, Hormones, Blood Glucose Regulation
What protein structure is this classified is?

Primary Structure
What are the roles of each of the RNAs?
tRNA:
mRNA:
rRNA:
tRNA: to serve as an adaptor molecule that translates the genetic code from messenger RNA (mRNA) into a sequence of amino acids to build proteins
mRNA: to act as a "messenger" that carries genetic instructions from DNA to the ribosomes to synthesize specific proteins
rRNA: forming the basic structure of the ribosome
Compare and contrast autophagy and apoptosis:
Autophagy aims to preserve the cell by recycling, while apoptosis is a mechanism for removing unwanted or damaged cells.
Draw out a combustion chemical structure and explain what the reactant and products is:
* Look up combustion chemical reaction*