Give an example foods high in carbohydrates.
potato, bread, pasta, glucose, sucrose, starch
What is the common name for lipids?
fats
What foods are proteins found in?
meats, peanuts, dairy
Nucleic Acids build....
DNA or RNA
What special lipid is found in the cell membrane? (It is made of a glycerol head and 2 fatty acid tails.)
phospholipid
What is one function of an enzyme?
speed up reactions
or
break down molecules
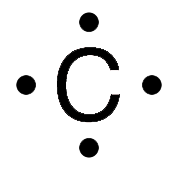
How many bonds does carbon form?
4
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
What is its energy storage?
1st energy source (short-term energy)
4 calories/gram
What is the main function of lipids?
What is its energy storage?
long term energy
9 calories/gram
What are proteins monomer?
amino acids
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
nucleotides
How are buffers helpful for the body?
They keep the drastic changes in pH from occurring when acids and bases are added. They help maintain homeostasis.
What makes carbon a unique atom?
It can bond with up to 4 different things.
carbon
what is the basic structure of a carbohydrate?
usually ring structure 
What is the polymer of a lipid?
triglyceride
What is the energy storage of a protein?
4 calories/gram
They are usually a last resort for energy!
Nucleotides are made up of
a pentose sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group
What are 5 nucleotides found in DNA and RNA
adenine
guanine
thymine
cytosine
uracil
Molecules that contain carbon are called ___ molecules.
organic
how many double bonds can carbon form?
2
What is the monomer of carbohydrate?
monosaccharide
simple sugar
What is a secondary function of lipids?
cushion and insulate vital organs
What is the polymer of a protein?
polypeptide
What is the function of nucleic acids?
store genetic information
Structurally, what is the difference between DNA and ATP?
DNA has just 1 phosphate while ATP has 3 phosphates.
What makes proteins the most diverse macromolecule?
It has a very complex structure and its structure helps determine its function.
Primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure
What word do we use for molecules that are made up of carbon?
organic
What is the process called where you break apart a maltose molecule into two glucose molecules by adding water?
What is the process called where you add together two glucose molecules to make maltose and lose a water molecule?
hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis (dehydration reaction)
What is the monomer of a lipid?
What are 2 types of fats due to their structure?
fatty acids
Long chains 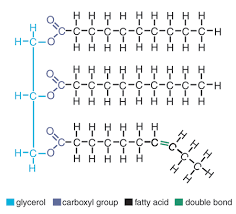
Saturated fats - long straight chains single bonds
Unsaturated fats - long chains with at least 1 double bond - making it bent
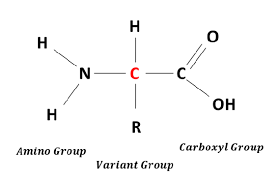
How many amino acids are there?
What are the parts of an amino acid's structure?
There are 20 amino acids.
What is the energy storage of a nucleic acid?
What foods can you eat to get them?
0 calories/gram
No foods - you are born with these, you cannot eat foods to get them
What is adhesion?
water sticking to other things
What kind of bonds hold one amino acid to another?
peptide bonds.
Draw the Lewis dot structure of carbon