Which force of evolution is characterized by random changes in allele frequencies?
Genetic drift
What are the 4 things that all cells have in common?
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA
What are the 4 levels of ecology?
Organismal, population, community, and ecosystem.
The warming of Earth due to excess CO2 and other greenhouse gases is called the ________.
 What kind of symmetry does a jellyfish have?
What kind of symmetry does a jellyfish have?
Radial symmetry
Traits that aid in male-male competition for females are called _____, while traits that aid in males attracting females are called _____.
Intrasexual selection; Intersexual selection
Which 2 plant groups produce seeds?
Gymnosperms and angiosperms
What type of species interaction benefits one organism and has no effect on the other?
Commensalism
____ is the potential reproductive capacity of an individual within a population.
The observable traits expressed by an organism is its ______, while the underlying genetic material consisting of alleles is an organism's _______.
Phenotype; Genotype
What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle assume about a population?
An infinitely large population and no forces of evolution.
Which kind of speciation involves geographic separation of populations?
Allopatric speciation
What does a negative population growth mean?
The death rate is higher than the birth rate
What are the characteristics of a Type III survivorship curve?
Few organisms survive to adulthood, large number of offspring, low parental care
What are the tree-like structures on neurons that receive messages?
Dendrites
Population change over time is called ______, while the creation of new species and higher taxonomic groups is called ______.
Microevolution; Macroevolution
What are the 3 post-zygotic isolating mechanisms?
A species whose presence is key to maintaining biodiversity in an ecosystem is called a ______ species.
Keystone
The effects of slight changes in the Earth's orbit on the Earth's climate are called _____ cycles.
Milankovitch
There are 207 bunnies in a population. Within one year, if 48 bunnies are born and 15 bunnies die, what is the per capita population growth rate (r)?
0.16
What are the 3 conditions necessary for evolution by natural selection to occur?
Inherited genes, high fitness, and genetic variation
Which species concept would be the most useful in defining species of bacteria?
Phylogenetic
This graph is representative of ____ growth. 
Logistic
What are 3 ways invasive species can threaten native species?
Competition for resources, predation, and disease
Which species is/are most closely related to A?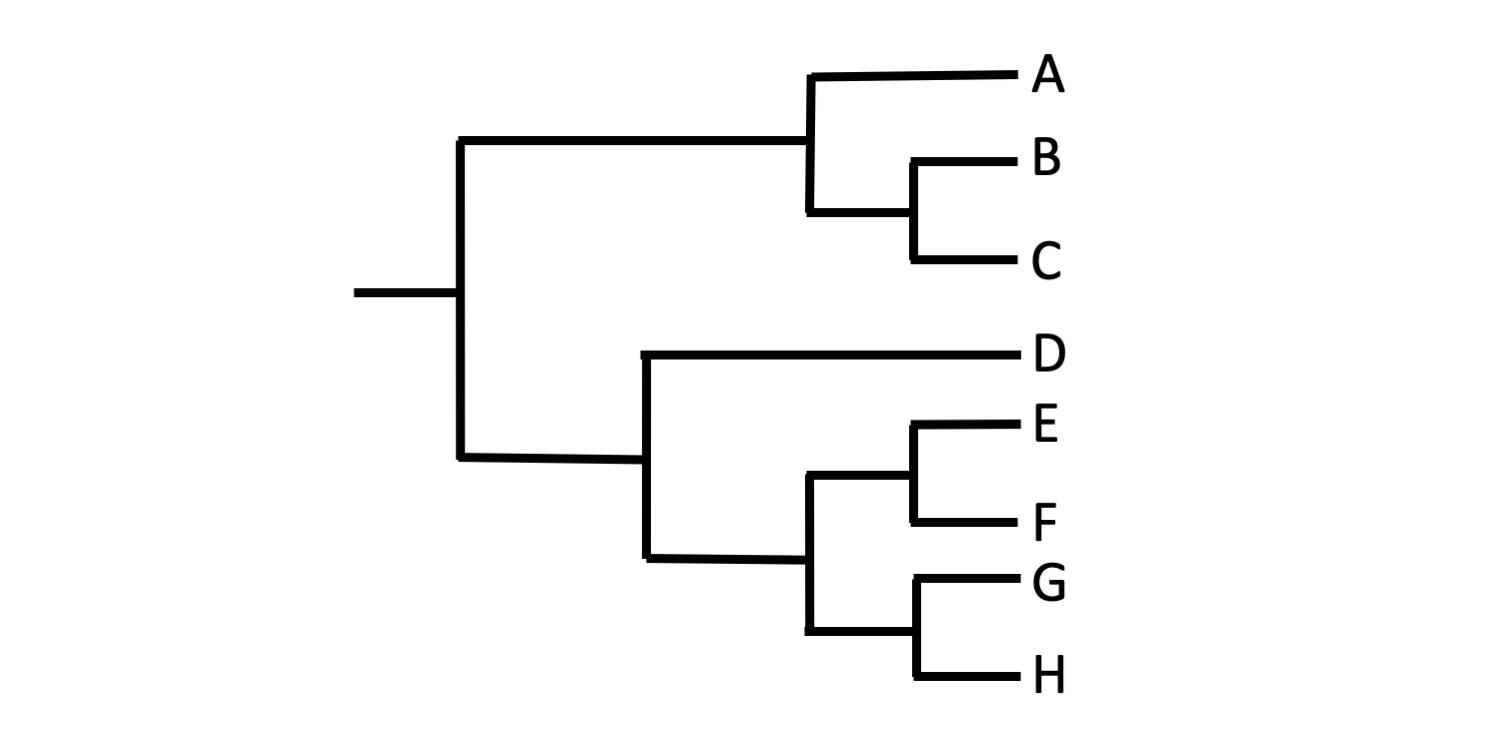
B and C